|
Wesselsbron Virus
''Wesselsbron'' (WSL) ''virus'' is an arthropod-borne virus in the genus ''Flavivirus'' of the family ''Flaviviridae'' that causes Wesselsbron disease in cattle, sheep, goats, camels, pigs, donkeys, horses, ostriches, and wild ruminants with occasional incidental spillover to humans. It is transmitted by mosquitoes in the genus ''Aedes'' including ''A. caballus'' and ''A. circumluteolus''. __TOC__ History The first known outbreak was reported in 1955 on a sheep farm in the town of Wesselsbrons in Orange Free State Province, South Africa after an increase of lamb deaths and ewe abortions. Since the flock had been vaccinated 2 weeks before for protection against the Rift Valley virus, the possibility of a "new" disease was not put into consideration; the vaccine was assumed to be the culprit. Although they both share similarities, the WSL virus was isolated as distinct from the Rift Valley virus after the examination of a dead lamb's liver and brain. Geographical Distributio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod-borne Virus
Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is transmitted by arthropod vectors. The term ''arbovirus'' is a portmanteau word (''ar''thropod-''bo''rne ''virus''). ''Tibovirus'' (''ti''ck-''bo''rne ''virus'') is sometimes used to more specifically describe viruses transmitted by ticks, a superorder within the arthropods. Arboviruses can affect both animals (including humans) and plants. In humans, symptoms of arbovirus infection generally occur 3–15 days after exposure to the virus and last three or four days. The most common clinical features of infection are fever, headache, and malaise, but encephalitis and viral hemorrhagic fever may also occur. Signs and symptoms The incubation period – the time between when infection occurs and when symptoms appear – varies from virus to virus, but is usually limited between 2 and 15 days for arboviruses. The majority of infections, however, are asymptomatic. Among cases in which symptoms do appear, symptoms tend to be non-spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavivirus
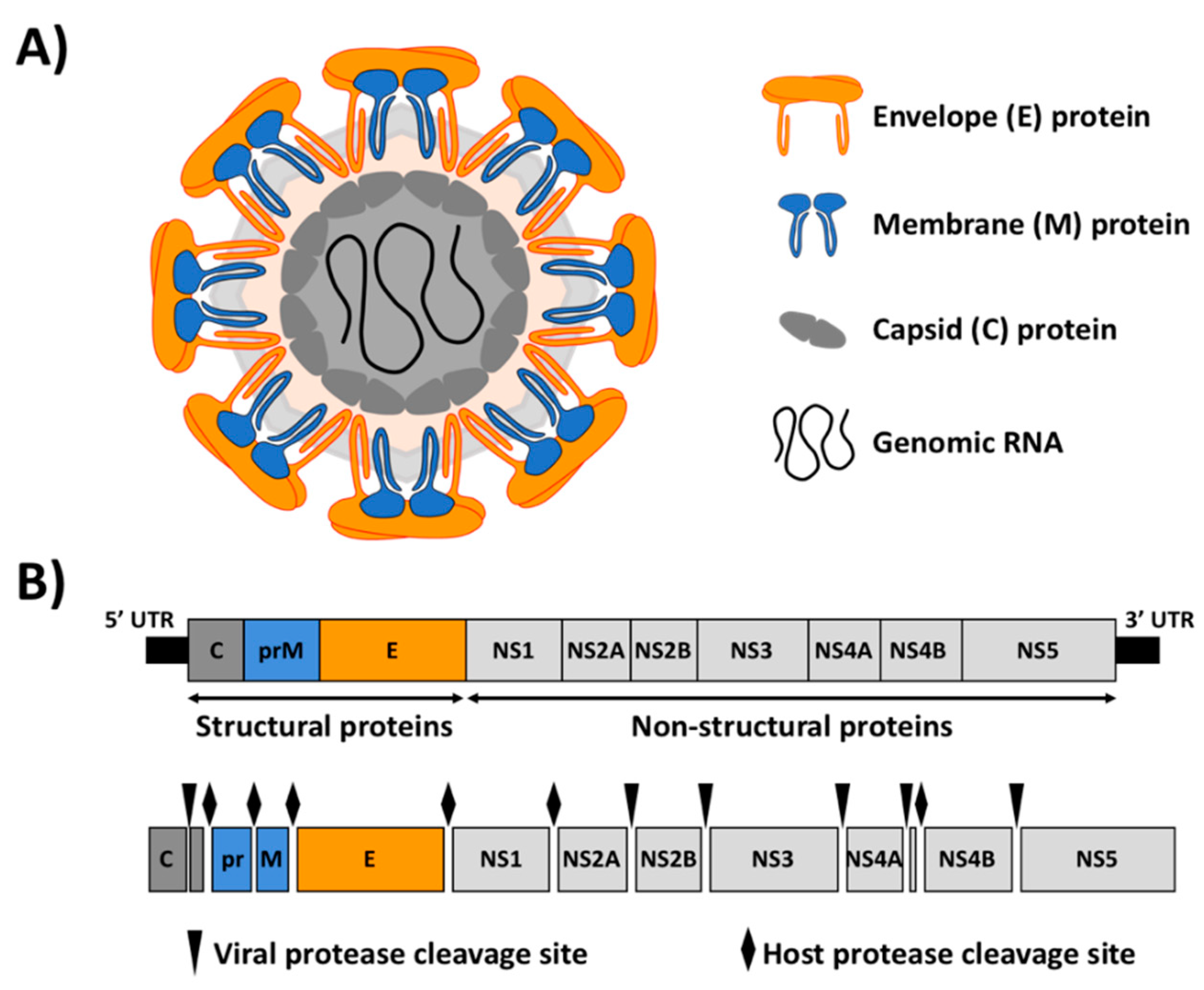
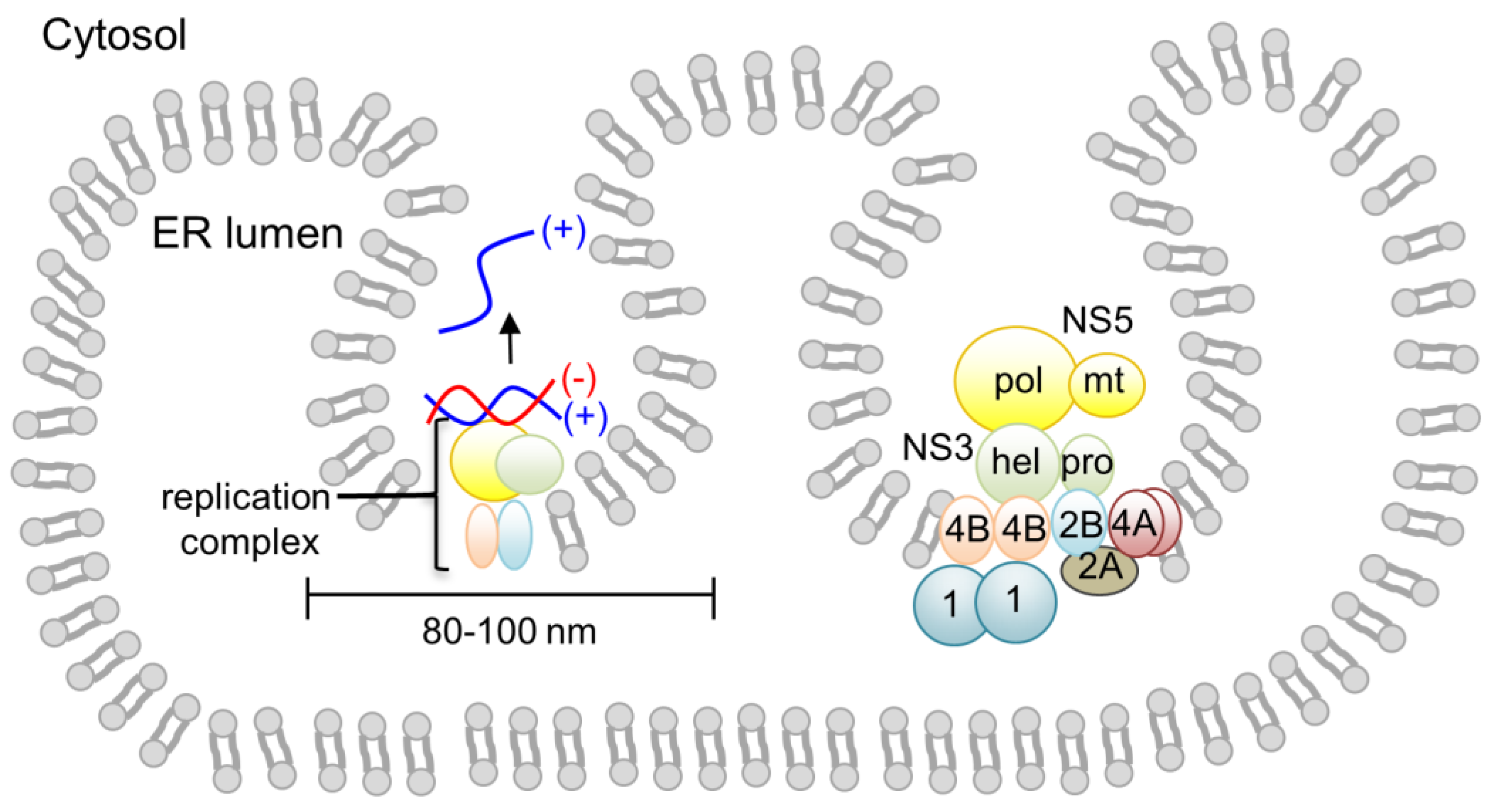
''Flavivirus'' is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family ''Flaviviridae''. The genus includes the West Nile virus, dengue virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus, yellow fever virus, Zika virus and several other viruses which may cause encephalitis, as well as insect-specific flaviviruses (ISFs) such as cell fusing agent virus (CFAV), Palm Creek virus (PCV), and Parramatta River virus (PaRV). While dual-host flaviviruses can infect vertebrates as well as arthropods, insect-specific flaviviruses are restricted to their competent arthropods. The means by which flaviviruses establish persistent infection in their competent vectors and cause disease in humans depends upon several virus-host interactions, including the intricate interplay between flavivirus-encoded immune antagonists and the host antiviral innate immune effector molecules. Flaviviruses are named for the yellow fever virus; the word ''flavus'' means 'yellow' in Latin, and yellow fever in turn is named from i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flaviviridae
''Flaviviridae'' is a family of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which mainly infect mammals and birds. They are primarily spread through arthropod vectors (mainly ticks and mosquitoes). The family gets its name from the yellow fever virus; ''flavus'' is Latin for "yellow", and yellow fever in turn was named because of its propensity to cause jaundice in victims. There are 89 species in the family divided among four genera. Diseases associated with the group include: hepatitis (hepaciviruses), hemorrhagic syndromes, fatal mucosal disease (pestiviruses), hemorrhagic fever, encephalitis, and the birth defect microcephaly (flaviviruses). Structure Virus particles are enveloped and spherical with icosahedral-like geometries that have pseudo T=3 symmetry. They are about 40–60 nm in diameter. Genome Members of the family ''Flaviviridae'' have monopartite, linear, single-stranded RNA genomes of positive polarity, and 9.6 to 12.3 kilobase in total length. The 5'-termini of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wesselsbron Disease
''Wesselsbron'' (WSL) ''virus'' is an arthropod-borne virus in the genus ''Flavivirus'' of the family ''Flaviviridae'' that causes Wesselsbron disease in cattle, sheep, goats, camels, pigs, donkeys, horses, ostriches, and wild ruminants with occasional incidental spillover to humans. It is transmitted by mosquitoes in the genus ''Aedes'' including ''A. caballus'' and ''A. circumluteolus''. __TOC__ History The first known outbreak was reported in 1955 on a sheep farm in the town of Wesselsbrons in Orange Free State Province, South Africa after an increase of lamb deaths and ewe abortions. Since the flock had been vaccinated 2 weeks before for protection against the Rift Valley virus, the possibility of a "new" disease was not put into consideration; the vaccine was assumed to be the culprit. Although they both share similarities, the WSL virus was isolated as distinct from the Rift Valley virus after the examination of a dead lamb's liver and brain. Geographical Distributio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aedes
''Aedes'' is a genus of mosquitoes originally found in tropical and subtropical zones, but now found on all continents except perhaps Antarctica. Some species have been spread by human activity: ''Aedes albopictus'', a particularly invasive species, was spread to the New World, including the United States, in the 1980s, by the used-tire trade. First described and named by German entomologist Johann Wilhelm Meigen in 1818, the generic name comes from the Ancient Greek ἀηδής, ''aēdēs'', meaning "unpleasant" or "odious". The type species for ''Aedes'' is ''Aedes cinereus''.. Systematics and phylogeny The genus was named by Johann Wilhelm Meigen in 1818. The generic name comes from the Ancient Greek ἀηδής, ''aēdēs'', meaning "unpleasant" or "odious". As historically defined, the genus contains over 700 species (see the list of ''Aedes'' species). The genus has been divided into several subgenera (''Aedes'', '' Diceromyia'', '' Finlaya'', ''Stegomyia'', etc.) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wesselsbron
Wesselsbron is a small maize farming town 75 kilometres south of Bothaville in Free State province of South Africa. Town 32 km east of Hoopstad and 48 km north-west of Welkom. It was laid out in 1920 and became a municipality in 1936. Named after Commandant Cornelis J Wessels who was in command of the Siege of Kimberley from 13 October 1899 to 12 February 1900. Bron is Afrikaans for ‘source’, ‘spring’. Wesselsbron has a vast district which stretches from the Vet River in the south to the Vaal River in the north. The main cultivation is corn, but also wheat, sunflower and peanuts are cultivated. The grain silos of Senwes are the biggest silo complex in the Southern Hemisphere and can cope with the enormous amount of 275,000 tons of grain. Escorted tours can be organized to visit the silos as well as a private milling complex next to Senwes. Because of the growing demand for liquidated fertilizer, Omnia opened a factory in Wesselsbron in 1997, one of the biggest f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orange Free State Province
The Province of the Orange Free State ( af, Provinsie Oranje-Vrystaat), commonly referred to as the Orange Free State ( af, Oranje-Vrystaat), Free State ( af, Vrystaat) or by its abbreviation OFS, was one of the four provinces of South Africa from 1910 to 1994. After 27 April 1994 it was dissolved following the first non-racial election in South Africa. It is now called the Free State Province. Its predecessor was the Orange River Colony which in 1902 had replaced the Orange Free State, a Boer republic. Its ''outside'' borders were the same as those of the modern Free State Province; except for the bantustans ("homelands") of QwaQwa and one part of Bophuthatswana, which were contained on land ''inside'' of the provincial Orange Free State borders. Districts in 1991 Districts of the province and population at the 1991 census. * Zastron: 14,122 * Rouxville: 11,904 * Bethulie: 9,333 * Smithfield: 7,946 * Wepener: 12,964 * Dewetsdorp: 13,521 * Reddersburg: 6,070 * Edenburg: 6,96 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa Free State Location Map
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz'' ("south"), possibly related to the same Proto-Indo-European root that the word ''sun'' derived from. Some languages describe south in the same way, from the fact that it is the direction of the sun at noon (in the Northern Hemisphere), like Latin meridies 'noon, south' (from medius 'middle' + dies 'day', cf English meridional), while others describe south as the right-hand side of the rising sun, like Biblical Hebrew תֵּימָן teiman 'south' from יָמִין yamin 'right', Aramaic תַּימנַא taymna from יָמִין yamin 'right' and Syriac ܬܰܝܡܢܳܐ taymna from ܝܰܡܝܺܢܳܐ yamina (hence the name of Yemen, the land to the south/right of the Levant). Navigation By convention, the ''bottom or down-facing side'' of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serologic
