|
Wavelength Switched Optical Network
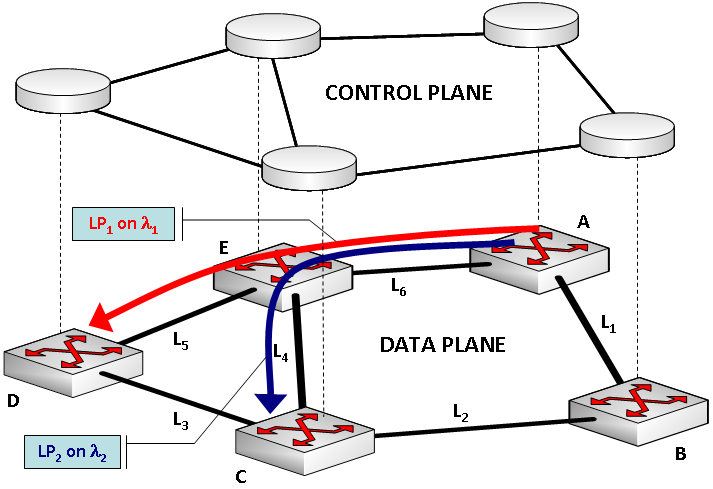
Wavelength switched optical network (WSON) is a type of telecommunications network. A WSON consist of two planes: the data and the control planes. The data plane comprises wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) fiber links connecting optical cross-connect (OXCs) through a comb of several tens of wavelength channels, with typical data rates of 10 or 40 Gbit/s. Optical end-to-end connections (i.e., lightpaths) are established in the optical domain and switched by OXCs at the wavelength granularity. The dynamic provisioning and maintenance of lightpaths is managed by the control plane. The control plane is implemented on a separate network and typically employs one network controller for each node in the data plane, as shown in the figure. The Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching (GMPLS) protocol suite, the de facto standard control plane for WSONs proposed by the IETF The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet and is respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications Network
A telecommunications network is a group of nodes interconnected by telecommunications links that are used to exchange messages between the nodes. The links may use a variety of technologies based on the methodologies of circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching, to pass messages and signals. Multiple nodes may cooperate to pass the message from an originating node to the destination node, via multiple network hops. For this routing function, each node in the network is assigned a network address for identification and locating it on the network. The collection of addresses in the network is called the address space of the network. Examples of telecommunications networks include computer networks, the Internet, the public switched telephone network (PSTN), the global Telex network, the aeronautical ACARS network, and the wireless radio networks of cell phone telecommunication providers. Network structure In general, every telecommunications network conceptually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength-division Multiplexing
In fiber-optic communications, wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) is a technology which multiplexes a number of optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths (i.e., colors) of laser light. This technique enables bidirectional communications over a single strand of fiber, also called wavelength-division duplexing, as well as multiplication of capacity. The term WDM is commonly applied to an optical carrier, which is typically described by its wavelength, whereas frequency-division multiplexing typically applies to a radio carrier which is more often described by frequency. This is purely conventional because wavelength and frequency communicate the same information. Specifically, frequency (in Hertz, which is cycles per second) multiplied by wavelength (the physical length of one cycle) equals the velocity of the carrier wave. In a vacuum, this is the speed of light, usually denoted by the lowercase letter, c. In glass fiber, it is subst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Cross-connect
{{unreferenced, date=February 2008 An optical cross-connect (OXC) is a device used by telecommunications carriers to switch high-speed optical signals in a fiber optic network, such as an optical mesh network. There are several ways to realize an OXC: * Opaque OXCs (electronic switching) - One can implement an OXC in the electronic domain: all the input optical signals are converted into electronic signals after they are demultiplexed by demultiplexers. The electronic signals are then switched by an electronic switch module. Finally, the switched electronic signals are converted back into optical signals by using them to modulate lasers and then the resulting optical signals are multiplexed by optical multiplexers onto outlet optical fibers. This is known as an "OEO" (Optical-Electrical-Optical) design. Cross-connects based on an OEO switching process generally have a key limitation: the electronic circuits limit the maximum bandwidth of the signal. Such an architecture preven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightpath (optical Network)
In optical networking, a lightpath is a path between two nodes in an optical network between which light passes through unmodified. Description When a lightpath can be established between source and destination node endpoints the connection is totally optical and avoids throttling by intermediate electronic conversions and processing. Where a lightpath passes through an Optical add-drop multiplexer (OADM) is known as a ''cut-through lightpath''. Where a lightpath is added or dropped at an OADM, it is known as an ''added/dropped lightpath''. Semi-lightpath Where endpoints are connected by a series of lightpaths with the intermediate nodes only changing the light wavelength at the junctions this may be referred to as a semi-lightpath. See also * Wavelength switched optical network * Multicast lightpaths * Network Description Language Network Description Language (NDL) is a tool to reduce the complexity as networks evolve into the future. NDL enables both humans and mach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching
Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching (GMPLS) is a protocol suite extending MPLS to manage further classes of interfaces and switching technologies other than packet interfaces and switching, such as time-division multiplexing, layer-2 switching, wavelength switching and fiber-switching. Differences between MPLS and GMPLS Generalized MPLS differs from traditional MPLS in that it extends support to multiple types of switching such as TDM, wavelength and fiber (port) switching. For instance, GMPLS is the ''de facto'' control plane of wavelength switched optical network (WSON). The support for the additional types of switching has driven GMPLS to extend certain base functions of traditional MPLS and, in some cases, to add functionality. These changes and additions impact basic label-switched path (LSP) properties: how labels are requested and communicated, the unidirectional nature of LSPs, how errors are propagated, and information provided for synchronizing the ingress and egr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Engineering Task Force
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster or requirements and all its participants are volunteers. Their work is usually funded by employers or other sponsors. The IETF was initially supported by the federal government of the United States but since 1993 has operated under the auspices of the Internet Society, an international non-profit organization. Organization The IETF is organized into a large number of working groups and birds of a feather informal discussion groups, each dealing with a specific topic. The IETF operates in a bottom-up task creation mode, largely driven by these working groups. Each working group has an appointed chairperson (or sometimes several co-chairs); a charter that describes its focus; and what it is expected to produce, and when. It is open to all who want to particip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |