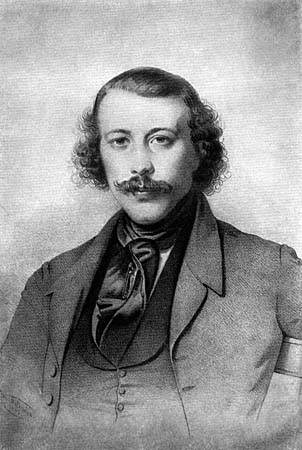|
Walerian Łukasiński
Walerian Łukasiński (15 April 1786 in Warsaw – 27 January 1868 in Shlisselburg) was a Polish officer and political activist. Sentenced by Russian Imperial authorities to 14 years' imprisonment, he was never released and died after 46 years of solitary incarceration, becoming a symbol of the Polish struggle for independence. Biography Born in Warsaw on 15 April 1786, as a child he lived through the last of the partitions of Poland that destroyed the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. He joined the Polish military early, serving in the army of Duchy of Warsaw from 1807 to 1815 and later in that of Congress Poland. In Congress Poland, a puppet state of the Russian Empire, ruled by the Grand Duke Constantine Pavlovich of Russia, the Polish army's morale was very low. Łukasiński, who reached the rank of a major in the 4th Regiment of Line Infantry, took it upon himself to restore it, creating a secret organization known as National Freemasonry (''Wolnomularstwo Narodowe''), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walerian Łukasiński
Walerian Łukasiński (15 April 1786 in Warsaw – 27 January 1868 in Shlisselburg) was a Polish officer and political activist. Sentenced by Russian Imperial authorities to 14 years' imprisonment, he was never released and died after 46 years of solitary incarceration, becoming a symbol of the Polish struggle for independence. Biography Born in Warsaw on 15 April 1786, as a child he lived through the last of the partitions of Poland that destroyed the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. He joined the Polish military early, serving in the army of Duchy of Warsaw from 1807 to 1815 and later in that of Congress Poland. In Congress Poland, a puppet state of the Russian Empire, ruled by the Grand Duke Constantine Pavlovich of Russia, the Polish army's morale was very low. Łukasiński, who reached the rank of a major in the 4th Regiment of Line Infantry, took it upon himself to restore it, creating a secret organization known as National Freemasonry (''Wolnomularstwo Narodowe''), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waler Lukas
The Waler is an Australian breed of horse developed from horses that were brought to the Australian colonies in the 19th century. The name comes from their breeding origins in New South Wales; they were originally known as "New South Walers". Origins and characteristics The Waler combined a variety of breeds; particularly the Thoroughbred, Arab, the Cape horse (from the Cape of Good Hope), Timor Pony and perhaps a little Clydesdale or Percheron. It was originally considered only a "type" of horse and not a distinct breed. However, as a landrace bred under the extreme climate and challenging working conditions of Australia, the Waler developed into a hardy horse with great endurance even when under extreme stress from lack of food and water. It was used as a stockman's horse and prized as a military remount. Walers were also used by bushrangers, troopers and exploration expeditions that traversed inland Australia.Mather, Jill, ''Forgotten Heroes – The Australian Waler Horse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1786 Births
Events January–March * January 3 – The third Treaty of Hopewell is signed, between the United States and the Choctaw. * January 6 – The outward bound East Indiaman '' Halsewell'' is wrecked on the south coast of England in a storm, with only 74 of more than 240 on board surviving. * February 2 – In a speech before The Asiatic Society in Calcutta, Sir William Jones notes the formal resemblances between Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, laying the foundation for comparative linguistics and Indo-European studies. * March 1 – The Ohio Company of Associates is organized by five businessmen at a meeting at the Bunch-of-Grapes Tavern in Boston, to purchase land from the United States government to form settlements in what is now the U.S. state of Ohio. * March 13 – Construction begins in Dublin on the Four Courts Building, with the first stone laid down by the United Kingdom's Viceroy for Ireland, the Duke of Rutland. April–June * Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tombeau
A tombeau (plural tombeaux) is a musical composition (earlier, in the early 16th century, a poem) commemorating the death of a notable individual. The term derives from the French word for "tomb" or "tombstone". The vast majority of tombeaux date from the 17th century and were composed for lute or other plucked string instruments. The genre gradually fell out of use during the 18th century, but reappeared in the early 20th. History "In instrumental music, ''tombeau'' signifies a musical 'tombstone' (French ''le tombeau'' = tomb). The musical genre of the tombeau is generally connected with music for the lute of the 17th and 18th centuries. Of some 60+ surviving pieces, most are intended for the lute or theorbo, 5 for the baroque guitar, 7 for the viola da gamba and 3 for harpsichord. The earliest example of this genre seems to be the ''Tombeau de Mezangeau'' (1638) by French lutenist Ennemond Gaultier." "Musical predecessors are memorial pavans like those by Anthony Holborne (''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Turovsky-Savchuk
Roman Turovsky-Savchuk (Ukrainian: Роман Туровський-Савчук) is an American artist-painter, photographer and videoinstallation artist, as well as a lutenist-composer,Suhayl Saadi Uncensored « Kitaab Kitaabonline.wordpress.com. Retrieved on 18 October 2011. born in Ukraine. His musical works were published under various s, including Johann Joachim Sautscheck. Biography Turovsky was born in , |
Noc Listopadowa
A network on a chip or network-on-chip (NoC or )This article uses the convention that "NoC" is pronounced . Therefore, it uses the convention "a" for the indefinite article corresponding to NoC ("a NoC"). Other sources may pronounce it as and therefore use "an NoC". is a network-based communications subsystem on an integrated circuit ("microchip"), most typically between modules in a system on a chip ( SoC). The modules on the IC are typically semiconductor IP cores schematizing various functions of the computer system, and are designed to be modular in the sense of network science. The network on chip is a router-based packet switching network between SoC modules. NoC technology applies the theory and methods of computer networking to on-chip communication and brings notable improvements over conventional bus and crossbar communication architectures. Networks-on-chip come in many network topologies, many of which are still experimental as of 2018. In 2000s resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanisław Wyspiański
Stanisław Mateusz Ignacy Wyspiański (; 15 January 1869 – 28 November 1907) was a Polish playwright, painter and poet, as well as interior and furniture designer. A patriotic writer, he created a series of symbolic, national dramas within the artistic philosophy of the Young Poland Movement. Wyspiański was one of the most outstanding and multifaceted artists of his time in Poland under the foreign partitions. He successfully joined the trends of modernism with themes of the Polish folk tradition and Romantic history. Unofficially, he came to be known as the Fourth Polish Bard (in addition to the earlier Three Bards: Adam Mickiewicz, Juliusz Słowacki, and Zygmunt Krasiński). Biography Stanisław Wyspiański was born to Franciszek Wyspiański and Maria Rogowska. His father, a sculptor, owned an atelier at the foot of Wawel Hill. His mother died of tuberculosis in 1876 when Stanisław was seven years old. Due to problems with alcohol, Stanisław's father could not fulfil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Culture
The culture of Poland ( pl, Kultura Polski ) is the product of its geography and distinct historical evolution, which is closely connected to an intricate thousand-year history. Polish culture forms an important part of western civilization and the western world, with significant contributions to art, music, philosophy, mathematics, science, politics and literature. Its unique character developed as a result of its geography at the confluence of various European regions. It is theorised and speculated that ethnic Poles and the other Lechites (Kashubians and Silesians) are the combination of descendants of West Slavs The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic lan ... and people indigenous to the region including Celts, Balts and Germanic tribes which were gradually Polonization, Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martyr
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an external party. In the martyrdom narrative of the remembering community, this refusal to comply with the presented demands results in the punishment or execution of an actor by an alleged oppressor. Accordingly, the status of the 'martyr' can be considered a posthumous title as a reward for those who are considered worthy of the concept of martyrdom by the living, regardless of any attempts by the deceased to control how they will be remembered in advance. Insofar, the martyr is a relational figure of a society's boundary work that is produced by collective memory. Originally applied only to those who suffered for their religious beliefs, the term has come to be used in connection with people killed for a political cause. Most martyrs are consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander II Of Russia
Alexander II ( rus, Алекса́ндр II Никола́евич, Aleksándr II Nikoláyevich, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ftɐˈroj nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪtɕ; 29 April 181813 March 1881) was Emperor of Russia, Congress Poland, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Finland from 2 March 1855 until Assassination of Alexander II of Russia, his assassination in 1881. Alexander's most significant reform as emperor was the emancipation reform of 1861, emancipation of Serfdom in Russia, Russia's serfs in 1861, for which he is known as Alexander the Liberator ( rus, Алекса́ндр Освободи́тель, r=Aleksándr Osvobodytel, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ɐsvəbɐˈdʲitʲɪlʲ). The tsar was responsible for other reforms, including reorganizing the judicial system, setting up elected local judges, abolishing corporal punishment, promoting local self-government through the ''zemstvo'' system, imposing universal military service, ending some privileges of the nobility, and promoting university e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Bakunin
Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin (; 1814–1876) was a Russian revolutionary anarchist, socialist and founder of collectivist anarchism. He is considered among the most influential figures of anarchism and a major founder of the revolutionary socialist and social anarchist tradition. Bakunin's prestige as a revolutionary also made him one of the most famous ideologues in Europe, gaining substantial influence among radicals throughout Russia and Europe. Bakunin grew up in Pryamukhino, a family estate in Tver Governorate. From 1840, he studied in Moscow, then in Berlin hoping to enter academia. Later in Paris, he met Karl Marx and Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, who deeply influenced him. Bakunin's increasing radicalism ended hopes of a professorial career. He was expelled from France for opposing The Russian Empire's occupation of Poland. In 1849, he was arrested in Dresden for his participation in the Czech rebellion of 1848 and deported to Russian Empire, where he was imprisoned fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shlisselburg Fortress
The fortress at Shlisselburg is one of a series of fortifications built in Shlisselburg on Orekhovy Island in Lake Ladoga, near the present-day city of Saint Petersburg, Russia. The first fortress was built in 1323. It was the scene of many conflicts between Russia and Sweden and changed hands between the two empires. During World War II, it was heavily damaged. Today it is part of the UNESCO World Heritage site Historic Centre of Saint Petersburg and Related Groups of Monuments. Origins A wooden fortress named Oreshek () or Orekhov () was built by Grand Prince Yury of Moscow (in his capacity as Prince of Novgorod) on behalf of the Novgorod Republic in 1323. It guarded the northern approaches to Novgorod and access to the Baltic Sea. The fortress is situated on Orekhovets Island whose name refers to nuts in Swedish as well as in Finnish (''Pähkinäsaari'', "Nut Island") and Russian languages. After a series of conflicts, a peace treaty was signed at Oreshek on August ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)