|
WAP 7
The Indian locomotive class WAP-7 is a class of 25 kV AC electric locomotives that was developed in 1999 by Chittaranjan Locomotive Works (CLW) for Indian Railways. The model name stands for broad gauge (W), AC Current (A), Passenger traffic (P) engine, 7th generation (7). They entered service in 2000. A total of 1424 WAP-7 have been built, with more units being built at CLW, Banaras Locomotive Works (BLW) and Patiala Locomotive Works (PLW). The WAP-7 is one of the most successful locomotives of Indian Railways serving passenger trains for over 22 years. It is a passenger variant of the WAG-9 freight locomotive with a modified gear ratio to pull lighter loads at higher speeds. With an output of , it is the most powerful passenger locomotive in the Indian Railways fleet, and the most numerous passenger locomotive in India. The WAP-7 is capable of hauling 24 coach trains at speeds . History It is now largely used by Northern Railways (NR), South Central Railways (SCR), Centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Locomotive
An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or on-board energy storage such as a battery or a supercapacitor. Locomotives with on-board fuelled prime movers, such as diesel engines or gas turbines, are classed as diesel-electric or gas turbine-electric and not as electric locomotives, because the electric generator/motor combination serves only as a power transmission system. Electric locomotives benefit from the high efficiency of electric motors, often above 90% (not including the inefficiency of generating the electricity). Additional efficiency can be gained from regenerative braking, which allows kinetic energy to be recovered during braking to put power back on the line. Newer electric locomotives use AC motor-inverter drive systems that provide for regenerative braking. Electric locomotives are quiet compared to diesel locomotives since there is no engine and exhaust noise and less mechanical noise. The lack of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
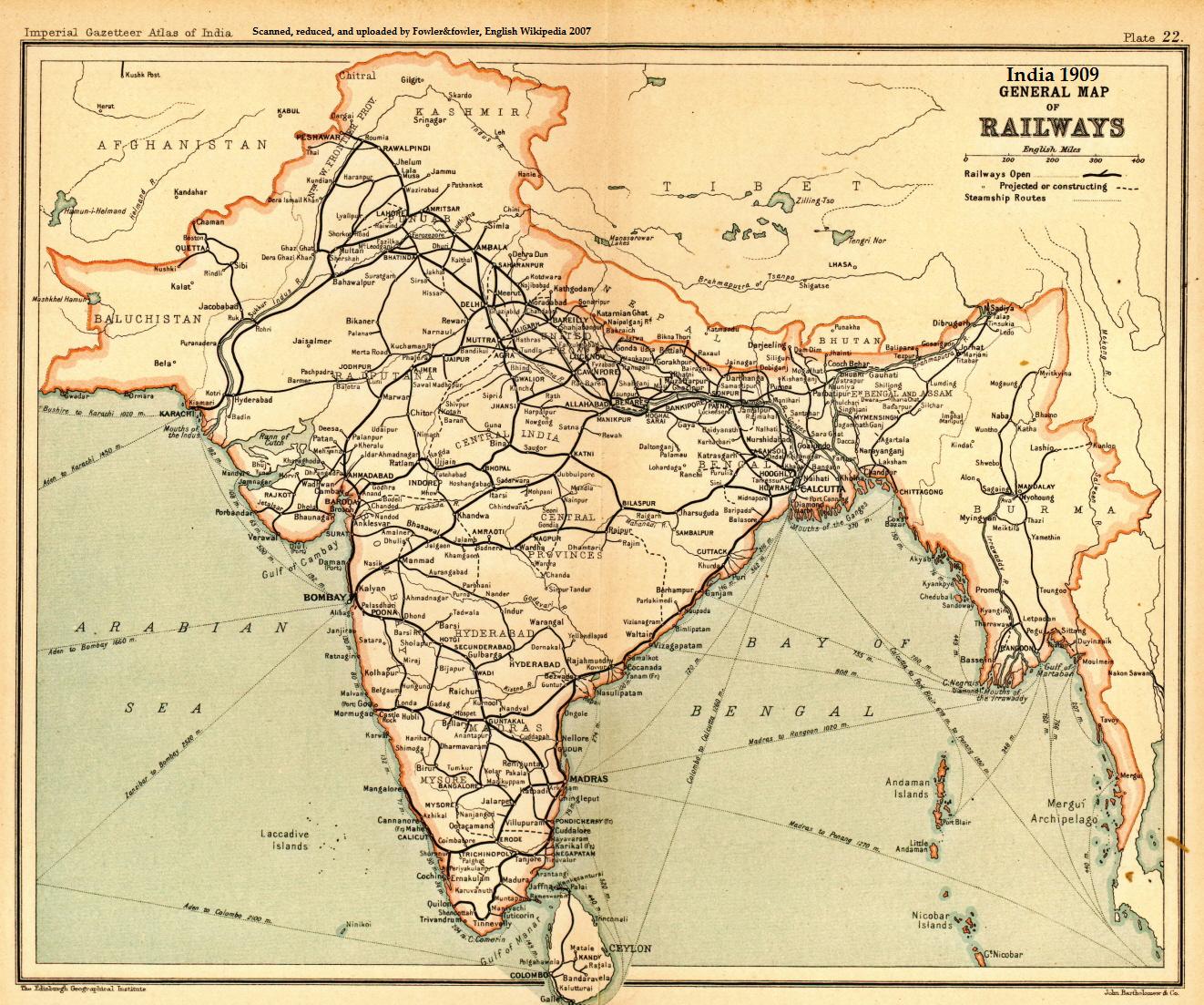
5 Ft 6 In Gauge Railway
, a broad gauge, is the track gauge used in India, Pakistan, western Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Argentina, Chile, and on BART in San Francisco, United States. In North America, it is called Indian Gauge, Provincial, Portland, or Texas gauge. In Argentina, it is known as "trocha ancha" (Spanish for ''broad gauge''). In the Indian subcontinent it is simply known as "broad gauge". Elsewhere it is known as Indian gauge. It is the widest gauge in regular passenger use anywhere in the world. Asia India In India, the initial freight railway lines were built using standard gauge. In the 1850s, the Great Indian Peninsula Railway adopted the gauge of for the first passenger railway in India between Bori Bunder and Thane.Indian Railways: Some Fascinating Facts“Train Atlas” ''Train Atlas'', Indian Railways, 2003 This was then adopted as the standard for the nationwide network. Indian Railways today predominantly operates on broad gauge. Most of the metre gauge and narrow gauge railw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Western Railway Zone
The South Western Railway (SWR) is one of the 19 railway zones in India, headquartered at Hubballi in Karnataka State. SWR was created from carving out the routes from Southern Railways, South Central Railways and Central Railways in 2003. History The South Western Railway zone came into existence on 1 April 2003 by bifurcating Mysuru and Bengaluru divisions from Southern Railway along with Hubballi division from South Central Railway. It is headquartered at Hubballi and comprises three divisions namely Hubballi, Mysuru, and Bengaluru. The fourth division at Kalaburagi was slated to be the fourth division which was supposed to be carved out from Hubli, Secunderabad, Guntakal and Solapur divisions. Currently the divisional office at Kalaburagi is on hold due to operational constraints. Jurisdiction South Western Railway covers most of the railway lines in the state of Karnataka and Goa except the Konkan Railway line, parts of Sri Sathya Sai district and Chittoor dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Central Railway Zone
The North Central Railway (abbreviated NCR) is one of the 19 railway zones in India. The largest railway station in NCR is Kanpur Central. It is headquartered at Prayagraj and comprises three divisions: Allahabad division, Jhansi division, Agra division of the erstwhile Northern Railway, Jhansi division of the erstwhile Central Railway, and new Agra division. History The North Central Railway, in its present form, came into existence on 1 April 2003. The North Central Railway present network extends over a large area of North Central India, covering the states of Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Haryana. By December 2017, railways for the first time installed 6,095 GPS-enabled "Fog Pilot Assistance System" railway signalling devices in four most affected zones, Northern Railway zone, North Central Railway zone, North Eastern Railway zone and North Western Railway zone, by doing away with the old practice of putting firecrackers on train tracks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Railway Zone
The Western Railway (abbreviated WR) is one of the 19 zones of Indian Railways and is among the busiest railway networks in India, headquartered at Mumbai, Maharashtra. The major railway routes of Indian Railways which come under Western Railways are: Mumbai Central– Ratlam, Mumbai Central– Ahmedabad and Palanpur–Ahmedabad. The railway system is divided into six operating divisions: , , , , , and . Vadodara railway station, being the junction point for the Ahmedabad–Mumbai route and the Mumbai–Ratlam route towards New Delhi, is the busiest junction station in Western Railways and one of the busiest junctions of Indian Railways too, while Ahmedabad Division earns highest revenue followed by Mumbai Division and Vadodara Division. Surat railway station is one of the busiest railway station in Western Railway in non-junction category where more than 180 trains pass per day. Western Railway General Manager's official bungalow 'Bombarci' (abbreviation of Bombay, Baroda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Railway Zone
The Eastern Railway (abbreviated ER) is among the 19 zones of the Indian Railways. Its headquarters is at Fairley Place, Kolkata and comprises four divisions: , , , and . Each division is headed by a Divisional Railway Manager (DRM). The name of the division denotes the name of the city where the divisional headquarters is located. Eastern Railway oversees the largest and second largest rail complexes in the country, Howrah Junction and Sealdah railway station, and also contains the highest number of A1 and A Category Stations like , , , , Kolkata, , Barddhaman, Rampurhat Junction, , Jasidih, Bandel and Naihati. Eastern Railways operates India's oldest train, Kalka Mail. History The East Indian Railway (EIR) Company was incorporated in 1845 to connect eastern India with Delhi. The first train ran here between and on 15 August 1854. The train left Howrah station at 8:30 a.m. and reached Hooghly in 91 minutes. The management of the East Indian Railway was taken o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Eastern Railway (India)
The South Eastern Railway (abbreviated SER) is one of the 19 railway zones in India and Part of Eastern Railways. It is headquartered at Garden Reach, Kolkata, West Bengal, India. It comprises Adra railway division, Chakradharpur railway division, Kharagpur railway division and Ranchi railway division. History Predecessor The Bengal Nagpur Railway (BNR) Company was incorporated in 1887 to take over from the Nagpur Chhattisgarh Railway and to convert the line to broad gauge. The work was completed in 1888. The extension of the main line from Nagpur to Asansol was completed by 1891. A 161-mile branch line (258 km) that connected Bilaspur to Umaria coal mine was built and linked to the existing line from Umaria to Katni (1891). By the turn of the twentieth century, work on the Calcutta–Bombay and Calcutta–Madras lines was completed. Through the first half of the twentieth century work on the BNR lines progressed steadily. In 1921 the Talcher coalfields were connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South East Central Railway Zone
The South East Central Railway (abbreviated SECR) is one of the 19 Railway Zones in India. The Zone Office is headquartered at Bilaspur and comprises the Bilaspur, Nagpur and Raipur Division. History This Zone was formerly part of the South Eastern Railway. It was inaugurated on 20 September 1998 and dedicated to the nation on 1 April 2003. Divisions * Bilaspur railway division * Raipur railway division * Nagpur SEC railway division Infrastructure Bilaspur Railway Station is a regional hub for the system. It is the busiest junction in Chhattisgarh and the fourth-busiest in Central India. The zone's major stations are Itwari railway station (ITR), Gondia (G), (BRD), Dongargarh (DGG), Rajnandgaon (RJN), Durg Junction railway station (DURG), Bhilai Power House railway station (BPHB), Bhilai (BIA), Raipur (R), Bhatapara (BYT), Tilda (TLD), Bilaspur (BSP), Gevra Road (GAD), Champa (CPH), Raigarh (RIG), and Anuppur (APR), all of which lie on the Mumbai-Howrah and Mumbai- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Railways
Central Railway (abbreviated CR) is one of the 19 zones of Indian Railways. Its headquarters is in Mumbai at Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus. It has the distinction of operating the first passenger railway line in India, which opened from Mumbai to Thane on . History The railway zone was formed on 5 November 1951 by grouping several government-owned railways, including the Great Indian Peninsula Railway, the Scindia State Railway of the former princely state of Gwalior, Nizam State Railway, Wardha Coal State Railway and the Dholpur Railways.Rao, M.A. (1988). ''Indian Railways'', New Delhi: National Book Trust, p.42 The Central Railway zone formerly included large parts of Madhya Pradesh and part of southern Uttar Pradesh, which made it the largest railway zone in India in terms of area, track mileage and staff. These areas became the new West Central Railway zone in April 2003. The Central Railway General Manager's official residence (erstwhile GIPR agent's residence) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Central Railway Zone
The South Central Railway (abbreviated SCR) is one of the 19 zones of Indian Railways. The jurisdiction of the zone is spread over the states of Telangana, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh. It has three divisions under its administration, which include Secunderabad, Hyderabad and Nanded. It was re-organized in 2019 and the divisions of Vijayawada, Guntur and Guntakal railway divisions were separated to form South Coast Railway zone. Secunderabad railway station is the current headquarter and ''Arun Kumar Jain'' is the present general manager of the zone. History Hon'ble Ex MP Bayya Suryanarayana Murthy requested in creation of New railway zone at While speaking about the size of the zones, I am tempted to speak about the Southern zone. This zone, as I said, consists of 6.017 miles. It spreads itself like a leviathan into five States— Bombay, Mysore, Andhra Pradesh, Madras and Kerala. It is not only over-sized but it is unwiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |