|
Warwick Fox
Warwick Fox (born 1 March 1954) is an Australian-UK philosopher. He is Emeritus Professor of Philosophy, University of Central Lancashire, and his books include ''Toward a Transpersonal Ecology: Developing New Foundations for Environmentalism;'' ''Ethics and the Built Environment'' (ed.); ''A Theory of General Ethics: Human Relationships, Nature, and the Built Environment''; and ''On Beautiful Days Such as This: A Philosopher's Search for Love, Work, Place, Meaning, and Suchlike''. His main areas of philosophical interest are environmental philosophy, General Ethics (a term coined and defined by Fox), and the nature of the interior lives of humans and other animals. Philosophical work Deep Ecology Fox's earlier work (1984 to mid-1990s) focused on analysing and developing the deep ecology approach to environmental philosophy. His central publication in this area was ''Toward a Transpersonal Ecology: Developing New Foundations for Environmentalism'' in which he argued that deep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Ecology
Deep ecology is an environmental philosophy that promotes the inherent worth of all living beings regardless of their instrumental utility to human needs, and the restructuring of modern human societies in accordance with such ideas. Deep ecology argues that the natural world is a complex of relationships in which the existence of organisms is dependent on the existence of others within ecosystems. It argues that non-vital human interference with or destruction of the natural world poses a threat therefore not only to humans but to all organisms constituting the natural order. Deep ecology's core principle is the belief that the living environment as a whole should be respected and regarded as having certain basic moral and legal rights to live and flourish, independent of its instrumental benefits for human use. Deep ecology is often framed in terms of the idea of a much broader sociality; it recognizes diverse communities of life on Earth that are composed not only through bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
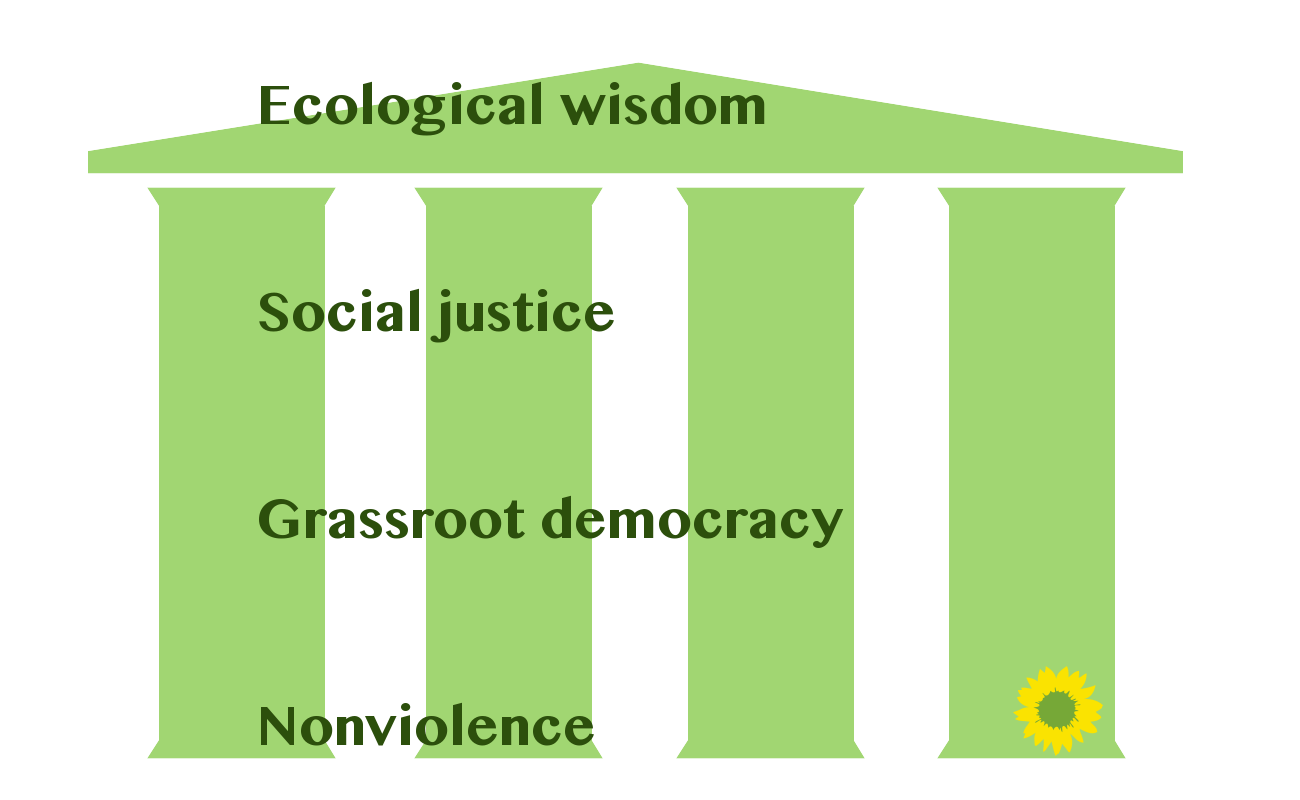
Green Movement
Green politics, or ecopolitics, is a political ideology that aims to foster an ecologically sustainable society often, but not always, rooted in environmentalism, nonviolence, social justice and grassroots democracy. Wall 2010. p. 12-13. It began taking shape in the western world in the 1970s; since then Green parties have developed and established themselves in many countries around the globe and have achieved some electoral success. The political term green was used initially in relation to ''die Grünen'' (German for "the Greens"), a green party formed in the late 1970s. The term political ecology is sometimes used in academic circles, but it has come to represent an interdisciplinary field of study as the academic discipline offers wide-ranging studies integrating ecological social sciences with political economy in topics such as degradation and marginalization, environmental conflict, conservation and control and environmental identities and social movements. Supporters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academics Of The University Of Central Lancashire
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulation, dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Philosophers
Australian(s) may refer to: Australia * Australia, a country * Australians, citizens of the Commonwealth of Australia ** European Australians ** Anglo-Celtic Australians, Australians descended principally from British colonists ** Aboriginal Australians, indigenous peoples of Australia as identified and defined within Australian law * Australia (continent) ** Indigenous Australians * Australian English, the dialect of the English language spoken in Australia * Australian Aboriginal languages * ''The Australian'', a newspaper * Australiana, things of Australian origins Other uses * Australian (horse), a racehorse * Australian, British Columbia, an unincorporated community in Canada See also * The Australian (other) * Australia (other) * * * Austrian (other) Austrian may refer to: * Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent ** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law * Austrian German dialect * Someth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Fetish
''Growth Fetish'' is a book about economics and politics by the Australian progressive political theorist Clive Hamilton. Published in 2003 it became a best-seller in Australia. The book argues that the policies of unfettered capitalism pursued by the west for the last 50 years has largely failed, since the underlying purpose of the creation of wealth is happiness, and Hamilton claims that people in general are no happier now than 50 years ago, despite the huge increase in personal wealth. Hamilton goes on to claim that the pursuit of growth has become a fetish, pursued at a tremendous cost in terms of the environment, erosion of democracy, and the values of society as a whole. Background Clive Hamilton is the former executive director of The Australia Institute, an independent think-tank which has been cited as playing a significant role in debate over social and environmental policies. Hamilton resigned from the Australia Institute in 2007. ''Growth Fetish'' itself reflects man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Ecology
Deep ecology is an environmental philosophy that promotes the inherent worth of all living beings regardless of their instrumental utility to human needs, and the restructuring of modern human societies in accordance with such ideas. Deep ecology argues that the natural world is a complex of relationships in which the existence of organisms is dependent on the existence of others within ecosystems. It argues that non-vital human interference with or destruction of the natural world poses a threat therefore not only to humans but to all organisms constituting the natural order. Deep ecology's core principle is the belief that the living environment as a whole should be respected and regarded as having certain basic moral and legal rights to live and flourish, independent of its instrumental benefits for human use. Deep ecology is often framed in terms of the idea of a much broader sociality; it recognizes diverse communities of life on Earth that are composed not only through bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Built Environment
The term built environment refers to human-made conditions and is often used in architecture, landscape architecture, urban planning, public health, sociology, and anthropology, among others. These curated spaces provide the setting for human activity and were created to fulfill human desires and needs. The term can refer to a plethora of components including the traditionally associated buildings, cities, public infrastructure, transportation, open space, as well as more conceptual components like farmlands, damned rivers, wildlife management, and even domesticated animals. The built environment is made up of physical features. However, when studied, the built environment often highlights the connection between physical space and social consequences. It impacts the environment and how society physically maneuvers and functions, as well as less tangible aspects of society such as socioeconomic inequity and health. Various aspects of the built environment contribute to scholarshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Ethics
In environmental philosophy, environmental ethics is an established field of practical philosophy "which reconstructs the essential types of argumentation that can be made for protecting natural entities and the sustainable use of natural resources." The main competing paradigms are anthropocentrism, physiocentrism (called ecocentrism as well), and theocentrism. Environmental ethics exerts influence on a large range of disciplines including environmental law, environmental sociology, ecotheology, ecological economics, ecology and environmental geography. There are many ethical decisions that human beings make with respect to the environment. For example: *Should humans continue to clear cut forests for the sake of human consumption? *Why should humans continue to propagate its species, and life itself? *Should humans continue to make gasoline-powered vehicles? *What environmental obligations do humans need to keep for future generations? *Is it right for humans to know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaia Hypothesis
