|
War Of Qi's Succession
The war of Qi's succession was a civil war in the State of Qi from 643 to 642 BCE, as the sons of Duke Huan of Qi fought against each other for the throne. Their struggle led to chaos in Qi and the intervention of several outside powers, until Duke Huan's intended heir, Prince Zhao (later known as Duke Xiao), emerged victorious. Nevertheless, four of Prince Zhao's rival brothers remained at large and continued to conspire for the throne, leading to a succession crisis that plagued Qi for decades. As a result, the succession war and its consequences greatly weakened Qi, which lost its status as China's predominant state. Background The state of Qi was a regionally powerful polity during the Western Zhou period (1046–771 BC), and as the Zhou dynasty's authority collapsed at the Spring and Autumn period's beginning, Qi grew into the dominating power of eastern China. As result, Qi was in an ideal position to expand its influence when Zheng's short-lived dominance over China d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring And Autumn Period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives from the ''Spring and Autumn Annals'', a chronicle of the state of Lu between 722 and 479 BCE, which tradition associates with Confucius (551–479 BCE). During this period, the Zhou royal authority over the various feudal states eroded as more and more dukes and marquesses obtained ''de facto'' regional autonomy, defying the king's court in Luoyi and waging wars amongst themselves. The gradual Partition of Jin, one of the most powerful states, marked the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the beginning of the Warring States period. Background In 771 BCE, a Quanrong invasion in coalition with the states of Zeng and Shen — the latter polity being the fief of the grandfather of the disinherited crown prince Yijiu — destroyed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of Succession
A war of succession is a war prompted by a succession crisis in which two or more individuals claim the Order of succession, right of successor to a demise of the Crown, deceased or deposition (politics), deposed monarch. The rivals are typically supported by Political faction, factions within the Court (royal), royal court. Foreign powers sometimes Interventionism (politics)#Foreign interventionism, intervene, alliance, allying themselves with a faction. This may widen the war into one between those powers. Wars of succession were some of the most prevalent types of Casus belli#Categorisation, wars by cause throughout human history, but the replacement of absolute monarchy, absolute monarchies by an international order based on democracy with constitutional monarchy, constitutional monarchies or republics ended almost all such wars by 1900. Terminology Descriptions In historiography and literature, a ''war of succession'' may also be referred to as a ''succession disput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Linzi
Linzi () was the capital of the ancient Chinese state of Qi during the Zhou dynasty. The ruins of the city lie in modern-day Linzi District, Shandong, China. The city was one of the largest and richest in China during the Spring and Autumn Period. Upon occupying Linzi in 221 BC, King Ying Zheng of Qin completed his conquest of the Chinese rival states and declared himself the first emperor of China shortly afterwards. The ruins of the ancient city were excavated in 1926 by Japanese archaeologists and in 1964 by Chinese archaeologists. Layout Linzi covered an area of around with the city built between two parallel rivers that ran north–south, the Zi River to its east and the old course of the Xi River to its west. The city was surrounded by a perimeter wall of rammed earth. The city consisted of an outer city and an inner city. The outer city wall reached a maximum of in base width, averaging between in width. The inner city wall reached a maximum of in base width. The ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Grand Historian