Serology is the scientific study of serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given microorganism), against other foreign proteins (in response, for example, to a mismatched blood transfusion), or to one's own proteins (in instances of autoimmune disease). In either case, the procedure is simple. Serological tests Serological tests are diagnostic methods that are used to identify antibodies and antigens in a patient's sample. Serological tests may be performed to diagnose infections and autoimmune illnesses, to check if a person has immunity to certain diseases, and in many other situations, such as determining an individual's blood type. Serological tests may also be used in forensic serology to investigate crime scene evidence. Several methods can be used to detect antibodies and antigens, including ELISA, agglutination, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovine Diseases
Bovines (subfamily Bovinae) comprise a diverse group of 10 genera of medium to large-sized ungulates, including cattle, bison, African buffalo, water buffalos, and the four-horned and spiral-horned antelopes. The evolutionary relationship between the members of the group is still debated, and their classification into loose tribes rather than formal subgroups reflects this uncertainty. General characteristics include cloven hooves and usually at least one of the sexes of a species having true horns. The largest extant bovine is the gaur. In many countries, bovid milk and meat is used as food by humans. Cattle are kept as livestock almost everywhere except in parts of India and Nepal, where they are considered sacred by most Hindus. Bovids are used as draft animals and as riding animals. Small breeds of domestic bovid, such as the Miniature Zebu, are kept as pets. Bovid leather is durable and flexible and is used to produce a wide range of goods including clothing and bags. Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flaviviruses
''Flavivirus'' is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family ''Flaviviridae''. The genus includes the West Nile virus, dengue virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus, yellow fever virus, Zika virus and several other viruses which may cause encephalitis, as well as insect-specific flaviviruses (ISFs) such as cell fusing agent virus (CFAV), Palm Creek virus (PCV), and Parramatta River virus (PaRV). While dual-host flaviviruses can infect vertebrates as well as arthropods, insect-specific flaviviruses are restricted to their competent arthropods. The means by which flaviviruses establish persistent infection in their competent vectors and cause disease in humans depends upon several virus-host interactions, including the intricate interplay between flavivirus-encoded immune antagonists and the host antiviral innate immune effector molecules. Flaviviruses are named for the yellow fever virus; the word ''flavus'' means 'yellow' in Latin, and yellow fever in turn is named from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |