|
Wigan North Western Railway Station
Wigan North Western railway station is one of two railway stations serving the town centre of Wigan, Greater Manchester, England. It is a moderately-sized station on the West Coast Main Line. It is operated by Avanti West Coast, and is also served by Northern Trains. Wigan's other station is Wigan Wallgate, which is about away, on the opposite side of the street named Wallgate, for services to Manchester (Victoria, Deansgate, Oxford Road & Piccadilly), Southport and Kirkby. Both stations are centrally located on the southern fringe of Wigan town centre. The station is named North Western, not because of its location but because it formerly belonged to the London and North Western Railway. The drop in usage figures for Wigan North Western in 2006/07 was due to the adjustment of the allocation between the town's two stations. In 2009 North Western station was identified as one of the ten worst category B interchange stations for mystery shopper assessment of fabric and envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wigan
Wigan ( ) is a large town in Greater Manchester, England, on the River Douglas, Lancashire, River Douglas. The town is midway between the two cities of Manchester, to the south-east, and Liverpool, to the south-west. Bolton lies to the north-east and Warrington to the south. It is the largest settlement in the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan and is its administrative centre. The town has a population of 107,732 and the wider borough of 330,713. Wigan was formerly within the Historic counties of England, historic county of Lancashire. Wigan was in the territory of the Brigantes, an ancient Celtic tribe that ruled much of what is now northern England. The Brigantes were subjugated in the Roman conquest of Britain and the Roman settlement of ''Coccium'' was established where Wigan lies. Wigan was incorporated as a Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough in 1246, following the issue of a charter by Henry III of England, King Henry III of England. At the end of the Middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool And Manchester Railway
The Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR) was the first inter-city railway in the world. It opened on 15 September 1830 between the Lancashire towns of Liverpool and Manchester in England. It was also the first railway to rely exclusively on locomotives driven by steam power, with no horse-drawn traffic permitted at any time; the first to be entirely double track throughout its length; the first to have a true signalling system; the first to be fully timetabled; and the first to carry mail. Trains were hauled by company steam locomotives between the two towns, though private wagons and carriages were allowed. Cable haulage of freight trains was down the steeply-graded Wapping Tunnel to Liverpool Docks from Edge Hill junction. The railway was primarily built to provide faster transport of raw materials, finished goods and passengers between the Port of Liverpool and the cotton mills and factories of Manchester and surrounding towns. Designed and built by George Stephen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 86
The British Rail Class 86 is a class of electric locomotives built during the 1960s. Developed as a 'standard' electric locomotive from earlier prototype models, one hundred of these locomotives were built from 1965 to 1966 to haul trains on the then newly electrified West Coast Main Line (WCML) from London Euston to Birmingham, , Liverpool, Manchester and later Glasgow and . Introduction of the class enabled the replacement of many steam locomotives, which were finally withdrawn by British Rail in 1968. Under the earlier BR classification system, the type was given the designation AL6 (meaning the sixth design of AC locomotive) and locomotives were numbered E3101-E3200. In 1968, this was changed to Class 86 when British Rail introduced the TOPS classification system. The class was built to haul passenger and freight trains alike on the West Coast Main Line, however some members of the class also saw use on the Great Eastern Main Line (GEML) between and , after that line was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 50
The British Rail Class 50 is a class of diesel locomotives designed to haul express passenger trains at . Built by English Electric at the Vulcan Foundry in Newton-le-Willows between 1967 and 1968, the Class 50s were initially on a 10-year lease from English Electric Leasing, and were employed hauling express passenger trains on the, then non-electrified, section of the West Coast Main Line between Crewe and Scotland. Initially numbered D400–D449 and known as English Electric Type 4s, the locomotives were purchased outright by British Rail (BR) at the end of the lease and became Class 50 in the TOPS renumbering of 1973. The class gained the nickname "Hoovers" because of the noise made by the clean air plant at the No. 2 end, prior to refurbishment, which was likened to that of a vacuum cleaner, a name believed given to them by the staff at Paddington Station. Once the electrification from Crewe to Glasgow was completed the locomotives were moved to the Great Western Main Line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyldesley Railway Station
Tyldesley railway station is a closed railway station in Greater Manchester. It was situated within the historic county of Lancashire. Background Coal mining was the chief motivation for building a railway in the area and the railway's supporters included many local colliery owners and industrialists. The London and North Western Railway obtained an Act of Parliament to build a line through Tyldesley in 1861 and the first sod was cut by the Earl of Ellesmere at Worsley in the September. At that time the Tyldesley had the largest population of all the townships in the old Leigh parish and was destined to become the line's "premier station". At a junction to the west of Tyldesley station, the line to Wigan headed north west and the branch to Bedford Leigh, Bradshaw Leach and Kenyon Junction headed south west. History The ceremonial opening of the line took place on 24 August 1864. A special train of 18 coaches decorated with flags set off from Hunt's Bank in Manches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester Exchange Railway Station
Manchester Exchange was a railway station in Salford, England, immediately north of Manchester city centre, which served the city between 1884 and 1969. The main approach road ran from the end of Deansgate, near Manchester Cathedral, passing over the River Irwell, the Manchester-Salford boundary and Chapel Street; a second approach road led up from Blackfriars Road. Most of the station was in Salford, with only the 1929 extension to platform 3 east of the Irwell in Manchester. Construction and opening The station was built by the London and North Western Railway (LNWR) and opened on 30 June 1884. The station had five platforms: 1 and 2 were bays and 3, 4 and 5 were through. Platforms 4 and 5 were reached by a footbridge from near the station entrance. The opening of Exchange allowed the LNWR to vacate Manchester Victoria station to the east, which it (and its predecessors, including the Liverpool and Manchester Railway) had shared with the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester And Wigan Railway
The Manchester and Wigan Railway refers to a railway in North West England, opened in 1864 and closed to passengers on 3 May 1969, which was part of the London and North Western Railway before the Grouping of 1923. This route was an alternative to the surviving route through Swinton, Walkden and Atherton (which was part of the Lancashire & Yorkshire Railway before 1923). Route The first part of the route remains between Manchester Victoria and Eccles on part of the original Liverpool and Manchester Railway opened in 1831. After Eccles, the line branched off in a north westerly direction crossing what is now the M602 motorway, calling at stations at Monton Green and Worsley. After Roe Green the line split, with one branch continuing to Bolton; and the Manchester to Wigan line continuing westward to stations at Ellenbrook and Tyldesley. After Tyldesley the line split, the Tyldesley Loopline continued to Kenyon Junction while the Wigan line continued to the north west to Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wigan Rail Crash
The Wigan rail crash was a railway accident which occurred at Wigan North Western station, England, to a northbound excursion train in the early morning of 3 August 1873. Thirteen passengers were killed after derailed carriages collided with station buildings. The train was declared to have been travelling at excessive speed. Circumstances In Victorian times annual holidays to Scotland were popular amongst the affluent, inspired by Queen Victoria's visits to Balmoral Castle. The 'Tourist Special' which left London Euston at 20:00 on 2 August 1873 drawn by two locomotives consisted of 25 vehicles by the time it left Crewe including many private family coaches. Many of the passengers were aristocrats travelling north for the opening of the grouse season. As the long train ran through Wigan North Western station the driver glanced back and saw sparks flying to the rear of the train. After drawing to a stand he walked back to find an appalling sight at the south end of the down p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow Central Railway Station
, symbol_location = gb , symbol = rail , image = Main Concourse at Glasgow Central Station.JPG , caption = The main concourse , borough = Glasgow, City of Glasgow , country = Scotland , coordinates = , grid_name = Grid reference , grid_position = , manager = Network Rail , platforms = 17 (including 2 on lower level) , code = GLC , zone = G2 , transit_authority = SPT , years = 1 August 1879 , events = High Level Station openedButt (1995), page 103 , years1 = 10 August 1896 , events1 = Low Level Station opened , years2 = 1901–1905 , events2 = High Level Station rebuilt , years3 = 1960 , events3 = Re-signalling , years4 = 5 October 1964 , events4 = Closure of Low Level Station , years5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euston Railway Station
Euston railway station ( ; also known as London Euston) is a central London railway terminus in the London Borough of Camden, managed by Network Rail. It is the southern terminus of the West Coast Main Line, the UK's busiest inter-city railway. Euston is the eleventh-busiest station in Britain and the country's busiest inter-city passenger terminal, being the gateway from London to the West Midlands, North West England, North Wales and Scotland. Intercity express passenger services are operated by Avanti West Coast and overnight services to Scotland are provided by the Caledonian Sleeper. London Northwestern Railway and London Overground provide regional and commuter services. Trains run from Euston to the major cities of Birmingham, Manchester, Liverpool, Glasgow and Edinburgh. It is also the mainline station for services to and through to for connecting ferries to Dublin. Local suburban services from Euston are run by London Overground via the Watford DC Line which runs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caledonian Railway
The Caledonian Railway (CR) was a major Scottish railway company. It was formed in the early 19th century with the objective of forming a link between English railways and Glasgow. It progressively extended its network and reached Edinburgh and Aberdeen, with a dense network of branch lines in the area surrounding Glasgow. It was absorbed into the London, Midland and Scottish Railway in 1923. Many of its principal routes are still used, and the original main line between Carlisle and Glasgow is in use as part of the West Coast Main Line railway (with a modified entry into Glasgow itself). Introduction In the mid-1830s, railways in England evolved from local concerns to longer routes that connected cities, and then became networks. In Scotland it was clear that this was the way forward, and there was a desire to connect the Central Belt to the incipient English network. There was controversy over the route that such a line might take, but the Caledonian Railway was formed on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Junction Railway
The Grand Junction Railway (GJR) was an early railway company in the United Kingdom, which existed between 1833 and 1846 when it was amalgamated with other railways to form the London and North Western Railway. The line built by the company was the first trunk railway to be completed in England, and arguably the world's first long-distance railway with steam traction. The lines which comprised the GJR now form the central section of the West Coast Main Line. History The Grand Junction Railway Company was established in the second half of 1832 by the consolidation of two rival companies: the Birmingham and Liverpool Railway Company and the Liverpool and Birmingham Railway Company. Authorised by Parliament on 6 May 1833 and designed by George Stephenson and Joseph Locke, the Grand Junction Railway opened for business on 4 July 1837, running for from Birmingham through Wolverhampton (via Perry Barr and Bescot), Stafford, Crewe, and Warrington, then via the existing Warrington ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

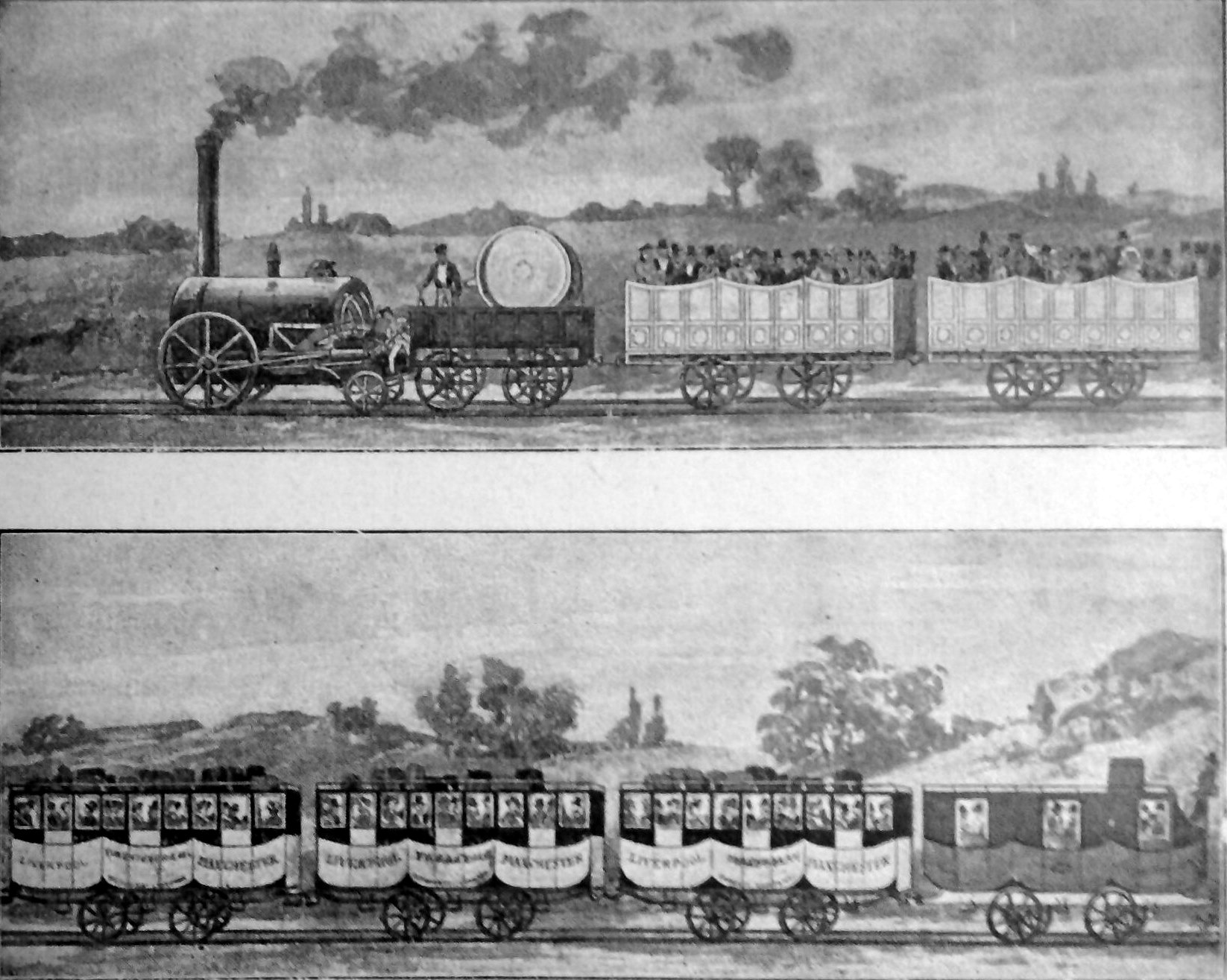




_Central_Station%2C_Glasgow.jpg)

