|
White Fuming Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% , it is referred to as ''fuming nitric acid''. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%. Nitric acid is the primary reagent used for nitration – the addition of a nitro group, typically to an organic molecule. While some resulting nitro compounds are shock- and thermally-sensitive explosives, a few are stable enough to be used in munitions and demolition, while others are still more stable and used as pigments in inks and dyes. Nitric acid is also commonly used as a strong oxidizing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etching
Etching is traditionally the process of using strong acid or mordant to cut into the unprotected parts of a metal surface to create a design in intaglio (incised) in the metal. In modern manufacturing, other chemicals may be used on other types of material. As a method of printmaking, it is, along with engraving, the most important technique for old master prints, and remains in wide use today. In a number of modern variants such as microfabrication etching and photochemical milling it is a crucial technique in much modern technology, including circuit boards. In traditional pure etching, a metal plate (usually of copper, zinc or steel) is covered with a waxy ground which is resistant to acid. The artist then scratches off the ground with a pointed etching needle where the artist wants a line to appear in the finished piece, exposing the bare metal. The échoppe, a tool with a slanted oval section, is also used for "swelling" lines. The plate is then dipped in a bath of acid, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Fuming Nitric Acid
Red fuming nitric acid (RFNA) is a storable oxidizer used as a rocket propellant. It consists of 84% nitric acid (), 13% dinitrogen tetroxide and 1–2% water. The color of red fuming nitric acid is due to the dinitrogen tetroxide, which breaks down partially to form nitrogen dioxide. The nitrogen dioxide dissolves until the liquid is saturated, and produces toxic fumes with a suffocating odor. RFNA increases the flammability of combustible materials and is highly exothermic when reacting with water. It is usually used with an inhibitor (with various, sometimes secret, substances, including hydrogen fluoride; any such combination is called ''inhibited RFNA'', ''IRFNA'') because nitric acid attacks most container materials. Hydrogen fluoride for instance will passivate the container metal with a thin layer of metal fluoride, making it nearly impervious to the nitric acid. It can also be a component of a monopropellant; with substances like amine nitrates dissolved in it, it ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . This colorless gas or liquid is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often as an aqueous solution called hydrofluoric acid. It is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers, e.g. polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Hydrogen fluoride boils at near room temperature, much higher than other hydrogen halides. Hydrogen fluoride is an extremely dangerous gas, forming corrosive and penetrating hydrofluoric acid upon contact with moisture. The gas can also cause blindness by rapid destruction of the corneas. History In 1771 Carl Wilhelm Scheele prepared the aqueous solution, hydrofluoric acid in large quantities, although hydrofluoric acid had been known in the glass industry before then. French chemist Edmond Frémy (1814–1894) is credited with discov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Fuming Nitric Acid
Red fuming nitric acid (RFNA) is a storable oxidizer used as a rocket propellant. It consists of 84% nitric acid (), 13% dinitrogen tetroxide and 1–2% water. The color of red fuming nitric acid is due to the dinitrogen tetroxide, which breaks down partially to form nitrogen dioxide. The nitrogen dioxide dissolves until the liquid is saturated, and produces toxic fumes with a suffocating odor. RFNA increases the flammability of combustible materials and is highly exothermic when reacting with water. It is usually used with an inhibitor (with various, sometimes secret, substances, including hydrogen fluoride; any such combination is called ''inhibited RFNA'', ''IRFNA'') because nitric acid attacks most container materials. Hydrogen fluoride for instance will passivate the container metal with a thin layer of metal fluoride, making it nearly impervious to the nitric acid. It can also be a component of a monopropellant; with substances like amine nitrates dissolved in it, it ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is also often used to refer to the thermal energy contained in a system as a component of its internal energy and that is reflected in the temperature of the system. For both uses of the term, heat is a form of energy. An example of formal vs. informal usage may be obtained from the right-hand photo, in which the metal bar is "conducting heat" from its hot end to its cold end, but if the metal bar is considered a thermodynamic system, then the energy flowing within the metal bar is called internal energy, not heat. The hot metal bar is also transferring heat to its surroundings, a correct statement for both the strict and loose meanings of ''heat''. Another example of informal usage is the term '' heat content'', used despite the fact that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McGraw-Hill
McGraw Hill is an American educational publishing company and one of the "big three" educational publishers that publishes educational content, software, and services for pre-K through postgraduate education. The company also publishes reference and trade publications for the medical, business, and engineering professions. McGraw Hill operates in 28 countries, has about 4,000 employees globally, and offers products and services to about 140 countries in about 60 languages. Formerly a division of The McGraw Hill Companies (later renamed McGraw Hill Financial, now S&P Global), McGraw Hill Education was divested and acquired by Apollo Global Management in March 2013 for $2.4 billion in cash. McGraw Hill was sold in 2021 to Platinum Equity for $4.5 billion. Corporate History McGraw Hill was founded in 1888 when James H. McGraw, co-founder of the company, purchased the ''American Journal of Railway Appliances''. He continued to add further publications, eventually establishin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baumé Scale
The Baumé scale is a pair of hydrometer scales developed by French pharmacist Antoine Baumé in 1768 to measure density of various liquids. The unit of the Baumé scale has been notated variously as ''degrees Baumé'', ''B°'', ''Bé°'' and simply Baumé (the accent is not always present). One scale measures the density of liquids heavier than water and the other, liquids lighter than water. The Baumé of distilled water is 0. The API gravity scale is based on errors in early implementations of the Baumé scale. Definitions Baumé degrees (heavy) originally represented the percent by mass of sodium chloride in water at . Baumé degrees (light) was calibrated with 0°Bé (light) being the density of 10% NaCl in water by mass and 10°Bé (light) set to the density of water. Consider, at near room temperature: * +100°Bé (specific gravity, 3.325) would be among the ''densest'' fluids known (except some liquid metals), such as diiodomethane. * Near 0°Bé would be approximately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
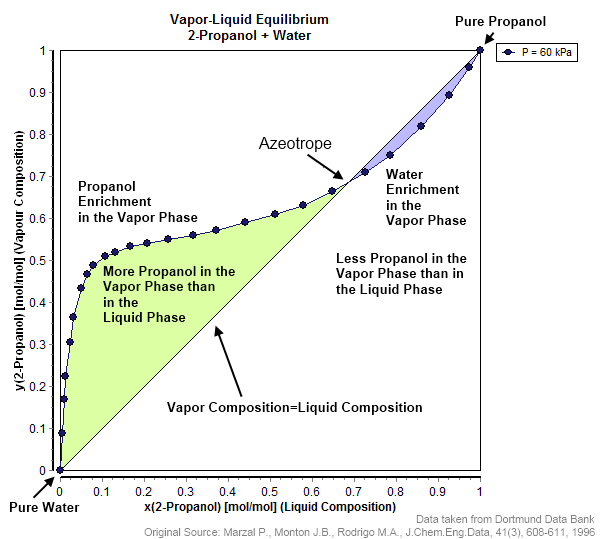
Azeotrope
An azeotrope () or a constant heating point mixture is a mixture of two or more liquids whose proportions cannot be altered or changed by simple distillation.Moore, Walter J. ''Physical Chemistry'', 3rd e Prentice-Hall 1962, pp. 140–142 This happens when an azeotrope is boiled, the vapour has the same proportions of constituents as the unboiled mixture. Because their composition is unchanged by distillation, azeotropes are also called (especially in older texts) ''constant boiling point mixtures''. Some azeotropic mixtures of pairs of compounds are known, and many azeotropes of three or more compounds are also known. In such a case it is not possible to separate the components by fractional distillation and azeotropic distillation is usually used instead. There are two types of azeotropes: minimum boiling azeotrope and maximum boiling azeotrope. A solution that shows greater positive deviation from Raoult's law forms a minimum boiling azeotrope at a specific composition. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidizing Agent
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxidizer is any substance that oxidizes another substance. The oxidation state, which describes the degree of loss of electrons, of the oxidizer decreases while that of the reductant increases; this is expressed by saying that oxidizers "undergo reduction" and "are reduced" while reducers "undergo oxidation" and "are oxidized". Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide and the halogens. In one sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that undergoes a chemical reaction in which it gains one or more electrons. In that sense, it is one component in an oxidation–reduction (redox) reaction. In the second sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that transfers electronegative atoms, usually oxygen, to a substrate. Comb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may either be composed solely of one ingredient or be a mixture containing at least two substances. The potential energy stored in an explosive material may, for example, be * chemical energy, such as nitroglycerin or grain dust * pressurized gas, such as a gas cylinder, aerosol can, or BLEVE * nuclear energy, such as in the fissile isotopes uranium-235 and plutonium-239 Explosive materials may be categorized by the speed at which they expand. Materials that detonate (the front of the chemical reaction moves faster through the material than the speed of sound) are said to be "high explosives" and materials that deflagrate are said to be "low explosives". Explosives may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitro Compound
In organic chemistry, nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups (). The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores (functional group that makes a compound explosive) used globally. The nitro group is also strongly electron-withdrawing. Because of this property, bonds alpha (adjacent) to the nitro group can be acidic. For similar reasons, the presence of nitro groups in aromatic compounds retards electrophilic aromatic substitution but facilitates nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Nitro groups are rarely found in nature. They are almost invariably produced by nitration reactions starting with nitric acid. Synthesis Preparation of aromatic nitro compounds Aromatic nitro compounds are typically synthesized by nitration. Nitration is achieved using a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid, which produce the nitronium ion (), which is the electrophile: + The nitration product produced on the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |