|
Wepwawetemsaf
Sekhemraneferkhau Wepwawetemsaf was an Egyptian pharaoh during the Second Intermediate Period. According to the Egyptologists Kim Ryholt and Darrell Baker, he was a king of the Abydos Dynasty, although they leave his position within this dynasty undetermined.Darrell D. Baker: ''The Encyclopedia of the Pharaohs: Volume I - Predynastic to the Twentieth Dynasty 3300–1069 BC'', Stacey International, , 2008, p. 496-497 K.S.B. Ryholt: ''The Political Situation in Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period, c. 1800 – 1550 BC'', Carsten Niebuhr Institute Publications, vol. 20. Copenhagen: Museum Tusculanum Press, 1997 Alternatively, the Egyptologist Jürgen von Beckerath sees Wepwawetemsaf as a king of the late 13th Dynasty, while Marcel Marée proposes that he was a king of the late 16th Dynasty.Jürgen von Beckerath: ''Handbuch der ägyptischen Königsnamen'', Münchner ägyptologische Studien 49, Mainz 1999. Attestations The only contemporaneous attestation of Wepwawetems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wepwawetemsaf Beni Hasan
Sekhemraneferkhau Wepwawetemsaf was an Egyptian pharaoh during the Second Intermediate Period. According to the Egyptologists Kim Ryholt and Darrell Baker, he was a king of the Abydos Dynasty, although they leave his position within this dynasty undetermined.Darrell D. Baker: ''The Encyclopedia of the Pharaohs: Volume I - Predynastic to the Twentieth Dynasty 3300–1069 BC'', Stacey International, , 2008, p. 496-497 K.S.B. Ryholt: ''The Political Situation in Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period, c. 1800 – 1550 BC'', Carsten Niebuhr Institute Publications, vol. 20. Copenhagen: Museum Tusculanum Press, 1997 Alternatively, the Egyptologist Jürgen von Beckerath sees Wepwawetemsaf as a king of the late 13th Dynasty, while Marcel Marée proposes that he was a king of the late 16th Dynasty.Jürgen von Beckerath: ''Handbuch der ägyptischen Königsnamen'', Münchner ägyptologische Studien 49, Mainz 1999. Attestations The only contemporaneous attestation of Wepwawetems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantjeny
Sekhemrekhutawy Pantjeny was an Egyptian pharaoh during the Second Intermediate Period. According to the Egyptologists Kim Ryholt and Darrell Baker, he was a king of the Abydos Dynasty, although they leave his position within this dynasty undetermined.K.S.B. Ryholt, ''The Political Situation in Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period, c.1800–1550 BC'', Carsten Niebuhr Institute Publications, vol. 20. Copenhagen: Museum Tusculanum Press, 1997excerpts available online here./ref>Darrell D. Baker: ''The Encyclopedia of the Pharaohs: Volume I - Predynastic to the Twentieth Dynasty 3300–1069 BC'', Stacey International, , 2008, p. 289-290 Alternatively, Pantjeny could be a king of the late 16th Dynasty. According to Jürgen von Beckerath, Pantjeny is to be identified with Sekhemrekhutawy Khabaw, whom he sees as the third king of the 13th Dynasty. Attestation Stela BM EA 630 Pantjeny is known from a single limestone stela "of exceptionally crude quality" found in Abydos by Flind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
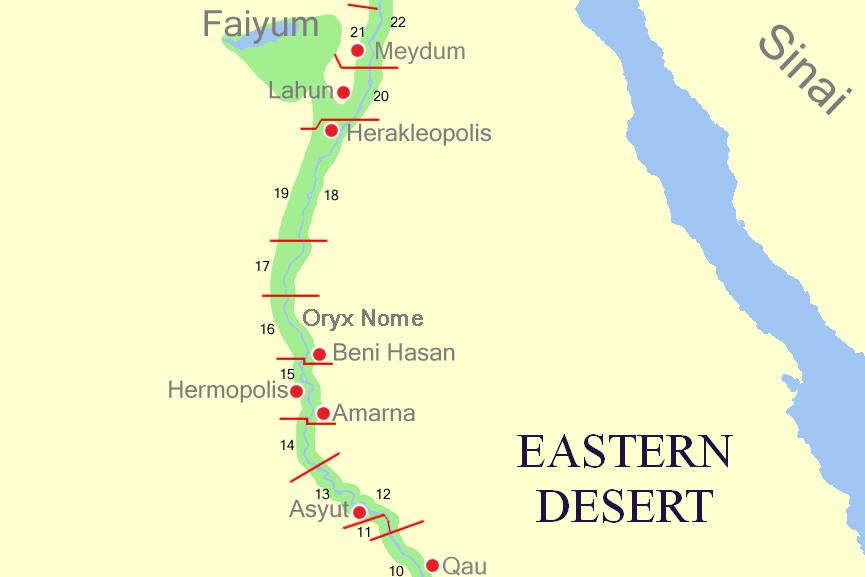
Amenemhat (BH2)
Amenemhat, often reported with his short form Ameny (''Jmnjj''), was an ancient Egyptian "Overlord of the Oryx nome" (the 16th nome of Upper Egypt) and chief priest during the reign of pharaoh Senusret I of the 12th Dynasty (20th century BCE). Biography Amehemhat's mother was a noblewoman called Henu, whilst his father's name is unknown. Amenemhat was married to Hetepet, a "mistress of the house" and daughter of a governor, and the couple had a son called Khnumhotep. However, any relationship between Amenemhat and the ruling family of governors founded earlier by Khnumhotep I is unknown, and it was proposed that he could rather have been a member of the previous family of local governors. In any case, he administered his governorate from the city of Men'at Khufu from Year 18 to at least Year 43 of Senusret I.Wolfram Grajetzki, ''The Middle Kingdom of ancient Egypt: history, archaeology and society''. London, Duckworth Egyptology, 2006, pp. 113-14 Amenemhat accompanied the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wepwawet
In late Egyptian mythology, Wepwawet (hieroglyphic ''wp-w3w.t''; also rendered Upuaut, Wep-wawet, Wepawet, and Ophois) was originally a war deity, whose cult centre was Asyut in Upper Egypt (Lycopolis in the Greco-Roman period). His name means ''opener of the ways'' and he is often depicted as a wolf standing at the prow of a solar-boat. Some interpret that Wepwawet was seen as a scout, going out to clear routes for the army to proceed forward. One inscription from the Sinai states that Wepwawet "opens the way" to king Sekhemkhet's victory.Remler, p.170 Wepwawet originally was seen as a wolf deity, thus the Greek name of Lycopolis, meaning ''city of wolves'', and it is likely the case that Wepwawet was originally just a symbol of the pharaoh, seeking to associate with wolf-like attributes, that later became deified as a mascot to accompany the pharaoh. Likewise, Wepwawet was said to accompany the pharaoh on hunts, in which capacity he was titled ''(one with) sharp arrow more pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Intermediate Period
The Second Intermediate Period marks a period when ancient Egypt fell into disarray for a second time, between the end of the Middle Kingdom and the start of the New Kingdom. The concept of a "Second Intermediate Period" was coined in 1942 by German Egyptologist Hanns Stock. It is best known as the period when the Hyksos people of West Asia made their appearance in Egypt and whose reign comprised the 15th Dynasty, which, according to Manetho's ''Aegyptiaca'', was founded by a king by the name of Salitis. End of the Middle Kingdom The 12th Dynasty of Egypt came to an end at the end of the 19th century BC with the death of Queen Sobekneferu (1806–1802 BC).Kim S. B. Ryholt, ''The Political Situation in Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period, c. 1800–1550 B.C.'', Museum Tusculanum Press, Carsten Niebuhr Institute Publications 20. 1997, p.185 Apparently she had no heirs, causing the 12th Dynasty to come to a sudden end, and, with it, the Golden Age of the Middle Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rahotep
Sekhemre-Wahkhau Rahotep was an Egyptian pharaoh who reigned during the Second Intermediate Period, when Egypt was ruled by multiple kings. The Egyptologists Kim Ryholt and Darrell Baker believe that Rahotep was the first king of the 17th Dynasty. __FORCETOC__ Attestations Rahotep seem to be attested at Abydos and Coptos. Rahotep is known from a stele found at Coptos reporting the restoration of the temple of Min. The stele, now in the Petrie Museum (UC 14327), reads Rahotep is also attested on a limestone stele, now in the British Museum (BM EA 833), which shows him making an offering to Osiris for two deceased, an officer and a priest. The stela appears to have been made at a workshop at Abydos. Other stelae produced by this workshop belong to king Sekhemrekhutawy Pantjeny and king Wepwawetemsaf. All three kings reigned therefore quite close in time.Marcel Marée: ''A sculpture workshop at Abydos from the late Sixteenth or early Seventeenth Dynasty'', in: Marcel Marée ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventeenth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Seventeenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XVII, alternatively 17th Dynasty or Dynasty 17) was a dynasty of pharaohs that ruled in Upper Egypt during the late Second Intermediate Period, approximately from 1580 to 1550 BC. Its mainly Theban rulers are contemporary with the Hyksos of the Fifteenth Dynasty and succeed the Sixteenth Dynasty, which was also based in Thebes. In March 2012, French archeologists examining a limestone door in the Precinct of Amun-Re at Karnak discovered hieroglyphs with the name Senakhtenre, the first evidence of this king dating to his lifetime. The last two kings of the dynasty opposed the Hyksos rule over Egypt and initiated a war that would rid Egypt of the Hyksos kings and began a period of unified rule, the New Kingdom of Egypt. Kamose, the second son of Seqenenre Tao and last king of the Seventeenth Dynasty, was the brother of Ahmose I, the first king of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Some mainstream scholars have suggested that the Seventee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophoric Name
A theophoric name (from Greek: , ''theophoros'', literally "bearing or carrying a god") embeds the word equivalent of 'god' or God's name in a person's name, reflecting something about the character of the person so named in relation to that deity. For example, names embedding Apollo, such as ''Apollonios'' or ''Apollodorus'', existed in Greek antiquity. Theophoric personal names, containing the name of a god in whose care the individual is entrusted (or a generic word for ''god''), were also exceedingly common in the ancient Near East and Mesopotamia. Some names of theophoric origin remain common today, such as Theodore (''theo-'', "god"; ''-dore'', origin of word compound in Greek: ''doron'', "gift"; hence "God's gift"; in Greek: ''Theodoros'') or less recognisably as Jonathan (from Hebrew ''Yonatan/Yehonatan'', meaning "Yahweh has given"). Classical Greek and Roman theophoric names * Demetrius and its derivatives mean "follower of Demeter." * Dennis, in Latin ''Dionysius'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyksos
Hyksos (; Egyptian '' ḥqꜣ(w)- ḫꜣswt'', Egyptological pronunciation: ''hekau khasut'', "ruler(s) of foreign lands") is a term which, in modern Egyptology, designates the kings of the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt (fl. c. 1650–1550 BC). The seat of power of these kings was the city of Avaris in the Nile delta, from where they ruled over Lower and Middle Egypt up to Cusae. In the ''Aegyptiaca'', a history of Egypt written by the Greco-Egyptian priest and historian Manetho in the 3rd century BC, the term Hyksos is used ethnically to designate people of probable West Semitic, Levantine origin. While Manetho portrayed the Hyksos as invaders and oppressors, this interpretation is questioned in modern Egyptology. Instead, Hyksos rule might have been preceded by groups of Canaanite peoples who gradually settled in the Nile delta from the end of the Twelfth Dynasty onwards and who may have seceded from the crumbling and unstable Egyptian control at some point during the Thirteent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memphis, Egypt
, alternate_name = , image = , alt = , caption = Ruins of the pillared hall of Ramesses IIat Mit Rahina , map_type = Egypt#Africa , map_alt = , map_size = , relief = , coordinates = , location = Mit Rahina, Giza Governorate, Egypt , region = Lower Egypt , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = Unknown, was already in existence during Iry-Hor's reignP. Tallet, D. Laisnay: ''Iry-Hor et Narmer au Sud-Sinaï (Ouadi 'Ameyra), un complément à la chronologie des expéditios minière égyptiene'', in: BIFAO 112 (2012), 381–395available online/ref> , material = , built = Earlier than 31st century BC , abandoned = 7th century AD , epochs = Early Dynastic Period to Early Middle Ages , cultures = , dependency_of = , occupants = , event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detlef Franke
Detlef Franke (November 24, 1952 in Lüneburg – September 2, 2007) was a Germans, German Egyptologist specialist of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt. Biography Detlef Franke received his doctorate at the University of Hamburg in 1983 with his thesis "''Altägyptische Verwandtschaftsbezeichnungen im Mittleren Reich''" ("The ancient Egyptian kingship in the Middle Kingdom"). He then received his habilitation at the University of Heidelberg in 1994 with his work "''Das Heiligtum des Heqaib auf Elephantine. Geschichte eines Provinzheiligtums im Mittleren Reich''" ("On the sanctuary of Heqaib on Elephantine. History of a provincial sanctuary in the Middle Kingdom"). He subsequently taught as a lecturer at this university until his death. Throughout his career, Detlef Franke researched mainly the Middle Kingdom of ancient Egypt.Hans-Werner Fischer-Elfert: ''Detlef Franke (1952–2007).'' in: ''Zeitschrift für Ägyptische Sprache und Altertumskunde'', volume 135, 2010, p. III–XI () His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Egypt
Middle Egypt () is the section of land between Lower Egypt (the Nile Delta) and Upper Egypt, stretching upstream from Asyut in the south to Memphis in the north. At the time, Ancient Egypt was divided into Lower and Upper Egypt, though Middle Egypt was technically a subdivision of Upper Egypt. It was not until the 19th century that archaeologists felt the need to divide Upper Egypt in two. As a result, they coined the term "Middle Egypt" for the stretch of river between Cairo and the Qena Bend. It was also associated with a region termed "Heptanomis" (; Greek: , in Ptol. iv. 5. § 55; more properly or , in Dionysius Periegetes 251; and sometimes ; meaning "Seven Nomes", a " nome" being a subdivision of ancient Egypt), generally as the district which separates the Thebaïd from the Delta. Middle Egypt today can be identified as the part of the Nile Valley that, while geographically part of Upper Egypt, is culturally closer to Lower Egypt. For instance, in terms of language, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |