|
WAP-5
The Indian locomotive class WAP-5 is the name of a class of "High Speed" electric locomotives produced and used by Indian Railways. The first 10 locomotives were imported from ABB in Switzerland in 1995. They are supposed to be a variant of the Swiss Lok 2000 (Design concept) and German DB Class 120 (mechanical chassis). One of the notable features of WAP-5 is regenerative braking. Other notable features of this loco are the provision of taps from the main loco transformer for hotel load, pantry loads, flexible gear coupling, wheel-mounted disc brakes, and a potential for speed enhancement to . Braking systems include regenerative brakes, loco disc brakes, automatic train air brakes, and a charged spring parking brake. On 3 July 2014, a WAP-5 set an Indian speed record by hauling a train from Delhi to Agra within 90 minutes at a speed of . The Gatimaan Express and Bhopal Shatabdi trains hauled by WAP-5 locomotives travel at and respectively in the New Delhi - Agra Cantt s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Loco Shed, Ghaziabad
Electric Loco Shed, Ghaziabad is a motive power depot performing locomotive maintenance and repair facility for electric locomotives of the Indian Railways, located at of the Northern Railway zone in Uttar Pradesh, India. It is one of the two electric locomotive sheds of the Northern Railway, the others being at Ludhiana (LDH) . History Steam locomotive sheds used to exist at Ghaziabad until the late 1960s. After Northern Railway set a deadline to eliminate all steam locomotive operations by 1990, a push was given towards establishing electric locomotion as the primary motive power, and the Steam locomotive sheds was decommissioned. To meet the needs of exponentially increasing rail traffic on the new continuous broad-gauge lines from Delhi to rest of India with the completion of gauge conversion, the Ghaziabad was selected by Indian railways for a new electric locomotive shed. New Electric locomotive shed was inaugurated in the late 1976s with WAM-4 which stayed until late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Loco Shed, Vadodara
Electric Loco Shed, Vadodara is an electric engine shed located in Vadodara, in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is located to south of Vadodara railway station, it falls under the Vadodara railway division of Western Railway. It is the largest of locomotive sheds in the Western Railway zone. History It was established in the 1970s specifically to home dual-power locos. It holds more than 50 WAG-5 class locomotives. It was an AC electric trip shed to house locos coming from other sheds and an AC/DC dual loco trip shed which houses WCAM class locomotives from Valsad shed and which allows locomotive changes at Vadodara because the trains which were coming from New Delhi mainline are AC Locomotives and the trains going to Mumbai need AC/DC Loco. Post AC conversion of Western Railway, WCAM-1 & WCAM-2/2P fleet transferred to Central Railway's Kalyan Loco Shed. WCAM-1 was gradually condemned and are out of service totally. Livery & markings BRC WAP-5 & WAP-7 has two brand adv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
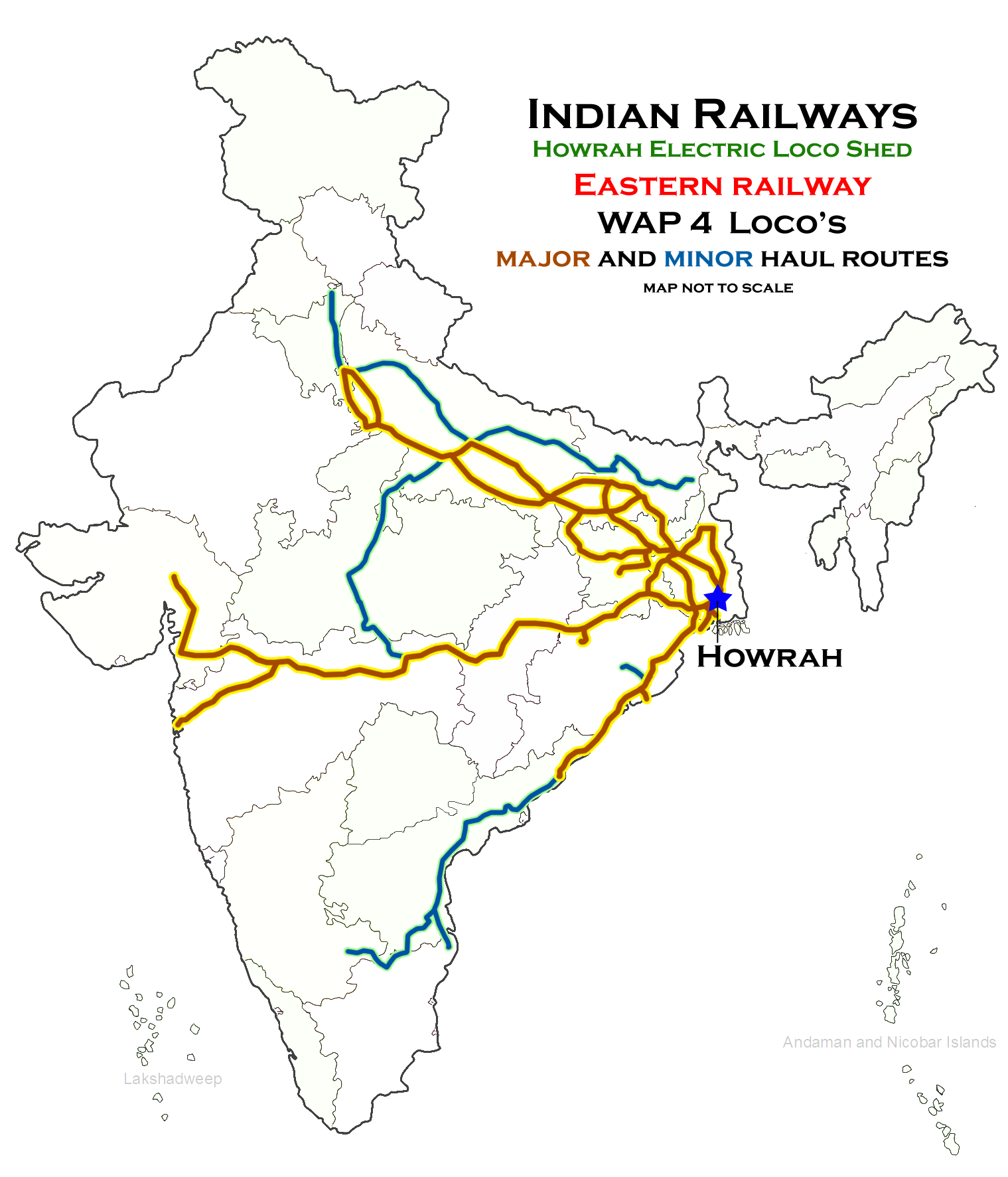
Electric Loco Shed, Howrah
Electric Loco Shed, Howrah is a motive power depot performing locomotive maintenance and repair facility for electric locomotives of the Indian Railways, located at Howrah of the Eastern Railway zone in West Bengal, India. It is one of the two electric locomotive sheds of the Eastern Railway, the others being at Asansol (ASN). there are 150 locomotives in the shed. History Steam locomotive sheds used to exist at Howrah until the late 1970s. After Eastern Railway set a deadline to eliminate all steam locomotive operations by 1990, a push was given towards establishing electric locomotion as the primary motive power, and the steam locomotive sheds was decommissioned. To meet the needs of exponentially increasing rail traffic on the new continuous broad-gauge lines from Kolkata to rest of India with the completion of gauge conversion, the Howrah was selected by Indian Railways for a new electric locomotive shed. New electric locomotive shed was inaugurated in the late 2001s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chittaranjan Locomotive Works
Chittaranjan Locomotive Works (CLW) is an electric locomotive manufacturer based in India. The works are located at Chittaranjan in the Asansol Sadar subdivision of West Bengal, with an ancillary unit in Dankuni. The main unit is 32 km from Asansol and 237 km from Kolkata. CLW has stores and offices in Kolkata, as well as inspection cells in New Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Bangalore. It is the largest locomotive manufacturer unit in the world, producing 431 locomotives in 2019–20. History In the late 1930s, a committee consisting of M/s Humphries and Shrinivasan was created to consider the economic possibilities of establishing locomotive manufacturing facilities in India. The initial project at Chandmari, east of Kalyani in West Bengal, was found to be unsuitable due to the partition. A new survey led to the present site at Chittaranjan being established, which was approved by the railway board in 1947. A survey of the proposed area began on January 9, 1948; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SBB-CFF-FFS Re 460
The Re 460 (popularly known as the Lok 2000) series are modern four-axle electric locomotives of the Swiss Federal Railways. Upon their entry into service in the early 1990s, they replaced the , Ae 4/7, and series units, and displaced many of the Re 4/4II series into lesser duties. The series was introduced as part of the Rail 2000 project, a massive project to modernise and improve the capacity of Switzerland's railways. While originally designed as a multipurpose locomotive, they are now used for passenger services only, often in conjunction with the IC 2000 double-decker trains (often used to pull InterCity and InterRegio trains in German and French language areas). Their freight role has been assumed by Re 482s. They are maintained at Yverdon. Assignment When SBB was split up on 1 September 1999, Re 460 079–118 were assigned to the freight division, later becoming SBB Cargo. It was seen as an advantage to use all Re 460, which had been designed for 200 km/h, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gatimaan Express
The 12049 / 12050 Gatimaan Express is India's first semi-high speed train that runs between Delhi and Jhansi. It takes 265 minutes (around 4.5 hours) to cover the journey from Hazrat Nizamuddin to Virangana Lakshmibai Junction railway stations with an average speed of . The top operating speed of the Gatimaan Express is up to 160 km/h between Tughlakabad railway station to Bilochpura , which makes it the fastest regularly scheduled train service in India. Trial runs of other trains have been faster, and if the rail infrastructure on Vande Bharat Express routes were to be improved, it could also go as fast as the Gatiman Express. History In October 2014, the railways applied for safety certificate from Commission of Railway Safety to start the service. In June 2015, the train was officially announced. The train was launched on 5 April 2016 and completed its maiden journey between Nizamuddin and Agra Cantt within 100 minutes. But due to low occupancy, Indian Railways ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Economic Times
''The Economic Times'' is an Indian English-language business-focused daily newspaper. It is owned by The Times Group. ''The Economic Times'' began publication in 1961. As of 2012, it is the world's second-most widely read English-language business newspaper, after ''The Wall Street Journal'', with a readership of over 800,000. It is published simultaneously from 14 cities: Mumbai, Bangalore, Delhi, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Ahmedabad, Nagpur, Chandigarh, Pune, Indore, and Bhopal. Its main content is based on the Indian economy, international finance, share prices, prices of commodities as well as other matters related to finance. This newspaper is published by Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. The founding editor of the paper when it was launched in 1961 was P. S. Hariharan. The current editor of ''The Economic Times'' is Bodhisattva Ganguli. ''The Economic Times'' is sold in all major cities in India. Other ventures In June 2009, The Economic Times launched a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zee News
Zee News is an Indian Hindi-language news channel owned by Subhash Chandra's Essel Group. It launched on 27 August 1999 and is the flagship channel of the Zee Media Corporation. The channel has been involved in several controversies and has broadcast fabricated news stories on multiple occasions.List of sources: * * * * * * * * The channel has been subjected to an ongoing criminal defamation case against legislator Mahua Moitra as of March 2020. History Zee Media Corporation Limited (formerly Zee News Ltd.) was founded by Essel Group. and it was incorporated in August 27, 1999 as Zee Sports Ltd. it was a subsidiary of the Zee Telefilms Ltd (later renamed to Zee Entertainment Enterprises).The company was Certificate of incorporation, reincorporated on 27 May 2004, as Zee News Ltd. It was demerged as a separate company of the Essel Group in 2006. In 2013, Zee News Ltd changed its name to Zee Media Corporation Limited. The chairman of the group is Subhash Chandra, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head-end Power
In rail transport, head-end power (HEP), also known as electric train supply (ETS), is the electrical power distribution system on a passenger train. The power source, usually a locomotive (or a generator car) at the front or 'head' of a train, provides the electricity used for heating, lighting, electrical and other 'hotel' needs. The maritime equivalent is hotel electric power. A successful attempt by the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway in October 1881 to light the passenger cars on the London to Brighton route heralded the beginning of using electricity to light trains in the world. History Oil lamps were introduced in 1842 to light trains. Economics drove the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway to replace oil with coal gas lighting in 1870, but a gas cylinder explosion on the train led them to abandon the experiment. Oil-gas lighting was introduced in late 1870. Electrical lighting was introduced in October 1881 by using twelve Swan carbon filament incandescent lamps c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantograph (transport)
A pantograph (or "pan" or "panto") is an apparatus mounted on the roof of an electric train, tram or electric bus to collect power through contact with an overhead line. By contrast, battery electric buses and trains are charged at charging stations. The pantograph is a common type of current collector; typically, a single or double wire is used, with the return current running through the rails. The term stems from the resemblance of some styles to the mechanical pantographs used for copying handwriting and drawings. Invention The pantograph, with a low-friction, replaceable graphite contact strip or "shoe" to minimise lateral stress on the contact wire, first appeared in the late 19th century. Early versions include the bow collector, invented in 1889 by Walter Reichel, chief engineer at Siemens & Halske in Germany, and a flat slide-pantograph first used in 1895 by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad The familiar diamond-shaped roller pantograph was devised and patented b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Railway Zone
The Western Railway (abbreviated WR) is one of the 19 zones of Indian Railways and is among the busiest railway networks in India, headquartered at Mumbai, Maharashtra. The major railway routes of Indian Railways which come under Western Railways are: Mumbai Central–Ratlam, Mumbai Central–Ahmedabad and Palanpur–Ahmedabad. The railway system is divided into six operating divisions: , , , , , and . Vadodara railway station, being the junction point for the Ahmedabad–Mumbai route and the Mumbai–Ratlam route towards New Delhi, is the busiest junction station in Western Railways and one of the busiest junctions of Indian Railways too, while Ahmedabad Division earns highest revenue followed by Mumbai Division and Vadodara Division. Surat railway station is one of the busiest railway station in Western Railway in non-junction category where more than 180 trains pass per day. Western Railway General Manager's official bungalow 'Bombarci' (abbreviation of Bombay, Baroda and Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Railway Zone
The Northern Railway (NR) is one of the 19 Railway zones of India and the northernmost zone of the Indian Railways. It is headquartered at Baroda House in New Delhi. History Officially notified as a new railway zone on 14 April 1952, its origin goes back to 3 March 1859. On 14 April 1952, the Northern Railway zone was created by merging Jodhpur Railway, Bikaner Railway, Eastern Punjab Railway and three divisions of the East Indian Railway north-west of Mughalsarai (Uttar Pradesh). On 3 March 1859, Allahabad– Kanpur, the first passenger railway line in North India was opened, which falls under Northern Railway zone. In 1864, a broad-gauge track from Calcutta to Delhi was laid. In 1864, the railway line between Old Delhi and Meerut City railway station was constructed. Meerut Cantt railway station was established by British India government around 1865 after the sepoy mutiny of 1857. In 1866, through trains started running on the East Indian Railway Company's H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |