|
Wakoku
Wakoku is the name used by early imperial China and its neighbouring states to refer to the nation usually identified as Japan. There are various theories regarding the extent of power of the early kings of Japan. According to the Book of Sui and the History of the Northern Dynasties, its borders were five months from east to west and three months from north to south. The Wajin appear in historical documents such as the Book of Han and the Geographical Survey of Japan from around the 2nd century BC. In the late 7th century, the Yamato kingdom, which had been called Yamato, changed its external name to Japan, but its relation to Japan since Book of the Later Han is not clear. There are discrepancies in the descriptions of the Old Book of Tang and the New Book of Tang. History Formation of small states and the Civil War of Wa The word "wa (倭)" or "wajin (倭人)" first appeared in Chinese annals around 150 BC in the middle of the Yayoi period and corresponds to the Western H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wajinden
The ''Wajinden'' refers to the passages in the 30th volume of the Chinese history chronicle ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' that talk about the Wa people who would later be known as the Japanese people. It describes the mores, geography, and other aspects of the Wa, the people and inhabitants of the Japanese archipelago at the time. The ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' was written by Chen Shou of the Western Jin Dynasty at the end of the 3rd century (between 280 ( Demise of Wu) and 297, the year of Chen Shou's death). Overview There was no independent biography called "Wajinden" in "records of the three kingdoms".、and the description of Yamato is part of the "Biography of Wei", vol. 30, "Biography of Wushan Sunbei Dongbi". Therefore, some believe that it is meaningless unless one reads not only the article on the Yamato but also the whole of the Biography of the Eastern Yi.. Yoshihiro Watanabe, a researcher of "Records of the Three Kingdoms," states that, like the "Book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wajin (ancient People)
is *in the narrow sense, the old name of the ethnic group of the Yayoi people who lived in the Japanese archipelago. *In the wider sense, an ethnic group that was mainly active at sea between Mainland China, the Korean Peninsula and the Japanese archipelago. In general the Wajin that established themself on the Japanese archipelago became the Yayoi people, the ancestors of the Yamato people. The word "Wajin" also refers to related groups outside of Japan. The first secure appearance of Wajin is in " Treatise on Geography" (地理志) of the ''Book of Han'' (漢書). After that, in "Gishi Wajinden" ((魏志倭人伝), a Japanese abbreviation for the "account of Wajin" in the "Biographies of the Wuhuan, Xianbei, and Dongyi" (烏丸鮮卑東夷傳), Volume 30 of the "Book of Wei" (魏書) of the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (三国志)), their lifestyle, habits and the way of society are described and by cultural commonality such as lifestyle, customs and languages, they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okimi
Ōkimi (, ''Ōkimi'', ''Daiō'') or Ame no shita Siroshimesu Ōkimi (, Chi Tenka Daiō) is the title of the Head of the Yamato Kingship or the monarch title of Wakoku (Old Japan) from the Kofun period through the Asuka period in the ancient Japan. The terms The title "" (Ōkimi or Daiō) which is an honorific title of Head (King) of the Yamato Kingship was established around the 5th century. Thereafter, this title was used in Japan until 680s when the compilation of the Asuka Kiyomihara Code started. There are several theories upon whether the title holder in the early period is a king of the unified kingship or not. As to ''Ōkimi'' in Japanese reading, this is created by adding the prefix "ō/oho", which indicates greatness and particular nobleness, to the title "kimi" (lord), which indicates a master or nobleman, thus the title "Ōkimi/Ohokimi" is created. However, according to the other theory, "Ōkimi" is only an honorific form of "kimi", that is the title of Japan, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamato Kingship
