|
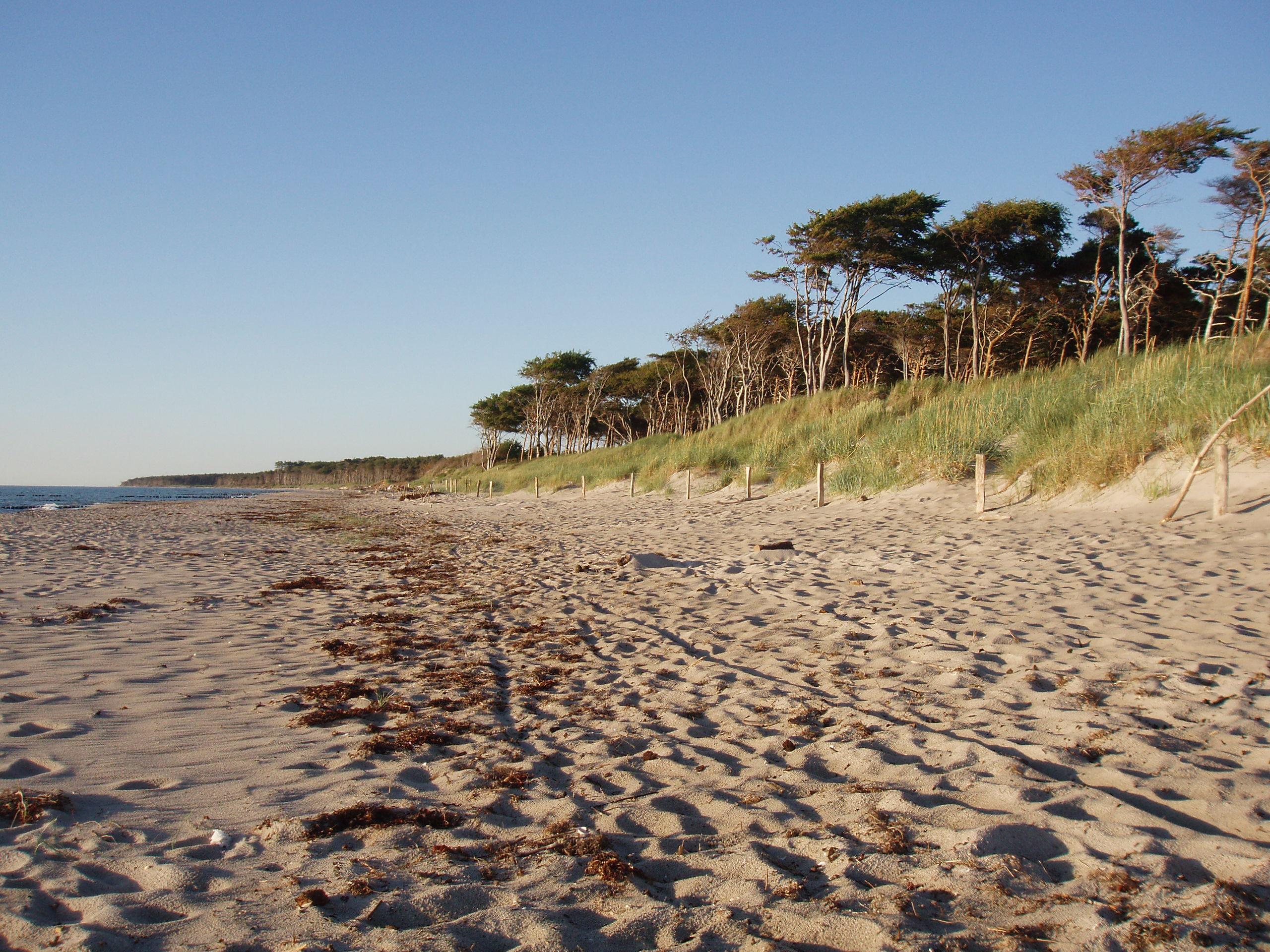
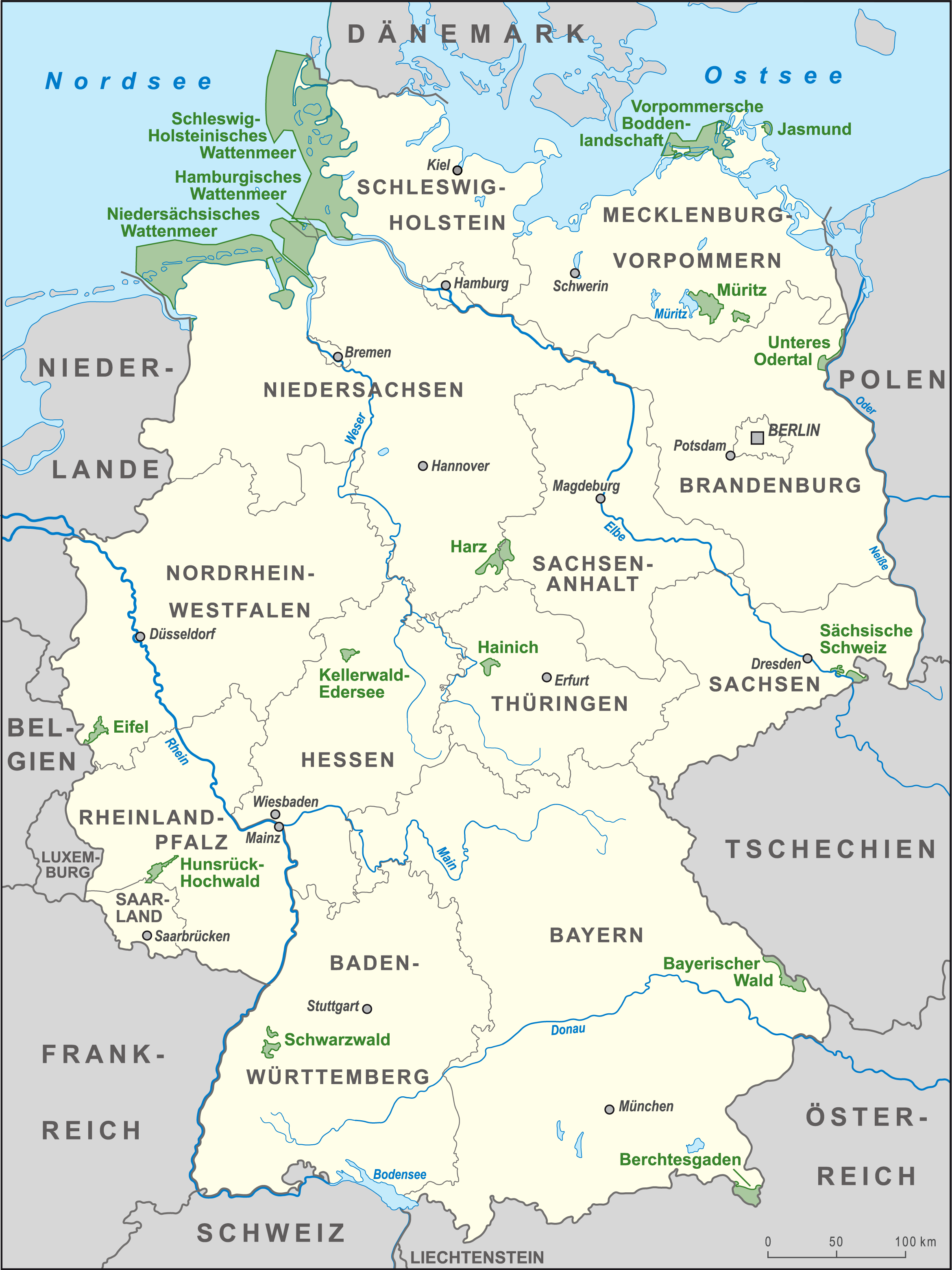
Western Pomerania Lagoon Area National Park
The Western Pomerania Lagoon Area National Park at www.naturefund.de. Accessed on 27 June 2012. (''Nationalpark Vorpommersche Boddenlandschaft'') is Mecklenburg-Vorpommern's largest national park, situated at the coast of the Baltic Sea. It consists of several peninsulas, islands and lagoon shore areas in the Baltic Sea, belonging to the district of Vorpommern-Rügen. The national park includes: * the Darss, Darß peninsula * the western coast of the island of Rügen * the island of Hiddensee * the island of Ummanz * several tiny islets between the above places * the multiple lagoons in between the land masses The national park is characterised by very shallow water housing a unique coastal fauna. All portions of the national park are famous for being a resting place for tens of thousands of crane (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV; ; nds, Mäkelborg-Vörpommern), also known by its anglicized name Mecklenburg–Western Pomerania, is a state in the north-east of Germany. Of the country's sixteen states, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern ranks 14th in population; it covers an area of , making it the sixth largest German state in area; and it is 16th in population density. Schwerin is the state capital and Rostock is the largest city. Other major cities include Neubrandenburg, Stralsund, Greifswald, Wismar, and Güstrow. It was named after the 2 regions of Mecklenburg and Vorpommern (which means West Pomerania). The state was established in 1945 after World War II through the merger of the historic regions of Mecklenburg and the Prussian Western Pomerania by the Soviet military administration in Allied-occupied Germany. It became part of the German Democratic Republic in 1949, but was dissolved in 1952 during administrative reforms and its territory divided into the districts of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root '' brak''. Certain human activities can produce brackish water, in particular civil engineering projects such as dikes and the flooding of coastal marshland to produce brackish water pools for freshwater prawn farming. Brackish water is also the primary waste product of the salinity gradient power process. Because brackish water is hostile to the growth of most terrestrial plant species, without appropriate management it is damaging to the environment (see article on shrimp farms). Technically, brackish water contains between 0.5 and 30 grams of salt per litre—more often expressed as 0.5 to 30 parts per thousand (‰), which is a specific grav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagoons Of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') and ''atoll lagoons''. They have also been identified as occurring on mixed-sand and gravel coastlines. There is an overlap between bodies of water classified as coastal lagoons and bodies of water classified as estuaries. Lagoons are common coastal features around many parts of the world. Definition and terminology Lagoons are shallow, often elongated bodies of water separated from a larger body of water by a shallow or exposed shoal, coral reef, or similar feature. Some authorities include fresh water bodies in the definition of "lagoon", while others explicitly restrict "lagoon" to bodies of water with some degree of salinity. The distinction between "lagoon" and "estuary" also varies between authorities. Richard A. Davis Jr. restricts "l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fischland-Darß-Zingst
Fischland-Darß-Zingst or Fischland-Darss-Zingst at www.fischland-darss-zingst.net. Accessed on 18 Dec 2011. is a long in the coastal district of , in the German state of . The three parts of the peninsula, from west to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Areas Established In 1990
Protection is any measure taken to guard a thing against damage caused by outside forces. Protection can be provided to physical objects, including organisms, to systems, and to intangible things like civil and political rights. Although the mechanisms for providing protection vary widely, the basic meaning of the term remains the same. This is illustrated by an explanation found in a manual on electrical wiring: Some kind of protection is a characteristic of all life, as living things have evolved at least some protective mechanisms to counter damaging environmental phenomena, such as ultraviolet light. Biological membranes such as bark on trees and skin on animals offer protection from various threats, with skin playing a key role in protecting organisms against pathogens and excessive water loss. Additional structures like scales and hair offer further protection from the elements and from predators, with some animals having features such as spines or camouflage servin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Areas Of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania
Protection is any measure taken to guard a thing against damage caused by outside forces. Protection can be provided to physical objects, including organisms, to systems, and to intangible things like civil and political rights. Although the mechanisms for providing protection vary widely, the basic meaning of the term remains the same. This is illustrated by an explanation found in a manual on electrical wiring: Some kind of protection is a characteristic of all life, as living things have evolved at least some protective mechanisms to counter damaging environmental phenomena, such as ultraviolet light. Biological membranes such as bark on trees and skin on animals offer protection from various threats, with skin playing a key role in protecting organisms against pathogens and excessive water loss. Additional structures like scales and hair offer further protection from the elements and from predators, with some animals having features such as spines or camouflage servin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Parks Of Germany
The following are the 16 national parks of Germany, sorted from North to South: Germany also has 14 Biosphere Reserves, as well as 98 nature parks. Including the national protected areas, about 25% of Germany's area is national parks or nature parks. See also * List of nature parks in Germany * Natural National Landscapes References External links National Parks and other Protected Areas * {{Europe in topic, List of national parks of, countries_only=yes |
Coastal Flooding
Coastal flooding normally occurs when dry and low-lying land is submerged by seawater. The range of a coastal flooding is a result of the elevation of floodwater that penetrates the inland which is controlled by the topography of the coastal land exposed to flooding. Flood damage modelling was limited to local, regional or national scales. However, with the presence of climate change and an increase in the population rates, flood events have intensified and called for a global interest in finding out different methods with both spatial and temporal dynamics. The seawater can flood the land via several different paths: direct flooding, overtopping of a barrier, breaching of a barrier. Coastal flooding is largely a natural event, however human influence on the coastal environment can exacerbate coastal flooding. Extraction of water from groundwater reservoirs in the coastal zone can instigate subsidence of the land, thus increasing the risk of flooding. Engineered protection struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darß Forest
The Darß Forest (pronounced "Darss", german: Darßwald) is a wooded region on the western coast of the peninsula of Darß on Germany's Baltic coast. There are no settlements in the forest. Villages on the outskirts are Ahrenshoop and Born in the south and Wieck and Prerow in the east. The Darß Forest covers an area of 5,800 hectares and is part of the Western Pomeranian Lagoon Region National Park. The area around Darßer Ort and the northwestern part of the forest belong to conservation zone 1. Here, the land may not be used for human exploitation and the aim is to allow the areas to develop naturally. History This area was formed during the development of a graded shoreline from rows of beach berms, which are recognisable today as a system of embankments (locally known as ''Reff'') and damp depressions (''Riegen''). Three thousand years ago the sea level was higher, so that old cliffed coastlines like the ''Alte Meerufer'' ("Old Seashore") may be found within the Dar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zingst
Zingst ( Polabian ''Sgoni'') is the easternmost portion of the three-part Fischland-Darß-Zingst Peninsula, located in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany, between the cities of Rostock and Stralsund on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea. The area is part of the Pomeranian coast. The Zingst Peninsula forms an eastward-running spit, nearly in length, and has a width of just . Zingst separates the Baltic Sea from the lagoon of Barther Bodden, which is part of the Darss-Zingst Bodden Chain, a large estuary. The shallow waters of the inlet are a major stopover for the migratory European crane. In spring and autumn, up to 3,000 birds gather here on their migration route to and from Spain. Most of the estuary and the eastern end of the peninsula are part of the Western Pomerania Lagoon Area National Park. Until the early 1870s, Zingst was an island, separated from Darß by the Prerowstrom, a narrow inlet. A storm tide in 1874 closed the inlet, which had connected the ''bodden'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darß
The Darß or Darss is the middle part of the peninsula of Fischland-Darß-Zingst on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in the German state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The peninsula's name is of Slavic origin. There is a large forest in the Darß. In recent times, the name "Darß" has also been used to refer to the entire peninsula. The Darß is famous for being a resting place for tens of thousands of migrating cranes and geese. Tourism has long been a source of income and has increased since German reunification, but the Darß is still far from being a crowded tourist place. Location and character The Darß lies northeast of Fischland and west of the peninsula of Zingst, its boundary with the latter being formed by the inlet of the Prerower Strom. To the north lies the Baltic Sea; to the south the lagoons of Saaler Bodden and Bodstedter Bodden, which belong to the Darss-Zingst Bodden Chain. The Darß measures between from north to south and from east to west and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Herring
Atlantic herring (''Clupea harengus'') is a herring in the family (biology), family Clupeidae. It is one of the most abundant fish species in the world. Atlantic herrings can be found on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean, congregating in large Shoaling and schooling, schools. They can grow up to in length and weigh up to . They feed on copepods, krill and small fish, while their natural predators are pinniped, seals, whales, cod and other larger fish. The Atlantic herring fishery has long been an important part of the economy of New England and the Canada, Canadian Atlantic provinces. This is because the fish congregate relatively near to the coast in massive schools, notably in the cold waters of the semi-enclosed Gulf of Maine and Gulf of Saint Lawrence, Gulf of St. Lawrence. North Atlantic herring schools have been measured up to in size, containing an estimated 4 billion fish. Description Atlantic herring have a wikt:fusiform, fusiform body. Gill rakers in their mouths fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)