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese historian Sima Qian, whose father Sima Tan had begun it several decades earlier. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Records'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and the First Emperor of Qin, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Records'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historical works, the ''Records'' do not treat history as "a cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warring States Period
The Warring States period () was an era in History of China#Ancient China, ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded with the Qin's wars of unification, Qin wars of conquest that saw the annexation of all other contender states, which ultimately led to the Qin (state), Qin state's victory in 221 BC as the first unified History of China#Imperial China, Chinese empire, known as the Qin dynasty. Although different scholars point toward different dates ranging from 481 BC to 403 BC as the true beginning of the Warring States, Sima Qian's choice of 475 BC is the most often cited. The Warring States era also overlaps with the second half of the Eastern Zhou Period, Eastern Zhou dynasty, though the Chinese sovereign, known as the king of Zhou, ruled merely as a figurehead and served as a backdrop against the machinations of the warring states. The "Warring St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanzi (text)
The ''Guanzi'' () is an ancient Chinese political and philosophical text. At over 135,000 characters long, the ''Guanzi'' is one of the longest early Chinese philosophical texts. This anonymously written foundational text covers broad subject matter, notably including price regulation of commodities via the concept of "light and heavy" (轻重). It is one of the most representative text of developing concepts of political economy Warring States era. Authorship The ''Guanzi'' is named for and traditionally attributed to the 7th century BCE philosopher and statesman Guan Zhong, who served as Prime Minister to Duke Huan of Qi. It was, however, written by several anonymous authors and precise date of creation remains subject to historical debate. The Han Dynasty scholar Liu Xiang edited the received ''Guanzi'' text circa 26 BCE. It contains a wide variety of material from many different authors over several successive centuries, largely associated with the 4th century BCE Jixia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Loulin
The Battle of Loulin was fought in Winter 645 BC between the states of Chu and Xu, the latter being supported by a coalition of northern states led by Qi. Xu, originally the most powerful state of the Huai River valley, had been weakened by internal unrest and several wars since the beginning of the Spring and Autumn period. As its influence over eastern Hubei, southern Henan and central Anhui waned, Chu began to expand into these regions. Threatened by these developments, Xu joined an alliance of several northern states against Chu. In spring 645 BC, when Chu invaded Xu's southern heartland, the northern states sent a relief expedition in order to aid Xu and stop Chu's eastern conquests. The coalition forces eventually met Chu's army at Loulin and were defeated, marking the beginning of Xu's final decline and accelerating the end of Qi's hegemony over China. Prelude The state of Xu, centered in northern Anhui, had controlled most of the middle and lower Huai River during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chu (state)
Chu, or Ch'u in Wade–Giles romanization, (, Hanyu Pinyin: Chǔ, Old Chinese: ''*s-r̥aʔ'') was a Zhou dynasty vassal state. Their first ruler was King Wu of Chu in the early 8th century BCE. Chu was located in the south of the Zhou heartland and lasted during the Spring and Autumn period. At the end of the Warring States period it was destroyed by the Qin in 223 BCE during the Qin's wars of unification. Also known as Jing () and Jingchu (), Chu included most of the present-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan, along with parts of Chongqing, Guizhou, Henan, Anhui, Jiangxi, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai. For more than 400 years, the Chu capital Danyang was located at the junction of the Dan and Xi Rivers near present-day Xichuan County, Henan, but later moved to Ying. The house of Chu originally bore the clan name Nai ( OC: /*rneːlʔ/) which was later written as Mi ( OC: /*meʔ/). They also bore the lineage name Yan ( OC: /*qlamʔ/, /*qʰɯːm/) which would later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
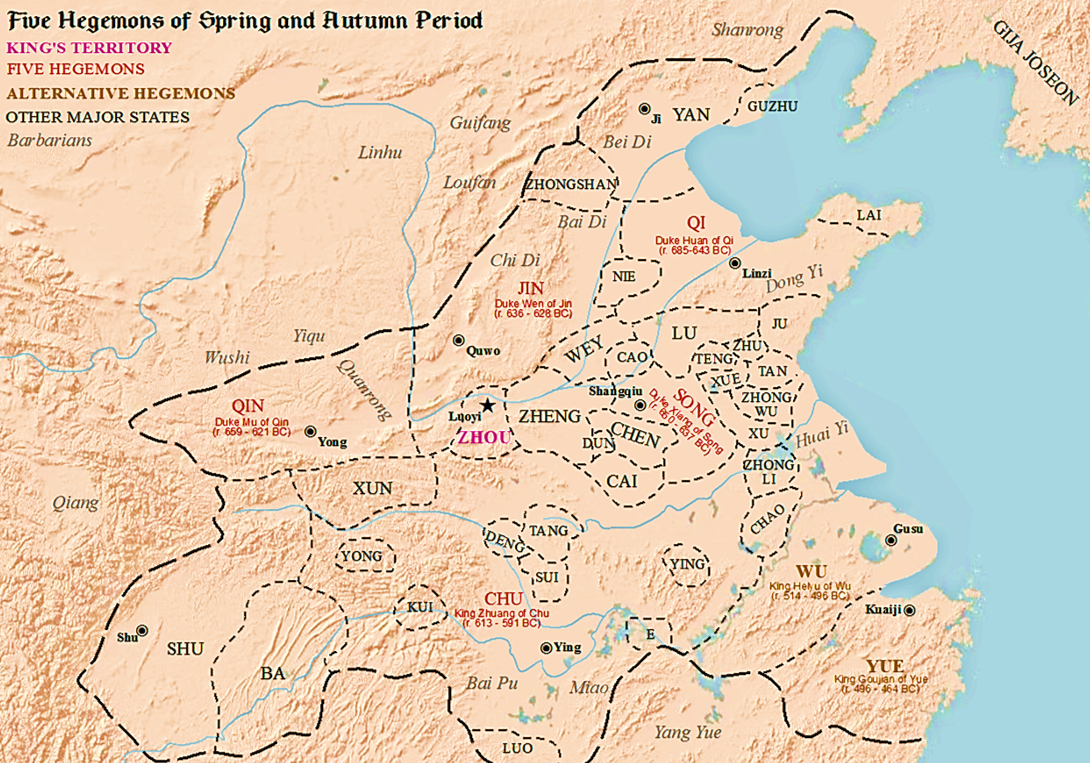
Five Hegemons
The Five Hegemons () refers to several especially powerful rulers of Chinese states of the Spring and Autumn period of Chinese history (770 to 476 BCE), sometimes alternatively referred to as the "Age of Hegemons". There are various lists of five rulers of those certain states which rose to power over the other states of this time period, states which were also formed during the period of dissolution of a once real and strong central state, namely the empire of the Zhou dynasty. The Hegemons mobilized the remnants of the Zhou empire, according to shared mutual political and martial interests. An especially prominent Hegemon was Duke Huan of Qi. Pronunciation and meaning In ancient Chinese, (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ) '' has a similar meaning and pronunciation to (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ), which means 'the eldest son in a family', or 'senator'. Both and can be translated as the 'Five Hegemons'. () literally means 'five', but in the context of ancient Chinese also has a more ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primus Inter Pares
''Primus inter pares'' is a Latin phrase meaning first among equals. It is typically used as an honorary title for someone who is formally equal to other members of their group but is accorded unofficial respect, traditionally owing to their seniority in office. Historically, the ''princeps senatus'' of the Roman Senate was such a figure and initially bore only the distinction that he was allowed to speak first during debate. Also, Constantine the Great was given the role of ''primus inter pares''. However, the term is also often used ironically or self-deprecatingly by leaders with much higher status as a form of respect, camaraderie or propaganda. After the fall of the Republic, Roman emperors initially referred to themselves only as ''princeps'' despite having enormous power. Various modern figures such as the chair of the United States Federal Reserve System, the prime minister of parliamentary countries, the President of Switzerland, the Chief Justice of the US Supr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guan Zhong
Guan Zhong (; c. 720–645 BC) was a Chinese philosopher and politician. He served as chancellor and was a reformer of the State of Qi during the Spring and Autumn period of Chinese history. His given name was Yiwu (). ''Zhong'' was his courtesy name. He is mainly remembered for his reforms as chancellor under Duke Huan of Qi, as well as his friendship with his colleague Bao Shuya, though his reputation remained controversial among the Confucians, as detailed in the Philosophy and appraisal section. Through Guan Zhong's reforms and skilful diplomacy Qi became the most powerful of the feudal states and Duke Huan became the first of the Five Hegemons. Though knowledge of his reforms is limited, in particular he instituted a famous fiscal policy known as "balancing the light and the heavy", associated with salt and iron monopolies. Though otherwise a diverse work, the Guanzi compilation making use of his name makes similar such recommendations. Life Youth and friendship with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |