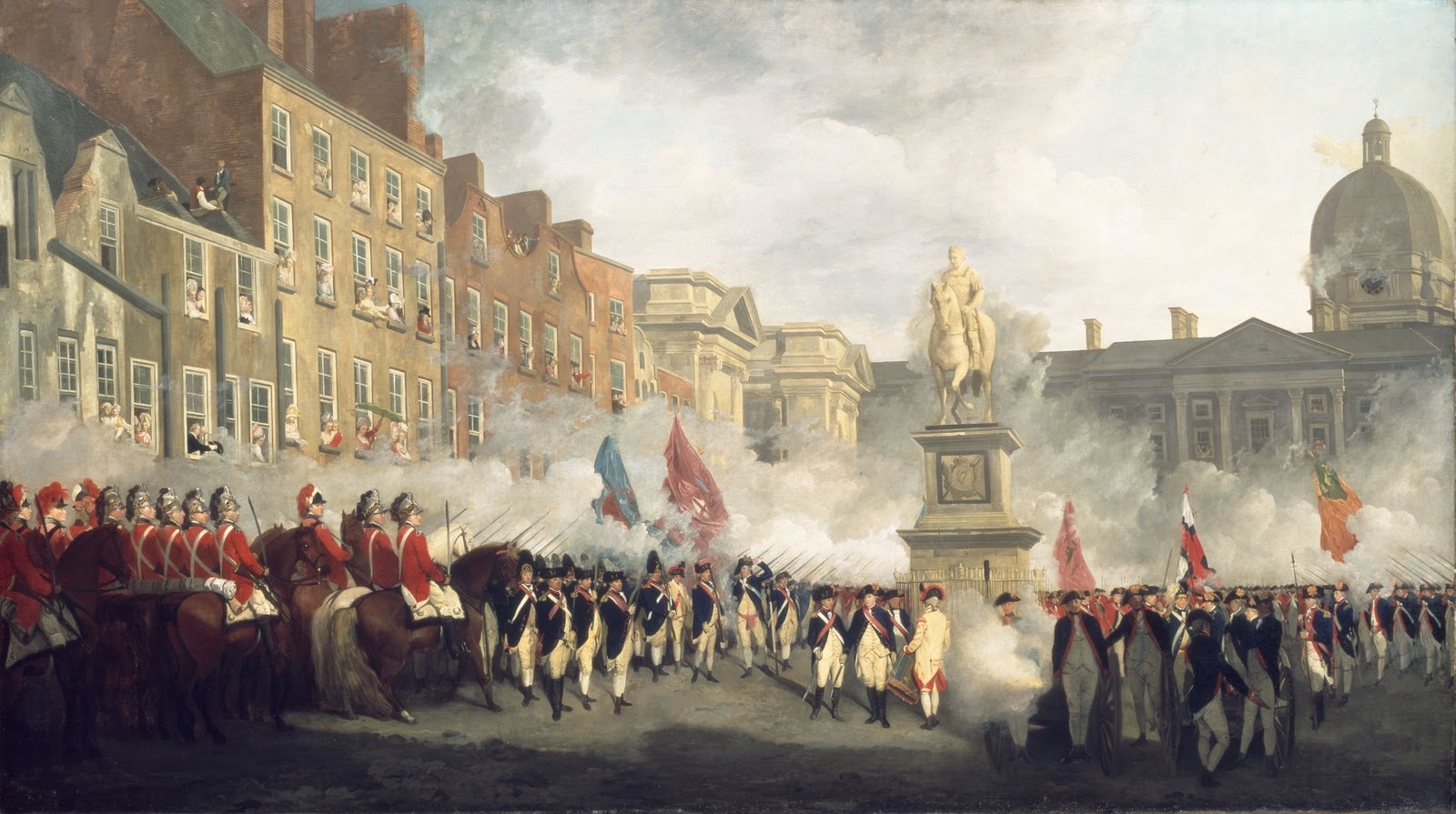|
Irish Volunteers (18th Century)
The Volunteers (also known as the Irish Volunteers) were militia units raised by local initiative in Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland in 1778. Their original purpose was to guard against invasion and to preserve law and order after much of the Irish Army (1661–1801), Irish Army was sent to fight abroad as part of the American Revolutionary War, American War of Independence and the Dublin Castle administration failed to expand the militia. Taking advantage of the Parliament of Great Britain's preoccupation with the American War of Independence, the Volunteers were able to pressure them into conceding legislative independence to the Parliament of Ireland. Members of the Belfast Volunteers laid the foundations for the establishment of the Society of United Irishmen. The majority of the Volunteers, however, were Unionism in Ireland, unionists, and later helped to suppress the Irish Rebellion of 1798.Ulster Museum, History of Belfast exhibition According to historian Thomas Bartlett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Wheatley - The Dublin Volunteers On College Green
Francis may refer to: People and characters *Pope Francis, head of the Catholic Church (2013–2025) *Francis (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters *Francis (surname) * Francis, a character played by YouTuber Boogie2988 Places * Rural Municipality of Francis No. 127, Saskatchewan, Canada * Francis, Saskatchewan, Canada ** Francis (electoral district) * Francis, Nebraska, USA *Francis Township, Holt County, Nebraska, USA * Francis, Oklahoma, USA *Francis, Utah, USA Arts, entertainment, media * ''Francis'' (film), the first of a series of comedies featuring Francis the Talking Mule, voiced by Chill Wills *''Francis'', a 1983 play by Julian Mitchell * Francis (band), a Sweden-based folk band *Francis (TV series), a Indian Bengali-language animated television series Other uses *FRANCIS, a bibliographic database * ''Francis'' (1793), a colonial schooner in Australia *Francis turbine, a type of water turbine See also *Saint Francis (other) * Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia versus Kingdom of France, France and Habsburg monarchy, Austria, the respective coalitions receiving by countries including Portuguese Empire, Portugal, Spanish Empire, Spain, Electorate of Saxony, Saxony, Age of Liberty, Sweden, and Russian Empire, Russia. Related conflicts include the Third Silesian War, French and Indian War, Carnatic wars, Third Carnatic War, Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763), Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763), and Spanish–Portuguese War (1762–1763), Spanish–Portuguese War. Although the War of the Austrian Succession ended with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748), none of the signatories were happy with the terms, and it was generally viewed as a temporary armistice. It led to a strategic realignment kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Aughrim
The Battle of Aughrim () was the decisive battle of the Williamite War in Ireland. It was fought between the largely Irish Army (Kingdom of Ireland), Irish Jacobitism, Jacobite army loyal to James II of England, James II and the forces of William III of England, William III on 12 July 1691 (Old Style and New Style dates, old style, equivalent to 22 July new style), near the village of Aughrim, County Galway. The battle was one of the bloodiest ever fought in the British Isles; 7,000 people were killed. The Jacobite defeat at Aughrim meant the effective end of James's cause in Ireland, although the city of Limerick held out until the autumn of 1691.G.A. Hayes McCoy, p. 244 Background By 1691, the Jacobites had adopted a defensive position. In the previous year they had retreated into Connacht behind the easily defensible line of the River Shannon, Shannon, with strongholds at Sligo, Athlone and Limerick guarding the routes into the province and the western ports. William Siege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Boyne
The Battle of the Boyne ( ) took place in 1690 between the forces of the deposed King James II, and those of King William III who, with his wife Queen Mary II (his cousin and James's daughter), had acceded to the Crowns of England and Scotland in 1689. The battle was fought across the River Boyne close to the town of Drogheda in the Kingdom of Ireland, modern-day Ireland, and resulted in a victory for William. This turned the tide in James's failed attempt to regain the British crown and ultimately aided in ensuring the continued Protestant ascendancy in Ireland. The battle took place on 1 July 1690 O.S. William's forces defeated James's army, which consisted mostly of raw recruits. Although the Williamite War in Ireland continued until the signing of the Treaty of Limerick in October 1691, James fled to France after the Boyne, never to return. Background The battle was a major encounter in James's attempt to regain the thrones of England and Scotland, resulting fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Lisburn And Lambeg Volunteers Firing A 'Feu De Joie' In Honour Of The Dungannon Convention, 1782
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Relief Act 1777
The Papists Act 1778 ( 18 Geo. 3. c. 60), also known as Sir George Savile's Act, the First Relief Act, or the Catholic Relief Act 1778 is an act of the Parliament of Great Britain and was the first act for Roman Catholic relief. Later in 1778 it was also enacted by the Parliament of Ireland as the (17 & 18 Geo. 3. c. 49 (I)), also known as Gardiner's Act or the Catholic Relief Act 1777. Before the act, a number of "Penal laws" had been enacted in Britain, which varied between the jurisdictions from time to time but effectively excluded those known to be Roman Catholics from public life. The timing of the act was partly based on the fact that the Papacy had stopped recognising the Jacobite cause on the death of the "Old Pretender" in 1766, and also the possibility that the ongoing American rebellion of 1775 might inspire a rebellion by Catholics in the Kingdom of Ireland. Effect of the act By this act, an oath was imposed, which besides a declaration of loyalty to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presbyterians
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Presbyterian'' is applied to churches that trace their roots to the Church of Scotland or to English Dissenter groups that were formed during the English Civil War, 1642 to 1651. Presbyterian theology typically emphasises the sovereignty of God, the authority of the Scriptures, and the necessity of grace through faith in Christ. Scotland ensured Presbyterian church government in the 1707 Acts of Union, which created the Kingdom of Great Britain. In fact, most Presbyterians in England have a Scottish connection. The Presbyterian denomination was also taken to North America, Australia, and New Zealand, mostly by Scots and Scots-Irish immigrants. Scotland's Presbyterian denominations hold to the Reformed theology of John Calvin and his i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penal Laws (Ireland)
In Ireland, the penal laws () were a series of Disabilities (Catholics), legal disabilities imposed in the seventeenth, and early eighteenth, centuries on the Kingdom of Ireland, kingdom's Catholic Church in Ireland, Roman Catholic majority and, to a lesser degree, on Nonconformist (Protestantism), Protestant "Dissenters". Enacted by the Parliament of Ireland, Irish Parliament, they secured the Protestant Ascendancy by further concentrating property and public office in the hands of those who, as communicants of the Established Church, established Church of Ireland, subscribed to the Oath of Supremacy. The Oath acknowledged the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarch as the "supreme governor" of matters both spiritual and temporal, and abjured "all foreign jurisdictions [and] powers"—by implication both the Pope in Rome and the House of Stuart, Stuart James Francis Edward Stuart, "Pretender" in the court of the Louis XIV, King of France. The laws included the Educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the largest branches of Christianity, with around 110 million adherents worldwide . Most are members of national or regional Ecclesiastical province#Anglican Communion, ecclesiastical provinces of the international Anglican Communion, one of the largest Christian bodies in the world, and the world's third-largest Christian communion. When united and uniting churches, united churches in the Anglican Communion and the breakaway Continuing Anglican movement were not counted, there were an estimated 97.4 million Anglicans worldwide in 2020. Adherents of Anglicanism are called ''Anglicans''; they are also called ''Episcopalians'' in some countries. The provinces within the Anglican ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hobart, 2nd Earl Of Buckinghamshire
John Hobart, 2nd Earl of Buckinghamshire (17 August 17233 August 1793) was a British politician, courtier and diplomat. Biography The son of John Hobart, 1st Earl of Buckinghamshire by his first wife Judith Britiffe, he was educated at Westminster School and Christ's College, Cambridge. He was Member of Parliament for Norwich from 1747 to 1756, having also been elected for St Ives in 1747 but opting to sit for Norwich. He held office as Comptroller of the Household in 1755-56 and as a Lord of the Bedchamber from 1756 to 1767, having succeeded his father as Earl in 1756. He was Ambassador from the United Kingdom to Russia from 1762 to 1765 and Lord Lieutenant of Ireland from 1776 to 1780, when his Chief Secretary was Sir Richard Heron, Bt. In the latter role, he had to concede free trade and, more importantly, the enactment of the Papists Act 1778 which partially repealed the Penal laws and provided measures for the relief of Roman Catholics and Dissenters. Family He mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Lieutenant Of Ireland
Lord Lieutenant of Ireland (), or more formally Lieutenant General and General Governor of Ireland, was the title of the chief governor of Ireland from the Williamite Wars of 1690 until the Partition of Ireland in 1922. This spanned the Kingdom of Ireland (1541–1800) and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922). The office, under its various names, was often more generally known as the Viceroy, and his wife was known as the vicereine. The government of Ireland in practice was usually in the hands of the Lord Deputy up to the 17th century, and later of the Chief Secretary for Ireland. Role The Lord Lieutenant possessed a number of overlapping roles. He was * the representative of the King (the "viceroy"); * the head of the executive in Ireland; * (on occasion) a member of the English or British Cabinet; * the fount of mercy, justice and patronage; * (on occasion) commander-in-chief in Ireland. * Grand Master of the Order of St. Patrick Prior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |