|
Lactic Acidosis
Lactic acidosis is a medical condition characterized by a build-up of lactate (especially -lactate) in the body, with formation of an excessively low pH in the bloodstream. It is a form of metabolic acidosis, in which excessive acid accumulates due to a problem with the body's oxidative metabolism. Lactic acidosis is typically the result of an underlying acute or chronic medical condition, medication, or poisoning. The symptoms are generally attributable to these underlying causes, but may include nausea, vomiting, Kussmaul breathing (laboured and deep), and generalised weakness. The diagnosis is made on biochemical analysis of blood (often initially on arterial blood gas samples), and once confirmed, generally prompts an investigation to establish the underlying cause to treat the acidosis. In some situations, hemofiltration (purification of the blood) is temporarily required. In rare chronic forms of lactic acidosis caused by mitochondrial disease, a specific diet or dichloro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactic Acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula . It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natural sources. Lactic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) due to the presence of a hydroxyl group adjacent to the carboxyl group. It is used as a synthetic intermediate in many organic synthesis industries and in various biochemical industries. The conjugate base of lactic acid is called lactate (or the lactate anion). The name of the derived acyl group is lactoyl. In solution, it can ionize by loss of a proton to produce the lactate ion . Compared to acetic acid, its p''K'' is 1 unit less, meaning lactic acid is ten times more acidic than acetic acid. This higher acidity is the consequence of the intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the α-hydroxyl and the carboxylate group. Lactic acid is chiral, consisting of two enantiomers. One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trauma (medicine)
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, or overexertion. Injuries can occur in any part of the body, and different symptoms are associated with different injuries. Treatment of a major injury is typically carried out by a health professional and varies greatly depending on the nature of the injury. Traffic collisions are the most common cause of accidental injury and injury-related death among humans. Injuries are distinct from chronic conditions, psychological trauma, infections, or medical procedures, though injury can be a contributing factor to any of these. Several major health organizations have established systems for the classification and description of human injuries. Occurrence Injuries may be intentional or unintentional. Intentional injuries may be acts of vio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linezolid
Linezolid is an antibiotic used for the treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics. Linezolid is active against most Gram-positive bacteria that cause disease, including streptococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), and methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA). The main uses are infections of the skin and pneumonia although it may be used for a variety of other infections including drug-resistant tuberculosis. It is used either by injection into a vein or by mouth. When given for short periods, linezolid is a relatively safe antibiotic. It can be used in people of all ages and in people with liver disease or poor kidney function. Common side effects with short-term use include headache, diarrhea, rash, and nausea. Serious side effects may include serotonin syndrome, bone marrow suppression, and high blood lactate levels, particularly when used for more than two weeks. If used for longer periods it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leigh Syndrome
Leigh syndrome (also called Leigh disease and subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy) is an inherited neurometabolic disorder that affects the central nervous system. It is named after Archibald Denis Leigh, a British neuropsychiatrist who first described the condition in 1951. Normal levels of thiamine, thiamine monophosphate, and thiamine diphosphate are commonly found but there is a reduced or absent level of thiamine triphosphate. This is thought to be caused by a blockage in the enzyme thiamine-diphosphate kinase, and therefore treatment in some patients would be to take thiamine triphosphate daily. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of Leigh syndrome are classically described as beginning in infancy and leading to death within a span of several years; however, as more cases are recognized, it is apparent that symptoms can emerge at any age—including adolescence or adulthood—and patients can survive for many years following diagnosis. Symptoms are often first seen after a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyruvate Carboxylase Deficiency
Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency is an inherited disorder that causes lactic acid to accumulate in the blood. High levels of these substances can damage the body's organs and tissues, particularly in the nervous system. Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency is a rare condition, with an estimated incidence of 1 in 250,000 births worldwide. Type A of the disease appears to be much more common in some Algonkian Indian tribes in eastern Canada, while the type B disease is more present in European populations. Signs and symptoms Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency causes lactic acidosis and hyperammonaemia. Lactic acidosis may then lead to liver failure, hepatomegaly, reduced ketone body synthesis, and demyelination of neurons. Genetics Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency is caused by mutations in the ''PC'' gene. The ''PC'' gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called pyruvate carboxylase. This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means two copies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Deficiency
Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency (also known as pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency or PDCD) is a rare neurodegenerative disorders associated with abnormal mitochondrial metabolism. PDCD is a genetic disease resulting from mutations in one of the components of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC). The PDC is a multi-enzyme complex that plays a vital role as a key regulatory step in the central pathways of energy metabolism in the mitochondria. The disorder shows heterogeneous characteristics in both clinical presentation and biochemical abnormality. Signs and symptoms PDCD is generally presented in one of two forms. The metabolic form appears as lactic acidosis. The neurological form of PDCD contributes to hypotonia, poor feeding, lethargy and structural abnormalities in the brain. Patients may develop seizures and/or neuropathological spasms. These presentations of the disease usually progress to mental retardation, microcephaly, blindness, and spasticity. Females w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, And Stroke-like Episodes
Mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) is one of the family of mitochondrial diseases, which also include MIDD (maternally inherited diabetes and deafness, MERRF syndrome, and Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. It was first characterized under this name in 1984. A feature of these diseases is that they are caused by defects in the mitochondrial genome which is inherited purely from the female parent. The most common MELAS mutation is mitochondrial mutation, mtDNA, referred to as m.3243A>G. Signs and symptoms MELAS is a condition that affects many of the body's systems, particularly the brain and nervous system (encephalo-) and muscles (myopathy). In most cases, the signs and symptoms of this disorder appear in childhood following a period of normal development. Children with MELAS often have normal early psychomotor development until the onset of symptoms between 2 and 10 years old. Though less common, infantile onset may occur and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GRACILE Syndrome
GRACILE syndrome is a very rare lethal autosomal recessive genetic disorder, one of the Finnish heritage diseases. GRACILE syndrome has also been found in the UK and Sweden, but not nearly as much as in Finland. It is caused by a mutation in the '' BCS1L'' gene and it occurs in approximately 1 out of 50,000 live births in Finnish people. To date, there have only been 32 cases of GRACILE syndrome reported. GRACILE is an acronym for growth retardation, aminoaciduria (amino acids in the urine), cholestasis, iron overload, lactic acidosis and early death. Prior to birth, the growth of the fetus is abnormally slow. This slow growth leads to a smaller than average newborn that has difficulty growing at a normal rate. Signs and symptoms People with GRACILE syndrome can have a wide range of symptoms, but that does not mean every person affected will have the same symptoms as one another It has been determined that 80% - 99% of people with GRACILE syndrome have at least one of these: * C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
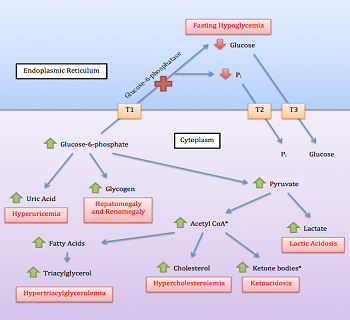
Glucose-6-phosphatase Deficiency
Glycogen storage disease type I (GSD I) is an inherited disease that results in the liver being unable to properly break down stored glycogen. This impairment disrupts the liver's ability to break down stored glycogen that is necessary to maintain adequate blood sugar levels. GSD I is divided into two main types, GSD Ia and GSD Ib, which differ in cause, presentation, and treatment. GSD Ia is caused by a deficiency in the enzyme glucose-6-phosphatase, while GSD Ib is caused a deficiency in the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate translocase. Since glycogenolysis is the principal metabolic mechanism by which the liver supplies glucose to the body during periods of fasting, both deficiencies cause severe low blood sugar and, over time, excess glycogen storage in the liver and (in some cases) the kidneys. GSD I patients typically present with an enlarged liver from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as the result of this glycogen buildup. Other functions of the liver and kidneys are initiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fructose Bisphosphatase Deficiency
In fructose bisphosphatase deficiency, there is not enough fructose bisphosphatase for gluconeogenesis to occur correctly. Glycolysis (the breakdown of glucose) will still work, as it does not use this enzyme. History Early research into the disorder was conducted by a team led by Anthony S. Pagliara and Barbara Illingworth Brown at Washington University Medical Center, based on the case of an infant girl from Oak Ridge, Missouri. Presentation Without effective gluconeogenesis (GNG), hypoglycaemia will set in after about 12 hours of fasting. This is the time when liver glycogen stores have been exhausted, and the body has to rely on GNG. When given a dose of glucagon (which would normally increase blood glucose) nothing will happen, as stores are depleted and GNG doesn't work. (In fact, the patient would already have high glucagon levels.) There is no problem with the metabolism of glucose or galactose, but fructose and glycerol cannot be used by the liver to maintain blood gluc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes Mellitus And Deafness
Diabetes and deafness (DAD) or maternally inherited diabetes and deafness (MIDD) or mitochondrial diabetes is a subtype of diabetes which is caused from a point mutation at position 3243 in human mitochondrial DNA, which consists of a circular genome. This affects the gene encoding tRNALeu.Murphy R, Turnbull DM, Walker M, Hattersley AT "Clinical features, diagnosis and management of maternally inherited diabetes and deafness (MIDD) associated with the 3243A>G mitochondrial point mutation. " Diabet. Med. 2008, 25(4), 383-99. de Andrade PB, Rubi B, Frigerio F, van den Ouweland JM, Maassen JA, Maechler P. "Diabetes-associated mitochondrial DNA mutation A3243G impairs cellular metabolic pathways necessary for beta cell function" ''Diabetologia''. 2006 Aug;49(8):1816-26. Because mitochondrial DNA is contributed to the embryo by the oocyte and not by spermatozoa, this disease is inherited from maternal family members only. As indicated by the name, MIDD is characterized by diabetes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotin
Biotin (or vitamin B7) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. The name ''biotin'', borrowed from the German , derives from the Ancient Greek word (; 'life') and the suffix "-in" (a suffix used in chemistry usually to indicate 'forming'). Chemical description Biotin is classified as a heterocyclic compound, with a sulfur-containing ring fused ureido and tetrahydrothiophene group. A C5-carboxylic acid side chain is appended to one of the rings. The ureido ring, containing the −N−CO−N− group, serves as the carbon dioxide carrier in carboxylation reactions. Biotin is a coenzyme for five carboxylase enzymes, which are involved in the catabolism of amino acids and fatty acids, synthesis of fatty acids, and gluconeogenesis. Biotinylation of histone proteins in nuclear chromatin plays a role in chromatin stability and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |