|
Wenshania
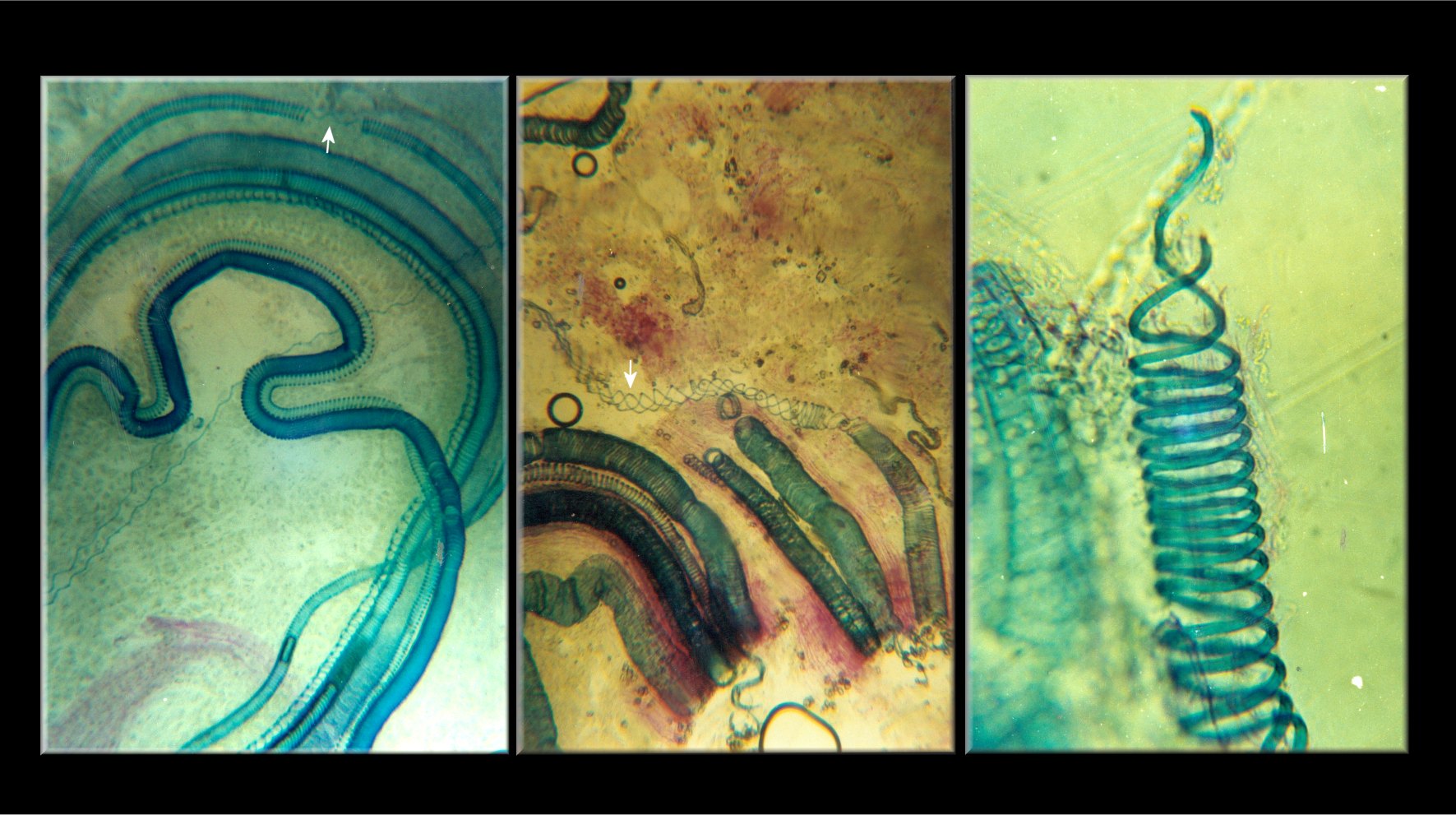
''Wenshania'' is a genus of extinct vascular plants found in the Posongchong Formation, Yunnan, China, which is of Early Devonian age (Pragian, around ). Plants consisted of leafless stems with simple dichotomous branching, and bore spore-forming organs or sporangia all around the sides of stems. ''Wenshania'' is part of the broadly defined group of zosterophylls. Description The sporophyte of ''Wenshania zhichangensis'', the type species of the genus, was described from compressed fossils preserved in siltstone. The basal part of the plant is not known, preventing a full reconstruction. The overall height is estimated to be greater than 10 cm, based on the length of the preserved parts. Stems (axes) were smooth and leafless, up to 3.1 mm in diameter, and branched dichotomously or pseudomonopodially (i.e. one branch formed more of a 'main' stem than the other). Specimens show up to three orders of branching. The internal anatomy of the stems is unknown. Spore-forming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zosterophyll
The zosterophylls are a group of extinct land plants that first appeared in the Silurian period. The taxon was first established by Banks in 1968 as the subdivision Zosterophyllophytina; they have since also been treated as the division Zosterophyllophyta or Zosterophyta and the class or plesion Zosterophyllopsida or Zosteropsida. They were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and had a world-wide distribution. They were probably stem-group lycophytes, forming a sister group to the ancestors of the living lycophytes. By the late Silurian (late Ludlovian, about ) a diverse assemblage of species existed, examples of which have been found fossilised in what is now Bathurst Island in Arctic Canada. Morphology The stems of zosterophylls were either smooth or covered with small spines known as enations, branched dichotomously, and grew at the ends by unrolling, a process known as circinate vernation. The stems had a central vascular column in which the protoxylem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zosterophylls
The zosterophylls are a group of extinct land plants that first appeared in the Silurian period. The taxon was first established by Banks in 1968 as the subdivision Zosterophyllophytina; they have since also been treated as the division Zosterophyllophyta or Zosterophyta and the class or plesion Zosterophyllopsida or Zosteropsida. They were among the first vascular plants in the fossil record, and had a world-wide distribution. They were probably stem-group lycophytes, forming a sister group to the ancestors of the living lycophytes. By the late Silurian (late Ludlovian, about ) a diverse assemblage of species existed, examples of which have been found fossilised in what is now Bathurst Island in Arctic Canada. Morphology The stems of zosterophylls were either smooth or covered with small spines known as enations, branched dichotomously, and grew at the ends by unrolling, a process known as circinate vernation. The stems had a central vascular column in which the protoxylem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue (the phloem) to conduct products of photosynthesis. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers), and angiosperms (flowering plants). Scientific names for the group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida ''sensu lato''. Some early land plants (the rhyniophytes) had less developed vascular tissue; the term eutracheophyte has been used for all other vascular plants, including all living ones. Historically, vascular plants were known as "higher plants", as it was believed that they were further evolved than other plants due to being more complex organisms. However, this is an antiquated remnant of the obsolete scala naturae, and the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in Southwest China, the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces of Guizhou, Sichuan, autonomous regions of Guangxi, and Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet as well as Southeast Asian countries: Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar. Yunnan is China's fourth least developed province based on disposable income per capita in 2014. Yunnan is situated in a mountainous area, with high elevations in the northwest and low elevations in the southeast. Most of the population lives in the eastern part of the province. In the west, the altitude can vary from the mountain peaks to river valleys by as much as . Yunnan is rich in natural resources and has the largest diversity of plant life in China. Of the approximately 30,000 species of Vascular plant, higher plants in China, Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Devonian
The Early Devonian is the first of three Epoch (geology), epochs comprising the Devonian period, corresponding to the Lower Devonian Series (stratigraphy), series. It lasted from and began with the Lochkovian Stage , which was followed by the Pragian from and then by the Emsian, which lasted until the Middle Devonian began, . During this time, the first Ammonoidea, ammonoids appeared, descending from Bactritida, bactritoid Nautiloidea, nautiloids. Ammonoids during this time period were simple and differed little from their nautiloid counterparts. These ammonoids belong to the order Agoniatitida, which in later epochs evolved to new ammonoid orders, for example Goniatite, Goniatitida and Clymeniida. This class of cephalopod molluscs would dominate the marine fauna until the beginning of the Mesozoic Era. References {{Geological history Early Devonian, Geological epochs Devonian geochronology, *01 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichotomous Branching
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary of leaf morphology. For other related terms, see Glossary of phytopathology, Glossary of lichen terms, and List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names. A B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporangium
A sporangium (; from Late Latin, ) is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. Virtually all plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle. Sporangia can produce spores by mitosis, but in nearly all land plants and many fungi, sporangia are the site of meiosis and produce genetically distinct haploid spores. Fungi In some phyla of fungi, the sporangium plays a role in asexual reproduction, and may play an indirect role in sexual reproduction. The sporangium forms on the sporangiophore and contains haploid nuclei and cytoplasm. Spores are formed in the sporangiophore by encasing each haploid nucleus and cytoplasm in a tough outer membrane. During asexual reproduction, these spores are dispersed via wind and germinate into haploid hyphae. Although sexual reproduction in fungi varies between phyla, for some fungi the sporangium plays an indirect role in sexual reprod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporophyte
A sporophyte () is the diploid multicellular stage in the life cycle of a plant or alga which produces asexual spores. This stage alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase. Life cycle The sporophyte develops from the zygote produced when a haploid egg cell is fertilized by a haploid sperm and each sporophyte cell therefore has a double set of chromosomes, one set from each parent. All land plants, and most multicellular algae, have life cycles in which a multicellular diploid sporophyte phase alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase. In the seed plants, the largest groups of which are the gymnosperms and flowering plants (angiosperms), the sporophyte phase is more prominent than the gametophyte, and is the familiar green plant with its roots, stem, leaves and cones or flowers. In flowering plants the gametophytes are very reduced in size, and are represented by the germinated pollen and the embryo sac. The sporophyte produces spores (hence t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the scientific name of every taxon is almost al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gametophyte
A gametophyte () is one of the two alternation of generations, alternating multicellular organism, multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has one set of chromosomes. The gametophyte is the Sexual reproduction of plants, sexual phase in the life cycle of plants and algae. It develops sex organs that produce gametes, haploid sex cells that participate in fertilization to form a diploid zygote which has a double set of chromosomes. Cell division of the zygote results in a new diploid multicellular organism, the second stage in the life cycle known as the sporophyte. The sporophyte can produce haploid spores by meiosis that on germination produce a new generation of gametophytes. Algae In some multicellular green algae (''Ulva lactuca'' is one example), red algae and brown algae, sporophytes and gametophytes may be externally indistinguishable (isomorphic). In ''Ulva (genus), Ulv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wenshan Zhuang And Miao Autonomous Prefecture
Wenshan Zhuang and Miao Autonomous Prefecture is an autonomous prefecture in southeastern Yunnan Province, People's Republic of China and the easternmost prefecture-level division of the province. It borders Baise, Guangxi to the east, Vietnam's Hà Giang Province to the south for , Honghe Hani and Yi Autonomous Prefecture to the west and Qujing to the north. Subdivisions Ethnic groups Wenshan is highly diverse. According to a local saying, "Han and Hui live by the market, Zhuang and Dai live by the water, Miao and Yi live on the mountains, and Yao live among the bamboos." () Some of Wenshan's ethnic groups include: *Han Chinese *Tai peoples ** Zhuang (3 branches according to Kaup (2000); 4 branches according to Johnson (2011)Johnson, Eric C. 2011.A Lexical and Phonological Comparison of the Central Taic Languages of Wenshan Prefecture, China: Getting More Out of Language Survey Wordlists Than Just Lexical Similarity Percentages. SIL Electronic Working Papers 2011-005: 170. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)