|
Wahkare Khety I
Wahkare Khety was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the 9th or 10th Dynasty during the First Intermediate Period. Identity The identity of Wahkare Khety is controversial. While some scholars believe that he was the founder of the 9th Dynasty, many others place him in the subsequent 10th Dynasty.William C. Hayes, in ''The Cambridge Ancient History'', vol 1, part 2, 1971 (2008), Cambridge University Press, , p. 996.Michael Rice, ''Who is who in Ancient Egypt'', 1999 (2004), Routledge, London, , p. 7. 9th Dynasty hypothesis If Wahkare Khety was the founder of the 9th Dynasty, he may be identified with the hellenized king Achthoês, the founder of this dynasty according to Manetho. Manetho reports: The first of these ings Achthoês, behaving more cruel than his predecessors, wrought woes for the people of all of Egypt, but afterwards he was smitten with madness and killed by a crocodile.William Gillian Waddell: ''Manetho (= The Loeb classical library. Bd. 350)''. Harvard University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakenranef
Bakenranef, known by the ancient Greeks as Bocchoris (Ancient Greek: , ; Latin: ) or Bochchoris (, ; Latin: ) was briefly a king of the 24th Dynasty of Egypt. Based at Sais in the western Delta, he ruled Lower Egypt from c. 725 to 720 BC. Though the Ptolemaic period Egyptian historian Manetho considers him the sole member of the 24th Dynasty, modern scholars include his father Tefnakht in that dynasty. Although Sextus Julius Africanus quotes Manetho as stating that "Bocchoris" ruled for six years, some modern scholars again differ and assign him a shorter reign of only five years, based on evidence from an Apis Bull burial stela. It establishes that Bakenranef's reign ended only at the start of his 6th regnal year which, under the Egyptian dating system, means he had a reign of 5 full years. Bakenranef's prenomen or royal name, ''Wahkare'', means "Constant is the Spirit of Re" in Egyptian. Literary sources Manetho is the source for two events from Bakenranef's reign. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile Crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed throughout sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the central, eastern, and southern regions of the continent, and lives in different types of aquatic environments such as lakes, rivers, swamps, and marshlands. In West Africa, it occurs along with two other crocodilians. Although capable of living in saline environments, this species is rarely found in saltwater, but occasionally inhabits deltas and brackish lakes. The range of this species once stretched northward throughout the Nile, as far north as the Nile Delta. On average, the adult male Nile crocodile is between in length and weighs including stomach stones. However, specimens exceeding in length and weighing up to have been recorded. It is the largest freshwater predator in Africa, and may be considered the second-largest extant reptile in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asyut
AsyutAlso spelled ''Assiout'' or ''Assiut'' ( ar, أسيوط ' , from ' ) is the capital of the modern Asyut Governorate in Egypt. It was built close to the ancient city of the same name, which is situated nearby. The modern city is located at , while the ancient city is located at . The city is home to one of the largest Coptic Catholic churches in the country. History Names and etymology The name of the city is derived from early Egyptian Zawty (''Z3JW.TJ'') (late Egyptian, Səyáwt) adopted into the Coptic as Syowt , which means "''Guardian''" of the northern approach of Upper Egypt. In Graeco-Roman Egypt, it was called Lycopolis or Lykopolis ( el, Λυκόπολις, ""), ('wolf city') Lycon, or Lyco. Ancient Asyut Ancient Asyut was the capital of the Thirteenth Nome of Upper Egypt (''Lycopolites Nome'') around 3100 BC. It was located on the western bank of the Nile. The two most prominent gods of ancient Egyptian Asyut were Anubis and Wepwawet, both funerary deit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean in South-western Asia,Gasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. }, ), meaning "the eastern place, where the Sun rises". In the 13th and 14th centuries, the term ''levante'' was used for Italian maritime commerce in the Eastern Mediterranean, including Greece, Anatolia, Syria-Palestine, and Egypt, that is, the lands east of Venice. Eventually the term was restricted to the Muslim countries of Syria-Palestine and Egypt. In 1581, England set up the Levant Company to monopolize commerce with the Ottoman Empire. The name ''Levant States'' was used to refer to the French mandate over Syria and Lebanon after World War I. This is probab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
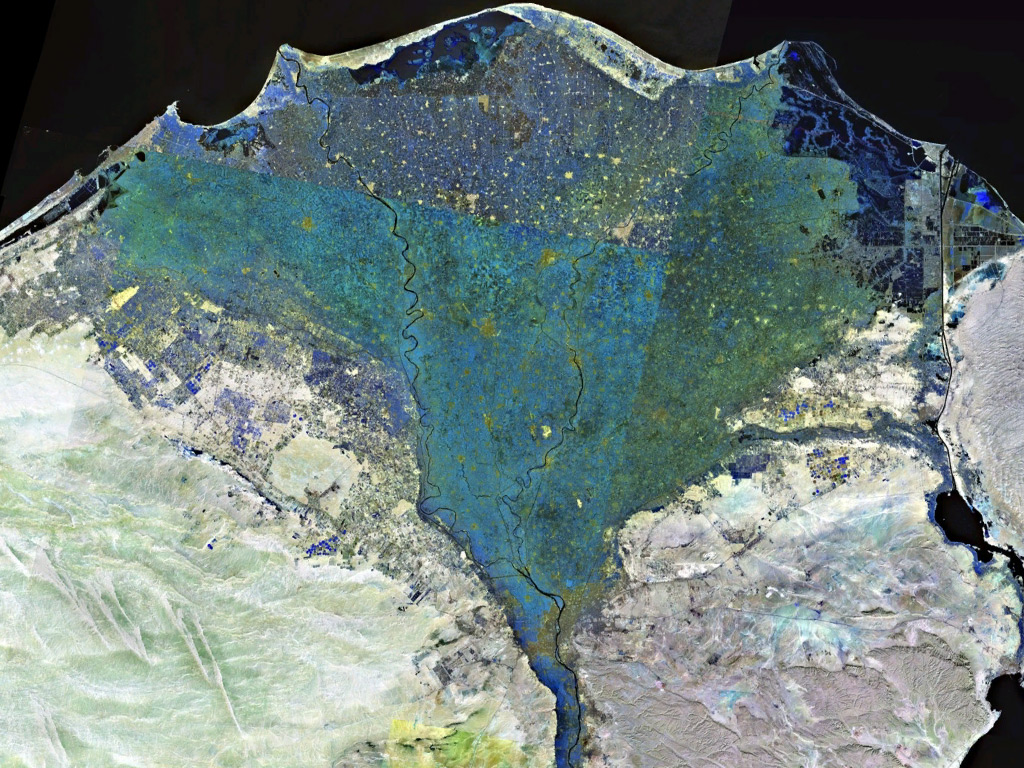
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers of Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same name. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta and enters the coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomarch
A nomarch ( grc, νομάρχης, egy, ḥrj tp ꜥꜣ Great Chief) was a provincial governor in ancient Egypt; the country was divided into 42 provinces, called nomes (singular , plural ). A nomarch was the government official responsible for a nome. Etymology The term ''nome'' is derived from grc, νομός ''nomós'' "province, district". ''Nomarch'' is derived from ''nomárkhēs'': "province" + "ruler". Egyptian history The division of the Egyptian kingdom into nomes can be documented as far back as the reign of Djoser of the 3rd Dynasty in the early Old Kingdom, c. 2670 BCE, and potentially dates even further back to the Predynastic kingdoms of the Nile valley. The earliest topographical lists of the nomes of Upper and Lower Egypt date back to the reign of Nyuserre Ini, of the mid 5th Dynasty, from which time the nomarchs no longer lived at royal capital but stayed in their nomes. The power of the nomarchs grew with the reforms of Nyuserre's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meryibre Khety
Meryibre Khety, also known by his Horus name Meryibtawy, was a pharaoh of the 9th or 10th Dynasty of Egypt, during the First Intermediate Period. Reign Some scholarsAlan Gardiner, ''Egypt of the Pharaohs. An introduction'', Oxford University Press, 1961, p. 112.William C. Hayes, in ''The Cambridge Ancient History'', vol 1, part 2, 1971 (2008), Cambridge University Press, , p. 464. believe that Meryibre Khety was the founder of the 9th Dynasty, a Herakleopolitan nomarch who gathered enough authority to claim himself the legitimate successor of the 6th Dynasty pharaohs. It seems that Meryibre ruled over his neighboring nomarchs with an iron fist, and it is likely for this reason that in later times this ruler became Manetho's infamous ''Achthoes'', a wicked king who went insane and then was killed by a crocodile. Alternatively, other Egyptologists such as Jürgen von Beckerath believe instead that Meryibre reigned toward the end of the subsequent 10th Dynasty, shortly before kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teaching For King Merykare
The ''Teaching for King Merykara'', alt. ''Instruction Addressed to King Merikare'', is a literary composition in Middle Egyptian, the classical phase of the Egyptian language, probably of Middle Kingdom date (2025–1700 BC). In this ''sebayt'' the author has a First Intermediate Period king of Egypt possibly named Kheti address his son, the future king Merykara, advising him on how to be a good king, and how to avoid evil. Merykara is the name of a king of the 9th or 10th Dynasty, the line or lines of kings who ruled northern Egypt during a period of division, the First Intermediate Period (about 2150–2025 BC). Perhaps this allowed the author of this composition greater freedom in describing the limits of royal authority than might have been possible in referring to kings of a unified Egypt; the ''Teaching for King Merykara'' is effectively a treatise on kingship in the form of a royal testament, the first of this genre. Similar works were created later in the Hellenistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Dynasty
The Tenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty X) is often combined with the 7th, 8th, 9th and early 11th Dynasties under the group title First Intermediate Period. Rulers The 9th Dynasty was founded at Herakleopolis Magna, and the 10th Dynasty continued there. At this time Egypt was not unified, and there is some overlap between these and other local dynasties. The Turin Canon lists eighteen kings for this royal line, but their names are damaged, unidentifiable, or lost.Sir Alan Gardiner Sir Alan Henderson Gardiner, (29 March 1879 – 19 December 1963) was an English Egyptologist, linguist, philologist, and independent scholar. He is regarded as one of the premier Egyptologists of the early and mid-20th century. Personal life G ..., ''Egypt of the Pharaohs'', Oxford University Press, 1961, pp. 112-13. The following is a ''possible'' list of rulers of the Tenth Dynasty based on the Turin Canon, as Egyptologists have differing opinions about the order of succession within t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian Shaw (Egyptologist)
Ian Shaw, (born 1961) is an Egyptologist and academic, who was formerly Reader in Egyptian Archaeology at the University of Liverpool. Life His field work was largely focused in el-Amarna, but in recent times, he has done extensive excavations of mining and quarrying sites from many different Ancient Egyptian periods. He primarily focuses his recent work on methods and mechanics of Egyptian craftsmen and laborers. However, he has produced several works regarding ancient Egyptian warfare; a topic that had long been ignored or only briefly commented on by other researchers. Besides writing original books, he also has edited several "dictionaries" of Ancient Egypt (which might more correctly be labeled "encyclopedias"; they are in no way lexicons). On 15 March 2018, Shaw was elected a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries (FSA). Bibliography *''Egyptian Warfare and Weapons'', 1991 *''A History of Ancient Egypt'', 1992 (Translated from French work by Nicholas Grimal) *''The Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephan Seidlmayer
Stephan may refer to: * Stephan, South Dakota, United States * Stephan (given name), a masculine given name * Stephan (surname), a Breton-language surname See also * Sankt-Stephan * Stefan (other) * Stephan-Oterma * Stephani * Stephen (other) Stephen is a masculine given name. Stephen may also refer to: People * Stephen (surname), including a list of people with the surname * Stephen (honorific), a South Slavic medieval honorific Places * Stephen, Minnesota, United States * Mount S ... * von Stephan {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Egypt
Lower Egypt ( ar, مصر السفلى '; ) is the northernmost region of Egypt, which consists of the fertile Nile Delta between Upper Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea, from El Aiyat, south of modern-day Cairo, and Dahshur. Historically, the Nile River split into seven branches of the delta in Lower Egypt. Lower Egypt was divided into nomes and began to advance as a civilization after 3600 BC. Today, it contains two major channels that flow through the delta of the Nile River – Mahmoudiyah Canal (ancient Agathos Daimon) and Muways Canal (, "waterway of Moses"). Name In Ancient Egyptian, Lower Egypt was as ''mḥw'' and means ''"north"''. Later on, during Antiquity and the Middle Ages, Greeks and Romans called it ''Κάτω Αἴγυπτος'' or ''Aegyptus Inferior'' both meaning "Lower Egypt", but Copts carried on using the old name related to the north – ''Tsakhet'' () or ''Psanemhit'' () meaning the "Northern part". It was further divided into number of regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)