The Gaia hypothesis (), also known as the Gaia theory, Gaia paradigm, or the Gaia principle, proposes that living organisms interact with their inorganic surroundings on Earth to form a synergistic and self-regulating, complex system that helps to maintain and perpetuate the conditions for life on the planet. The hypothesis was formulated by the chemist James Lovelock and co-developed by the microbiologist Lynn Margulis in the 1970s. Lovelock named the idea after Gaia, the primordial goddess who personified the Earth in Greek mythology. The suggestion that the theory should be called "the Gaia hypothesis" came from Lovelock's neighbour, William Golding. In 2006, the Geological Society of London awarded Lovelock the Wollaston Medal in part for his work on the Gaia hypothesis. Topics related to the hypothesis include how the biosphere and the evolution of organisms affect the stability of global temperature, salinity of seawater, atmospheric oxygen levels, the maintenance of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transpersonal Disciplines
Transpersonal disciplines are academic fields of interest that study the transpersonal. Definition and context According to Walsh & Vaughan,Walsh, R. & Vaughan, F. "On transpersonal definitions". ''Journal of Transpersonal Psychology'', 25 (2) 125-182, 1993 who conducted an extensive review on transpersonal definitions, transpersonal disciplines are ''those disciplines that focus on the study of transpersonal experiences and related phenomena. These phenomena include the causes, effects and correlates of transpersonal experiences and development, as well as the disciplines and practices inspired by them''. Transpersonal disciplines Among the disciplines that are considered to be transpersonal we find: * Transpersonal psychology; an area of psychology that studies transpersonal experiences and similar phenomena. Walsh, Roger. "The Transpersonal Movement: A History and State of the Art". ''Journal of Transpersonal Psychology'', 1993, Vol. 25, No.2 The field is supported by a memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Ethic
A land ethic is a philosophy or theoretical framework about how, ethically, humans should regard the land. The term was coined by Aldo Leopold (1887–1948) in his ''A Sand County Almanac'' (1949), a classic text of the environmental movement. There he argues that there is a critical need for a "new ethic", an "ethic dealing with human's relation to land and to the animals and plants which grow upon it".Leopold, A. 1949. ''A Sand County Almanac''. pp. 203. Oxford University Press, New York. Leopold offers an ecologically-based land ethic that rejects strictly human-centered views of the environment and focuses on the preservation of healthy, self-renewing ecosystems. ''A Sand County Almanac'' was the first systematic presentation of a holistic or ecocentric approach to the environment. Although Leopold is credited with coining the term "land ethic", there are many philosophical theories that speak to how humans should treat the land. Some of the most prominent land ethics include t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldo Leopold
Aldo Leopold (January 11, 1887 – April 21, 1948) was an American writer, philosopher, naturalist, scientist, ecologist, forester, conservationist, and environmentalist. He was a professor at the University of Wisconsin and is best known for his book ''A Sand County Almanac'' (1949), which has been translated into fourteen languages and has sold more than two million copies. Leopold was influential in the development of modern environmental ethics and in the movement for wilderness conservation. His ethics of nature and wildlife preservation had a profound impact on the environmental movement, with his ecocentric or holistic ethics regarding land. He emphasized biodiversity and ecology and was a founder of the science of wildlife management. Early life Rand Aldo Leopold was born in Burlington, Iowa on January 11, 1887. His father, Carl Leopold, was a businessman who made walnut desks and was first cousin to his wife, Clara Starker. Charles Starker, father of Carl and uncle to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)