The was a tribal alliance centered on the Yamato Province, Yamato region (Nara Prefecture) from the 4th century to the 7th century, and ruled over the alliance of Nobility, noble families in the central and western parts of the Japanese archipelago. The age is from the 4th to the 7th century, later than the Yamatai, Yamatai Kingdom. After the Taika Reform, the Okimi, ōkimi as an emperor, at that time, was in power, and the Yamato period ended. The time period is archaeologically known as the Kofun period. Regarding its establishment, due to the relationship between Yamatai and Yamato's succession to the king's power, there are very different views on it. The Yamato Kingship refers to the regime that emerged in the Nara Prefecture, Nara region (Yamato Province, Yamato region) since the 4th century. But the term does not imply the origin of Japan, which is disputed in History of Japan, Japanese history. At the same time as the rise of the , there were probably several or even do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State (polity)
A state is a centralized political organization that imposes and enforces rules over a population within a territory. There is no undisputed definition of a state. One widely used definition comes from the German sociologist Max Weber: a "state" is a polity that maintains a monopoly on the legitimate use of violence, although other definitions are not uncommon.Cudworth et al., 2007: p. 95Salmon, 2008p. 54 Absence of a state does not preclude the existence of a society, such as stateless societies like the Haudenosaunee Confederacy that "do not have either purely or even primarily political institutions or roles". The level of governance of a state, government being considered to form the fundamental apparatus of contemporary states, is used to determine whether it has failed. In a federal union, the term "state" is sometimes used to refer to the federated polities that make up the federation. (Other terms that are used in such federal systems may include “province”, � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conquered or otherwise threatened to conquer. In case of alliances, lesser parties may pay tribute to more powerful parties as a sign of allegiance and often in order to finance projects that would benefit both parties. To be called "tribute" a recognition by the payer of political submission to the payee is normally required; the large sums, essentially protection money, paid by the later Roman and Byzantine Empires to barbarian peoples to prevent them attacking imperial territory, would not usually be termed "tribute" as the Empire accepted no inferior political position. Payments ''by'' a superior political entity to an inferior one, made for various purposes, are described by terms including " subsidy". The ancient Persian Achaemenid Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Century
The 1st century was the century spanning AD 1 ( I) through AD 100 ( C) according to the Julian calendar. It is often written as the or to distinguish it from the 1st century BC (or BCE) which preceded it. The 1st century is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period. The 1st century also saw the appearance of Christianity. During this period, Europe, North Africa and the Near East fell under increasing domination by the Roman Empire, which continued expanding, most notably conquering Britain under the emperor Claudius ( AD 43). The reforms introduced by Augustus during his long reign stabilized the empire after the turmoil of the previous century's civil wars. Later in the century the Julio-Claudian dynasty, which had been founded by Augustus, came to an end with the suicide of Nero in AD 68. There followed the famous Year of Four Emperors, a brief period of civil war and instability, which was finally brought to an end by Vespasian, ninth Roman em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suishō
was a king of Wa (Japan). He is the earliest Japanese person whose name appeared in a Chinese history. He is mentioned in Volume 85 of the '' Book of the Later Han'', which was compiled in 445 C.E. Although Suishō is the earliest figure in Japanese history to be named in a text, he was not the first. Himiko , also known as , was a shamaness-queen of Yamatai-koku in . Early Chinese dynastic histories chronicle tributary relations between Queen Himiko and the Cao Wei Kingdom (220–265) and record that the Yayoi period people chose her as ruler fol ..., a shaman queen of Wa, lived over a century after Suishō, but was mentioned in a Chinese text written in 289 C.E., about 150 years before the text mentioning Suishō was written. Historical references The only historical record about Suishō is a brief sentence on Volume 85 of the Book of the Later Han. In the first year of Yongchu during the reign of the Emperor An (AD 107), Suishō, the king of Wa, presented 160 生口 ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AD 107
Year 107 ( CVII) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sura and Senico (or, less frequently, year 860 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 107 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Lucius Licinius Sura and Quintus Sosius Senecio become consuls of Rome. * An Indian ambassador is received by Emperor Trajan. Asia * First year of the ''yongchu'' era of the Chinese Eastern Han Dynasty. * Han Andi (An-ti) becomes emperor of China. Deaths * Titus Avidius Quietus Titus Avidius Quietus (died by 107 AD) was a Roman senator active during the reigns of the emperors Domitian, Nerva and Trajan. The offices he held included suffect consul in AD 93 and governor of Roman Britain around 98. Background The You .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itoshima, Fukuoka
is a city located in western Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. As of April 2018, the city has an estimated population of 96,540, with 34,685 households and a population density of 454 persons per km². The total area is 216.12 km². The modern city of Itoshima was established on January 1, 2010, from the merger of the city of Maebaru and the towns of Shima and Nijo (both from Itoshima district). Geography The city contains several mountains, islands, and moderately populated low-lying areas. Its highest point is Mt. Rai. It is bordered by Fukuoka to the east, the Genkai Sea to the north, and the Sefuri mountains to the south. Climate Itoshima has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen: ''Cfa''). The average annual temperature in Itoshima is . The average annual rainfall is with July as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around , and lowest in January, at around . The highest temperature ever recorded in Itoshima was on 5 August 2017 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Three Kingdoms
The ''Records or History of the Three Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese name as the Sanguo Zhi, is a Chinese historical text which covers the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty (c. 184–220 AD) and the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). It is widely regarded as the official and authoritative source historical text for that period. Written by Chen Shou in the third century, the work synthesizes the histories of the rival states of Cao Wei, Shu Han and Eastern Wu in the Three Kingdoms period into a single compiled text. The ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is the main source of influence for the 14th century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms,'' considered one of the great four novels of Chinese classical literature. Major chunks of the records have been translated into English, but the tome has yet to be fully translated. Origin and structure The ''Records of the Grand Historian'', ''Book of Han'' and '' Book of the Later Han'', and the ''Record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
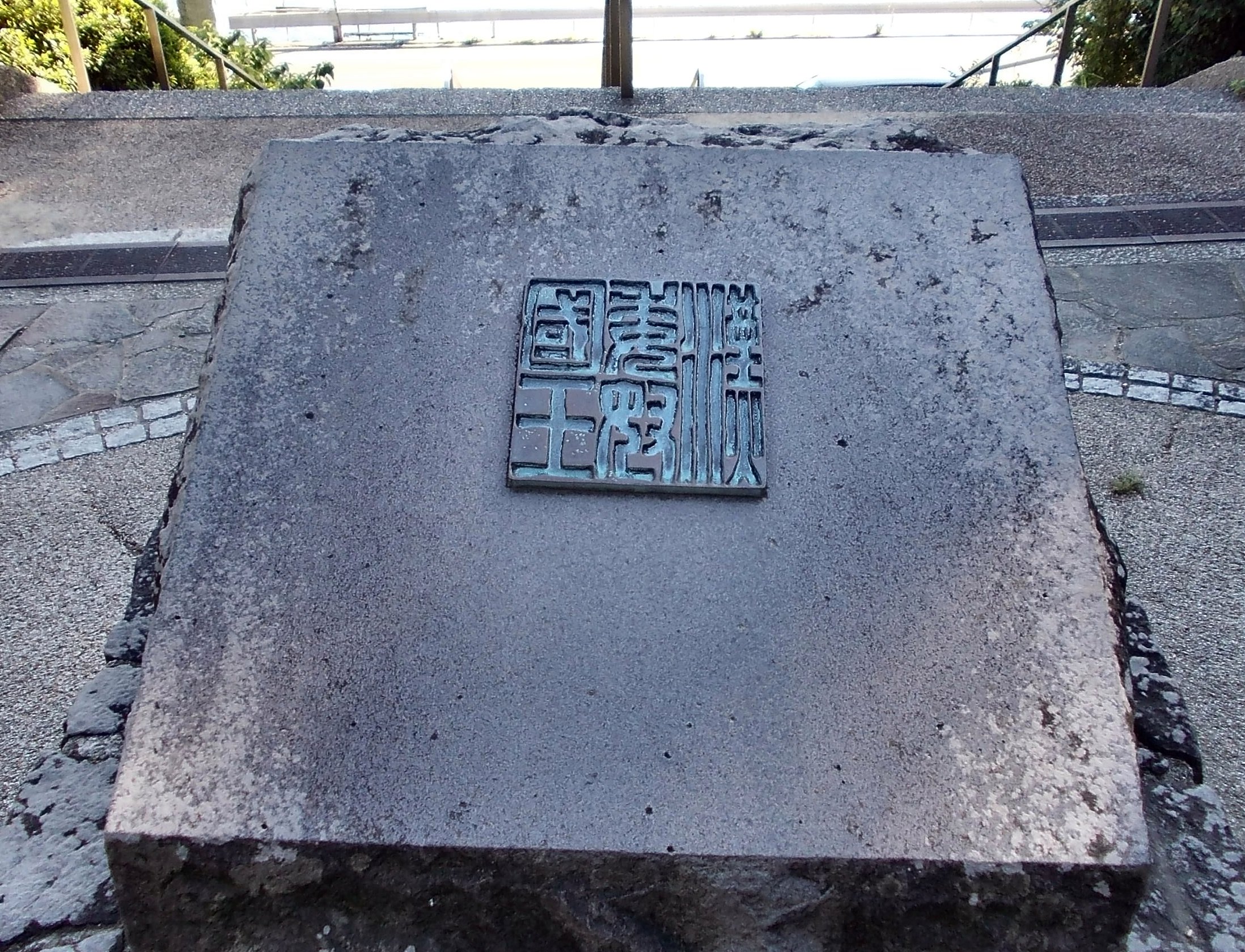
Nakoku
was a stateIn Japanese, the character 国/國, read as ''koku'' (in on'yomi) or ''kuni'' (in kun'yomi), can be translated as "country" or "province" which was located in and around modern-day Fukuoka City, on the Japanese island of Kyūshū, from the 1st to early 3rd centuries. Much of what is known about it comes from ancient records of both China and Japan. According to the ''Book of the Later Han'', in 57 CE, Emperor Guangwu of Han granted Nakoku an imperial seal, patterned after the Chinese jade seals, but made of gold: the king of Na gold seal. In return, that same year, Na sent envoys to the Chinese capital, offering tribute and formal New Year's greetings. This seal was discovered over 1500 years later, by an Edo period farmer on Shikanoshima Island, thus helping to verify the existence of Nakoku, which was otherwise known only from the ancient chronicles. Engraved upon it are the Chinese characters (''Kan no Wa no Na-no-Koku-ō'', "King of the Na state of the Wa (vass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |