|
WATFIV
WATFIV, or WATerloo FORTRAN IV, developed at the University of Waterloo, Canada is an implementation of the Fortran computer programming language. It is the successor of WATFOR. WATFIV was used from the late 1960s into the mid-1980s. WATFIV was in turn succeeded by later versions of WATFOR. Because it could complete the three usual steps ("compile-link-go") in just one pass, the system became popular for teaching students computer programming. History In the early 1960s, newly formed computer science departments started university programs to teach computer programming languages. The Fortran language had been developed at IBM, but suffered from slow and error-prone three-stage batch processing workflow. In the first stage, the compiler started with source code and produced object code. In the second stage, a linker constructed a complete program using growing libraries of common functions. Finally, the program was repeatedly executed with data for the typical scientific and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watcom
Watcom International Corporation was a software company, which was founded in 1981 by Wes Graham and Ian McPhee. Founding staff (Fred Crigger, Jack Schueler and McPhee) were formerly members of Professor Graham's Computer Systems Group at the University of Waterloo, in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. Watcom produced a variety of tools, including the well-known Watcom C/C++ compiler introduced in 1988. The first company started by Graham and McPhee was Structured Computing Systems, incorporated in 1974. Then the software development company, WATCOM Systems Inc, started in 1981 with three full-time employees, but had been incorporated two years earlier as Waterloo Basic Enterprises Limited. In 1984, the various subsidiary companies of The WATCOM Group software organization—marketing and sales, publications, seminars and systems (software development) -- were all renamed as WATCOM companies for consistent branding. These were later all merged into one full-service software company, W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WATBOL
WATBOL is a teaching compiler for the COBOL programming language developed in 1969 at the University of Waterloo. The compiler was a companion product, built under the design philosophy, of Waterloo’s earlier, widely used WATFOR teaching compiler. Since programs written by undergraduate students were unlikely to be run more than a few times, after they were successfully written and debugged, the efficiency of the program, once compiled was of secondary importance, compared with giving simpler, clearer error messages, and in simplifying the steps for the student to compile the program. At that time executing a program through the use of commercial compiler was a three-step process. First the Fortran, or COBOL, had to be compiled into assembly language, then the assembly language had to be assembled into binary code; finally the compiled and assembled code had to be linked with previously written libraries of subroutines. WATFOR and WATBOL allowed simple programs to be comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
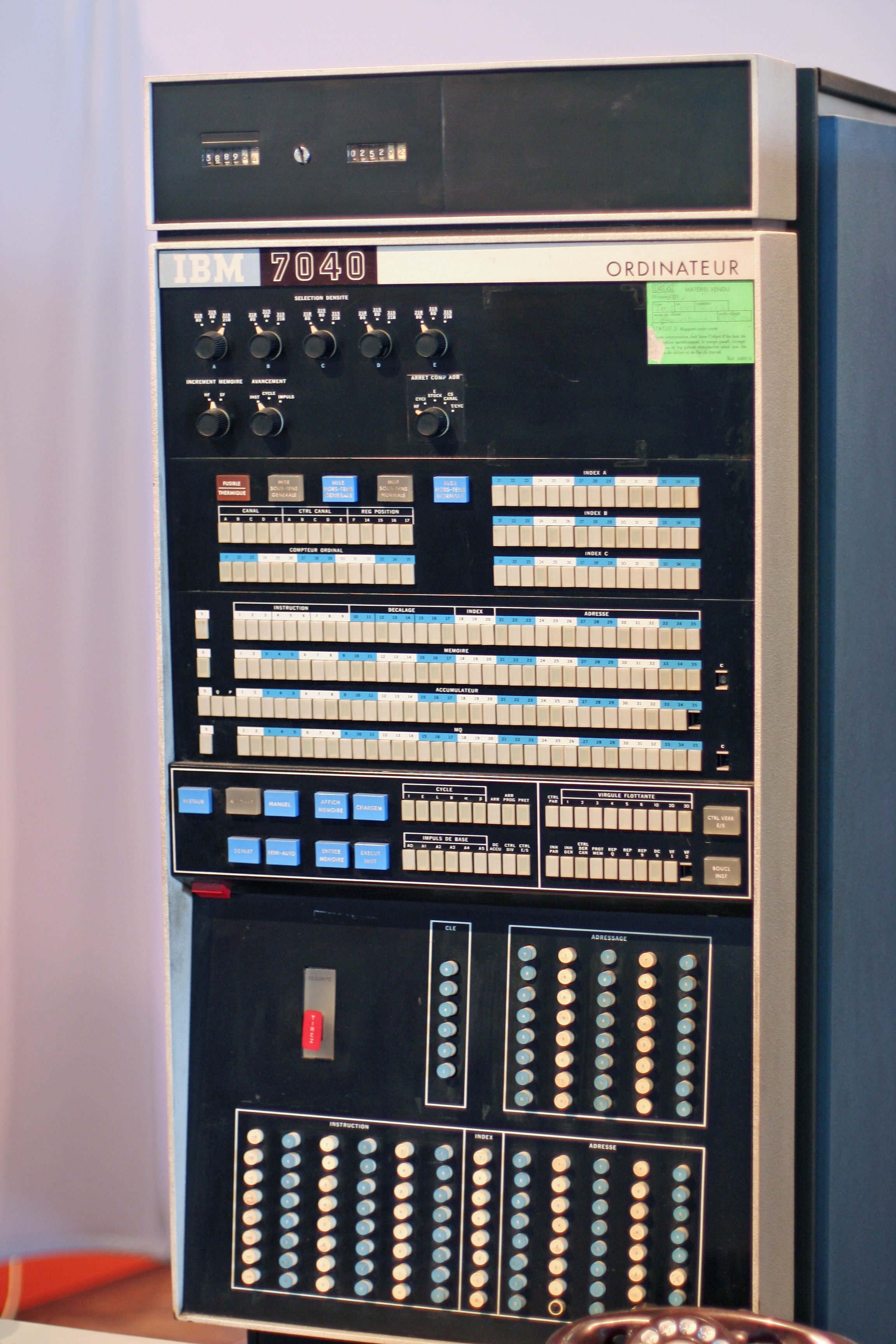
IBM 7040
The IBM 7040 was a historic but short-lived model of transistor computer built in the 1960s. History It was announced by IBM in December 1961, but did not ship until April 1963. A later member of the IBM 700/7000 series of scientific computers, it was a scaled-down version of the IBM 7090. It was not fully compatible with the 7090. Some 7090 features, including index registers, character instructions and floating point, were extra-cost options. It also featured a different input/output architecture, based on the IBM 1414 data synchronizer, allowing more modern IBM peripherals to be used. A model designed to be compatible with the 7040 with more performance was announced as the 7044 at the same time. Peter Fagg headed the development of the 7040 under executive Bob O. Evans. A number of IBM 7040 and 7044 computers were shipped, but it was eventually made obsolete by the IBM System/360 family, announced in 1964. The schedule delays caused by IBM's multiple incompatible architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
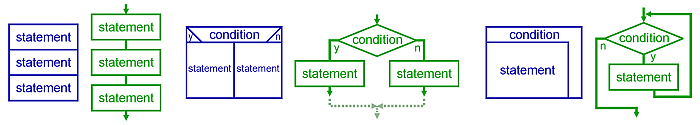
Structured Programming
Structured programming is a programming paradigm aimed at improving the clarity, quality, and development time of a computer program by making extensive use of the structured control flow constructs of selection ( if/then/else) and repetition ( while and for), block structures, and subroutines. It emerged in the late 1950s with the appearance of the ALGOL 58 and ALGOL 60 programming languages, with the latter including support for block structures. Contributing factors to its popularity and widespread acceptance, at first in academia and later among practitioners, include the discovery of what is now known as the structured program theorem in 1966, and the publication of the influential "Go To Statement Considered Harmful" open letter in 1968 by Dutch computer scientist Edsger W. Dijkstra, who coined the term "structured programming". Structured programming is most frequently used with deviations that allow for clearer programs in some particular cases, such as when exceptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian McPhee (computer Scientist)
Ian McPhee is a Canadian computer scientist, entrepreneur, and philanthropist. He earned a Bachelor of Mathematics in 1973, and his Masters of Mathematics in 1979. When McPhee was an undergraduate at the University of Waterloo he was a protege of influential professor Wes Graham. Graham assigned McPhee to work on Watfor, a Fortran compiler optimized for efficiently compiling the typical student program. McPhee continued to work for Graham, until 1981 when he co-founded Watcom with other associates of Graham. Watcom is characterized as the first spin-off company to come from Waterloo. McPhee became Watcom's President, in 1986.Ian McPhee, President, Watcom International Corporation, University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics, 1995 recipient of the J.W. Graham Medal. https://uwaterloo.ca/math/people-profiles/ian-mcphee McPhee became an executive at Sybase Sybase, Inc. was an enterprise software and services company. The company produced software to manage and analyze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDP-11
The PDP-11 is a series of 16-bit minicomputers sold by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) from 1970 into the 1990s, one of a set of products in the Programmed Data Processor (PDP) series. In total, around 600,000 PDP-11s of all models were sold, making it one of DEC's most successful product lines. The PDP-11 is considered by some experts to be the most popular minicomputer. The PDP-11 included a number of innovative features in its instruction set and additional general-purpose registers that made it much easier to program than earlier models in the PDP series. Further, the innovative Unibus system allowed external devices to be easily interfaced to the system using direct memory access, opening the system to a wide variety of peripherals. The PDP-11 replaced the PDP-8 in many real-time computing applications, although both product lines lived in parallel for more than 10 years. The ease of programming of the PDP-11 made it very popular for general-purpose computing uses also. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until forced to resign in 1992, after the company had gone into precipitous decline. The company produced many different product lines over its history. It is best known for the work in the minicomputer market starting in the mid-1960s. The company produced a series of machines known as the PDP line, with the PDP-8 and PDP-11 being among the most successful minis in history. Their success was only surpassed by another DEC product, the late-1970s VAX "supermini" systems that were designed to replace the PDP-11. Although a number of competitors had successfully competed with Digital through the 1970s, the VAX cemented the company's place as a leading vendor in the computer space. As microcomputers improved in the late 1980s, especially wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel D
Daniel is a masculine given name and a surname of Hebrew origin. It means "God is my judge"Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 68. (cf. Gabriel—"God is my strength"), and derives from two early biblical figures, primary among them Daniel from the Book of Daniel. It is a common given name for males, and is also used as a surname. It is also the basis for various derived given names and surnames. Background The name evolved into over 100 different spellings in countries around the world. Nicknames (Dan, Danny) are common in both English and Hebrew; "Dan" may also be a complete given name rather than a nickname. The name "Daniil" (Даниил) is common in Russia. Feminine versions (Danielle, Danièle, Daniela, Daniella, Dani, Danitza) are prevalent as well. It has been particularly well-used in Ireland. The Dutch names "Daan" and "Daniël" are also variations of Daniel. A related surname developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COBOL
COBOL (; an acronym for "common business-oriented language") is a compiled English-like computer programming language designed for business use. It is an imperative, procedural and, since 2002, object-oriented language. COBOL is primarily used in business, finance, and administrative systems for companies and governments. COBOL is still widely used in applications deployed on mainframe computers, such as large-scale batch and transaction processing jobs. However, due to its declining popularity and the retirement of experienced COBOL programmers, programs are being migrated to new platforms, rewritten in modern languages or replaced with software packages. Most programming in COBOL is now purely to maintain existing applications; however, many large financial institutions were still developing new systems in COBOL as late as 2006. COBOL was designed in 1959 by CODASYL and was partly based on the programming language FLOW-MATIC designed by Grace Hopper. It was created as part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grace Murray Hopper Award
The Grace Murray Hopper Award (named for computer pioneer RADM Grace Hopper) has been awarded by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) since 1971. The award goes to a computer professional who makes a single, significant technical or service contribution at or before age 35. __TOC__ Recipients * 1971 Donald Knuth * 1972 Paul H. Dirksen * 1972 Paul H. Cress * 1973 Lawrence M. Breed * 1973 Richard H. Lathwell * 1973 Roger Moore * 1974 George N. Baird * 1975 Allan L. Scherr * 1976 Edward H. Shortliffe * 1977 ''no award'' * 1978 Ray Kurzweil * 1979 Steve Wozniak * 1980 Robert M. Metcalfe * 1981 Daniel S. Bricklin * 1982 Brian K. Reid * 1983 ''no award'' * 1984 Daniel Henry Holmes Ingalls, Jr. * 1985 Cordell Green * 1986 William Nelson "Bill" Joy * 1987 John Ousterhout * 1988 Guy L. Steele Jr. * 1989 W. Daniel Hillis * 1990 Richard Stallman * 1991 Feng-hsiung Hsu * 1992 ''no award'' * 1993 Bjarne Stroustrup * 1994–1995 ''no award'' * 1996 Shafrira Goldwasser * 1997- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)