|
Wernicke Encephalopathy
Wernicke encephalopathy (WE), also Wernicke's encephalopathy, or wet brain is the presence of neurological symptoms caused by biochemical lesions of the central nervous system after exhaustion of B-vitamin reserves, in particular thiamine (vitamin B1). The condition is part of a larger group of thiamine deficiency disorders that includes beriberi, in all its forms, and alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome. When it occurs simultaneously with alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome it is known as Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome. Classically, Wernicke encephalopathy is characterised by a triad of symptoms: ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, and confusion. Around 10% of patients exhibit all three features, and other symptoms may also be present. While it is commonly regarded as a condition peculiar to malnourished people with alcohol misuse, it can be caused by a variety of diseases. It is treated with thiamine supplementation, which can lead to improvement of the symptoms and often complete resolution, part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements. Ataxia is a clinical manifestation indicating dysfunction of the parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum. Ataxia can be limited to one side of the body, which is referred to as hemiataxia. Several possible causes exist for these patterns of neurological dysfunction. Dystaxia is a mild degree of ataxia. Friedreich's ataxia has gait abnormality as the most commonly presented symptom. The word is from Greek α- negative prefix+ -τάξις rder= "lack of order". Types Cerebellar The term cerebellar ataxia is used to indicate ataxia due to dysfunction of the cerebellum. The cerebellum is responsible for integrating a significant amount of neural information that is used to coordinate smoothly ongoing movements and to participate in motor planning. Althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
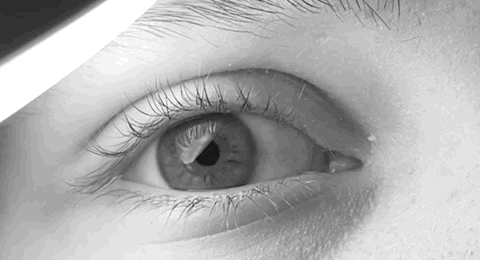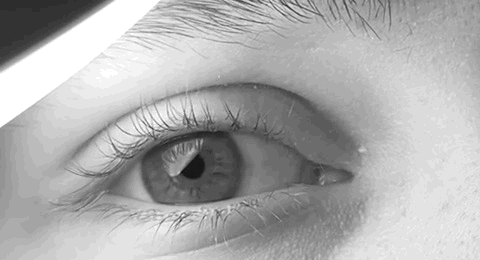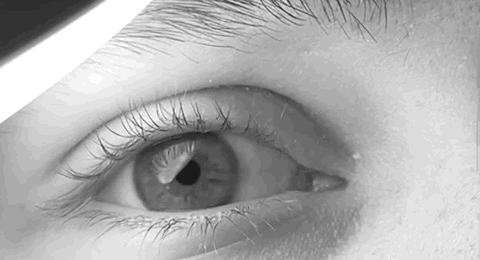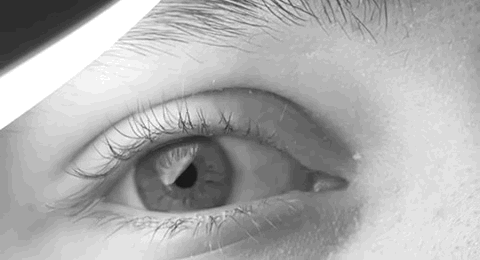
Nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the involuntary movement of the eye, it has been called "dancing eyes". In normal eyesight, while the head rotates about an axis, distant visual images are sustained by rotating eyes in the opposite direction of the respective axis. The semicircular canals in the vestibule of the ear sense angular acceleration, and send signals to the nuclei for eye movement in the brain. From here, a signal is relayed to the extraocular muscles to allow one's gaze to fix on an object as the head moves. Nystagmus occurs when the semicircular canals are stimulated (e.g., by means of the caloric test, or by disease) while the head is stationary. The direction of ocular movement is related to the semicircular canal that is being stimulated. There are two key form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a wide variety of high-volume biochemical reactions, including the synthesis and breakdown of small and complex molecule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and a number of hormones. There are two main types: acute pancreatitis, and chronic pancreatitis. Signs and symptoms of pancreatitis include pain in the upper abdomen, nausea and vomiting. The pain often goes into the back and is usually severe. In acute pancreatitis, a fever may occur, and symptoms typically resolve in a few days. In chronic pancreatitis weight loss, fatty stool, and diarrhea may occur. Complications may include infection, bleeding, diabetes mellitus, or problems with other organs. The two most common causes of acute pancreatitis are a gallstone blocking the common bile duct after the pancreatic duct has joined; and heavy alcohol use. Other causes include direct trauma, certain medications, infections such as mumps, and tumors. Chronic pancreatitis may develop as a result of acute pancreatitis. It is mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery (or weight loss surgery) includes a variety of procedures performed on people who are obese. Long term weight loss through the standard of care procedures ( Roux en-Y bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch) is largely achieved by altering gut hormone levels responsible for hunger and satiety, leading to a new hormonal weight set point. Bariatric surgery is the most effective treatment causing weight loss and reducing complications of obesity. As of October 2022, the American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) and International Federation for the Surgery of Obesity (IFSO) recommend bariatric surgery for adults with a body mass index (BMI) >35, regardless of obesity-associated conditions, and recommend considering surgery for people with BMI 30.0-34.9 who have metabolic disease. This is a recent change in guidelines (October 2022), so other guideline-producing organizations and health insurance plans may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confabulation
In psychology, confabulation is a memory error defined as the production of fabricated, distorted, or misinterpreted memories about oneself or the world. It is generally associated with certain types of brain damage (especially aneurysm in the anterior communicating artery) or a specific subset of dementias. While still an area of ongoing research, the basal forebrain is implicated in the phenomenon of confabulation. People who confabulate present with incorrect memories ranging from subtle inaccuracies to surreal fabrications, and may include confusion or distortion in the temporal framing (timing, sequence or duration) of memories. In general, they are very confident about their recollections, even when challenged with contradictory evidence. Description Confabulation is distinguished from lying as there is no intent to deceive and the person is unaware the information is false.Moscovitch M. 1995. "Confabulation". In (Eds. Schacter D.L., Coyle J.T., Fischbach G.D., Mesulum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korsakoff Syndrome
Korsakoff syndrome (KS) is a disorder of the central nervous system characterized by amnesia, deficits in explicit memory, and confabulation. This neurological disorder is caused by a deficiency of thiamine (vitamin B1) in the brain, and it is typically associated with and exacerbated by the prolonged, excessive ingestion of alcohol. Korsakoff syndrome is often accompanied by Wernicke encephalopathy; this combination is called Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome. Korsakoff syndrome is named after Sergei Korsakoff, the Russian neuropsychiatrist who described it during the late 19th century. Signs and symptoms There are seven major symptoms of Korsakoff syndrome, an amnestic- confabulatory syndrome: # anterograde amnesia, memory loss for events after the onset of the syndrome # retrograde amnesia, memory loss extends back for some time before the onset of the syndrome # amnesia of fixation, also known as fixation amnesia (loss of immediate memory, a person being unable to remember ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis is a condition characterized by abnormally increased sweating, in excess of that required for regulation of body temperature. Although primarily a benign physical burden, hyperhidrosis can deteriorate quality of life from a psychological, emotional, and social perspective. In fact, hyperhidrosis almost always leads to psychological as well as physical and social consequences. It is thus responsible for more than ¼ of the cases of social phobia. Patients suffering from it present difficulties in the professional field, more than 80% of patients experience a moderate to severe emotional impact from the disease and half are subject to depression. This excess of sweat happens even if the person is not engaging in tasks that require muscular effort, and it does not depend on the exposure to heat. Common places to sweat can include underarms, face, neck, back, groin, feet, and hands. It has been called by some researchers 'the silent handicap'. Both '' diaphoresis'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactic Acidosis
Lactic acidosis is a medical condition characterized by a build-up of lactate (especially -lactate) in the body, with formation of an excessively low pH in the bloodstream. It is a form of metabolic acidosis, in which excessive acid accumulates due to a problem with the body's oxidative metabolism. Lactic acidosis is typically the result of an underlying acute or chronic medical condition, medication, or poisoning. The symptoms are generally attributable to these underlying causes, but may include nausea, vomiting, Kussmaul breathing (laboured and deep), and generalised weakness. The diagnosis is made on biochemical analysis of blood (often initially on arterial blood gas samples), and once confirmed, generally prompts an investigation to establish the underlying cause to treat the acidosis. In some situations, hemofiltration (purification of the blood) is temporarily required. In rare chronic forms of lactic acidosis caused by mitochondrial disease, a specific diet or dichl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stupor
Stupor is the lack of critical mental function and a level of consciousness, in which an affected person is almost entirely unresponsive and responds only to intense stimuli such as pain. The word derives from the Latin '' stupor'' ("numbness, insensibility"). Signs and symptoms Stupor is characterised by impaired reaction to external stimuli. Those in a stuporous state are rigid, mute and only appear to be conscious, as the eyes are open and follow surrounding objects. If not stimulated externally, a patient with stupor will appear to be in a sleepy state most of the time. In some extreme cases of severe depressive disorders the patient can become motionless, lose their appetite and become mute. Short periods of restricted responsivity can be achieved by intense stimulation (e.g. pain, bright light, loud noise, shock). Causes Stupor is associated with infectious diseases, complicated toxic states (e.g. heavy metals), severe hypothermia, mental illnesses (e.g. schizophrenia, maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly such as broken bones or through causing accidents. In epilepsy, seizures tend to recur and may have no immediate underlying cause. Isolated seizures that are provoked by a specific cause such as poisoning are not deemed to represent epilepsy. People with epilepsy may be treated differently in various areas of the world and experience varying degrees of social stigma due to the alarming nature of their symptoms. The underlying mechanism of epileptic seizures is excessive and abnormal neuronal activity in the cortex of the brain which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG) of an individual. The reason this occurs in most cases of epilepsy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea, also spelled sleep apnoea, is a sleep disorder in which pauses in breathing or periods of shallow breathing during sleep occur more often than normal. Each pause can last for a few seconds to a few minutes and they happen many times a night. In the most common form, this follows loud snoring. There may be a choking or snorting sound as breathing resumes. Because the disorder disrupts normal sleep, those affected may experience sleepiness or feel tired during the day. In children, it may cause hyperactivity or problems in school. Sleep apnea may be either obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), in which breathing is interrupted by a blockage of air flow, central sleep apnea (CSA), in which regular unconscious breath simply stops, or a combination of the two. OSA is the most common form. OSA has four key contributors; these include a narrow, crowded, or collapsible upper airway, an ineffective pharyngeal dilator muscle function during sleep, airway narrowing during sleep a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |