|
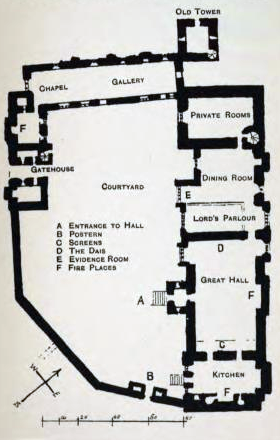
Wharton Hall
Wharton Hall in Wharton, Cumbria, England, is a medieval fortified manor house. History At the heart of Wharton Hall is a 15th-century hall, built from local limestone by the local Wharton, possibly Richard Wharton. During the Pilgrimage of Grace in 1536 the manor was besieged by the forces of Robert Aske and after 1544 Lord Wharton extended and fortified the manor, building a gatehouse, great hall, kitchen, and surrounding walls in a medieval style. The result was a grand property, with the great hall being 68 feet long. Francis Knollys escorted Mary, Queen of Scots from Lowther Castle to Wharton on 14 July 1568, and the next day she went to Bolton Castle. Her son, King James I stayed at Wharton on 8 August 1617, returning from his visit to Scotland. The Wharton family preferred to use Healaugh Priory near Tadcaster in North Yorkshire as their main residence after the 16th century, and the property fell into ruin. In 1785, Lord Lonsdale restored the building, adding more bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. Cumbria's county town is Carlisle, in the north of the county. Other major settlements include Barrow-in-Furness, Kendal, Whitehaven and Workington. The administrative county of Cumbria consists of six districts ( Allerdale, Barrow-in-Furness, Carlisle, Copeland, Eden and South Lakeland) and, in 2019, had a population of 500,012. Cumbria is one of the most sparsely populated counties in England, with 73.4 people per km2 (190/sq mi). On 1 April 2023, the administrative county of Cumbria will be abolished and replaced with two new unitary authorities: Westmorland and Furness (Barrow-in-Furness, Eden, South Lakeland) and Cumberland ( Allerdale, Carlisle, Copeland). Cumbria is the third largest ceremonial county in England by area. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadcaster
Tadcaster is a market town and civil parish in the Selby district of North Yorkshire, England, east of the Great North Road, north-east of Leeds, and south-west of York. Its historical importance from Roman times onward was largely as the lowest road crossing-point on the River Wharfe until the construction of the A64 Tadcaster by-pass some to the south, in 1978. There are two rail crossings downstream of the town before the Wharfe joins the River Ouse near Cawood. Tadcaster is twinned with Saint-Chély-d'Apcher in France. The town was part of the West Riding of Yorkshire until 1974, but is now part of North Yorkshire. Thanks to its position on the banks of the River Wharfe parts of the town adjacent to the bridge are prone to flooding. History Roman The Romans built a settlement and named it ''Calcaria'' from the Latin word for ''lime'', reflecting the importance of the area's limestone geology as a natural resource for quarrying, an industry which continues and has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Country Houses In Cumbria
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while the country of Wales is a component of a multi-part sovereign state, the United Kingdom. A country may be a historically sovereign area (such as Korea), a currently sovereign territory with a unified government (such as Senegal), or a non-sovereign geographic region associated with certain distinct political, ethnic, or cultural characteristics (such as the Basque Country). The definition and usage of the word "country" is flexible and has changed over time. ''The Economist'' wrote in 2010 that "any attempt to find a clear definition of a country soon runs into a thicket of exceptions and anomalies." Most sovereign states, but not all countries, are members of the United Nations. The largest country by area is Russia, while the smallest is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houses Completed In The 15th Century
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.Schoenauer, Norbert (2000). ''6,000 Years of Housing'' (rev. ed.) (New York: W.W. Norton & Company). Houses use a range of different roofing systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses may have doors or locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more bedrooms and bathrooms, a kitchen or cooking area, and a living room. A house may have a separate dining room, or the eating area may be integrated into another room. Some large houses in North America have a recreation room. In traditional agriculture-oriented societies, domestic animals suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Waistell Taylor
Michael Waistell Taylor (1824–1892) was a Scottish physician, known also as an antiquarian. Life The son of Michael Taylor, an Edinburgh merchant, was born at Portobello in Midlothian on 29 January 1824. He was educated at Portsmouth, and matriculated at the University of Edinburgh in 1840, studying botany and graduating with an MD in 1843. In the following year he obtained a diploma from the Edinburgh College of Physicians and Surgeons. He was appointed assistant to Professor John Hutton Balfour, and was also one of the founders and early presidents of the Hunterian Medical Society. During 1844 Taylor studied surgery at Paris for nine months, and then visited European cities collecting botanical specimens. In 1845 he settled at Penrith in Cumberland, and soon after that succeeded to the practice of Dr John Taylor. In 1858 he discovered that scarlet fever might be caused by contamination in the milk supply. In 1868 he assisted in founding the border counties branch of the Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Buildings In Wharton, Cumbria
Wharton is a civil parish in the Eden District, Cumbria, England. It contains three listed buildings that are recorded in the National Heritage List for England. Of these, one is listed at Grade I, the highest of the three grades, and the others are at Grade II, the lowest grade. The parish is almost entirely rural, and the listed buildings consist of a ruined tower house, a medieval In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ... house, and a farmhouse. __NOTOC__ Key Buildings References Citations Sources * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Wharton, Cumbria Lists of listed buildings in Cumbria Eden District ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade I Listed Buildings In Cumbria
There are over 9000 Grade I listed buildings in England. This page is a list of these buildings in the county of Cumbria, sub-divided by district. Allerdale Barrow-in-Furness Carlisle Copeland Eden South Lakeland See also * Listed buildings in Barrow-in-Furness * Grade II* listed buildings in Cumbria The county of Cumbria is divided into six districts. The districts of Cumbria are Borough of Barrow-in-Furness, District of South Lakeland, Borough of Copeland, Borough of Allerdale, District of Eden, City of Carlisle. As there are 460 G ... Notes External links {{GradeIListedbuilding Grade I listed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Castles In England
This list of castles in England is not a list of every building and site that has "castle" as part of its name, nor does it list only buildings that conform to a strict definition of a castle as a medieval fortified residence. It is not a list of every castle ever built in England, many of which have vanished without trace, but is primarily a list of buildings and remains that have survived. In almost every case the buildings that survive are either ruined, or have been altered over the centuries. For several reasons, whether a given site is that of a medieval castle has not been taken to be a sufficient criterion for determining whether or not that site should be included in the list. Castles that have vanished or whose remains are barely visible are not listed, except for some important or well-known buildings and sites. Fortifications from before the medieval period are not listed, nor are architectural follies. In other respects it is difficult to identify clear and cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles In Great Britain And Ireland
Castles have played an important military, economic and social role in Great Britain and Ireland since their introduction following the Norman invasion of England in 1066. Although a small number of castles had been built in England in the 1050s, the Normans began to build motte and bailey and ringwork castles in large numbers to control their newly occupied territories in England and the Welsh Marches. During the 12th century the Normans began to build more castles in stone – with characteristic square keep – that played both military and political roles. Royal castles were used to control key towns and the economically important forests, while baronial castles were used by the Norman lords to control their widespread estates. David I invited Anglo-Norman lords into Scotland in the early 12th century to help him colonise and control areas of his kingdom such as Galloway; the new lords brought castle technologies with them and wooden castles began to be established over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade I Listed Building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000. The statutory term in Ireland is " protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without special permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency, particularly for significant alterations to the more notable listed buildings. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to a listed building which involves any element of demolition. Exemption from secular listed building control is provided for some buildings in current use for worship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheduled Monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change. The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage and destruction are grouped under the term "designation." The protection provided to scheduled monuments is given under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Areas Act 1979, which is a different law from that used for listed buildings (which fall within the town and country planning system). A heritage asset is a part of the historic environment that is valued because of its historic, archaeological, architectural or artistic interest. Only some of these are judged to be important enough to have extra legal protection through designation. There are about 20,000 scheduled monuments in England representing about 37,000 heritage assets. Of the tens of thousands of scheduled monuments in the UK, most are inconspicuous archaeological sites, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battlements
A battlement in defensive architecture, such as that of city walls or castles, comprises a parapet (i.e., a defensive low wall between chest-height and head-height), in which gaps or indentations, which are often rectangular, occur at intervals to allow for the launch of arrows or other projectiles from within the defences. These gaps are termed " crenels" (also known as ''carnels'', or ''embrasures''), and a wall or building with them is called crenellated; alternative (older) terms are castellated and embattled. The act of adding crenels to a previously unbroken parapet is termed crenellation. The function of battlements in war is to protect the defenders by giving them something to hide behind, from which they can pop out to launch their own missiles. A defensive building might be designed and built with battlements, or a manor house might be fortified by adding battlements, where no parapet previously existed, or cutting crenellations into its existing parapet wall. A d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |