|
WAP-4
The Indian locomotive class WAP-4 is a class of 25 kV AC electric locomotives that was developed in 1993 by Chittaranjan Locomotive Works for Indian Railways. The model name stands for broad gauge (W), AC Current (A), Passenger traffic (P) engine, 4th generation (4). They entered service in late 1994. A total of 778 WAP-4 were built at CLW between 1993 and 2015, which made them the most numerous class of mainline electric passenger locomotive until the WAP-7. The WAP-4 is one of the most successful locomotives of Indian Railways serving both passenger and freight trains for over 28 years. This class provided the basic design for other locomotives like the WAP-6 . Despite the introduction of more modern types of locomotives like WAP-7, a significant number are still in use, both in mainline duties. Production of this class was halted in December 2015 with locomotive number 25051 being the last unit to be rolled out. As of September 2022, all locomotives except those lost in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
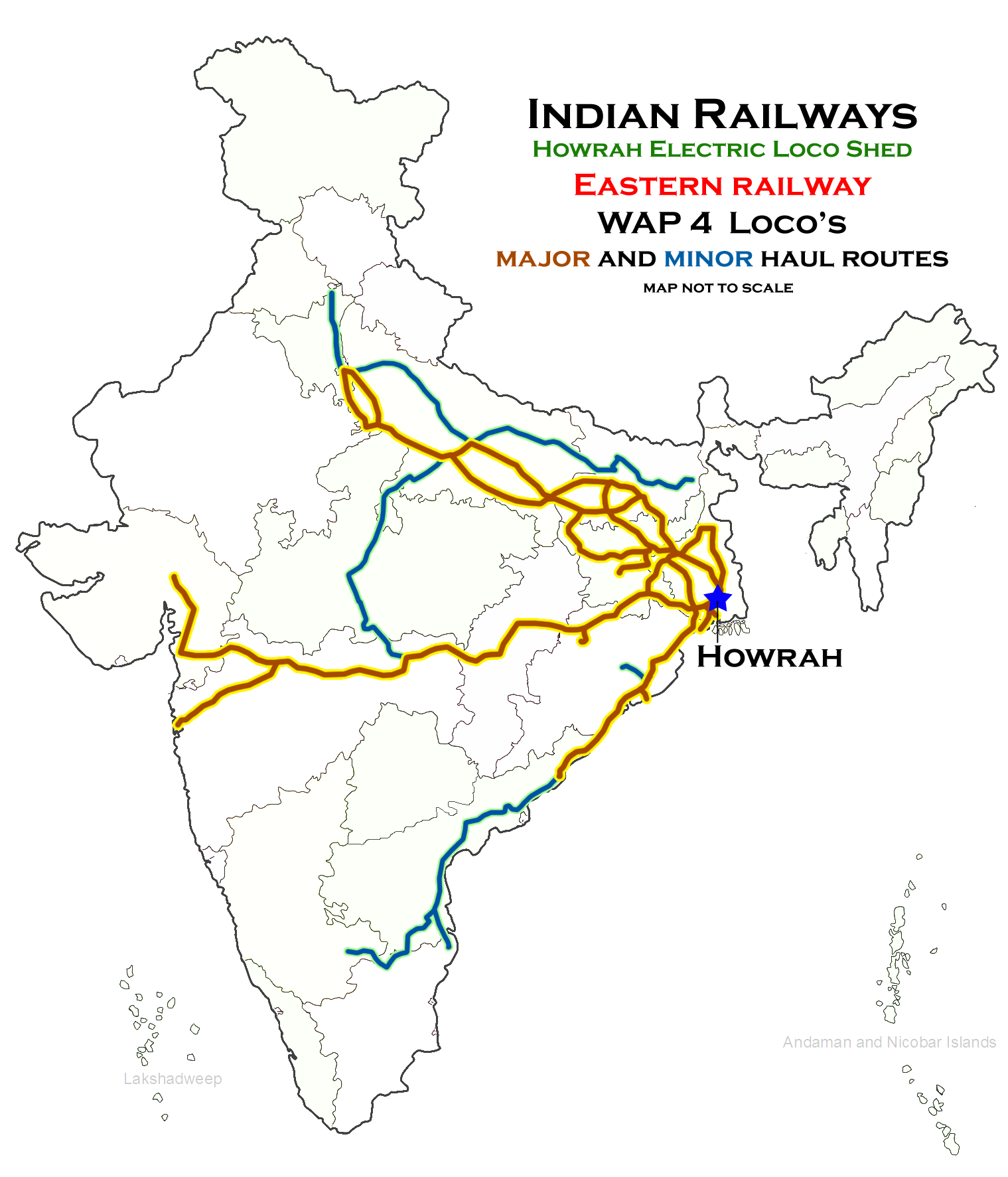
Electric Loco Shed, Howrah
Electric Loco Shed, Howrah is a motive power depot performing locomotive maintenance and repair facility for electric locomotives of the Indian Railways, located at Howrah of the Eastern Railway zone in West Bengal, India. It is one of the two electric locomotive sheds of the Eastern Railway, the others being at Asansol (ASN). there are 150 locomotives in the shed. History Steam locomotive sheds used to exist at Howrah until the late 1970s. After Eastern Railway set a deadline to eliminate all steam locomotive operations by 1990, a push was given towards establishing electric locomotion as the primary motive power, and the steam locomotive sheds was decommissioned. To meet the needs of exponentially increasing rail traffic on the new continuous broad-gauge lines from Kolkata to rest of India with the completion of gauge conversion, the Howrah was selected by Indian Railways for a new electric locomotive shed. New electric locomotive shed was inaugurated in the late 2001s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Loco Shed, Asansol
Electric Loco Shed, Asansol is a motive power depot performing locomotive maintenance and repair facility for electric locomotives of the Indian Railways, located at Asansol of the Eastern Railway zone in West Bengal, India. It is one of the two electric locomotive sheds of the Eastern Railway, the others being at Howrah (HWH). As of November,2022, there are 142 locomotives in the shed. History Steam locomotive sheds used to exist at Asansol (Howrah) until the late 1970s. After Eastern Railway set a deadline to eliminate all steam locomotive operations by 1990, a push was given towards establishing electric locomotion as the primary motive power, and the Steam locomotive sheds was decommissioned. To meet the needs of exponentially increasing rail traffic on the new continuous broad-gauge lines from kolkata to rest of India with the completion of gauge conversion, the Asansol was selected by Indian railways for a new electric locomotive shed. Asansol shed was started in May 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Locomotive Class WAP-6
The Indian locomotive class WAP-6 is a class of 25 kV AC electric locomotives that was developed in the mid 1990s by Chittaranjan Locomotive Works for Indian Railways. The model name stands for broad gauge (W), AC Current (A), Passenger traffic (P), 6th generation (6) locomotive. They entered service in April 1996. A total of 17 WAP-6 units were built at CLW between 1995 and 1998. The WAP-6 were intended to be the faster variant of the successful WAP-4, but failed trials and were restricted to a top speed of 105km/h. Now all units have been converted to WAP-4 specifications. All were homed at Asansol (ASN) shed but after conversion reallocated to Howrah (HWH) shed. History This class was actually variant of the WAP-4 design where Co-Co Flexicoil Mark 1 cast bogies of the usual WAP4 was replaced by Fabricated Flexicoil Mark IV bogies. All other specifications were same as WAP4. WAP-1 unit no. 22212 was the first to be rebuilt into a WAP-6. It was provided with Flexicoil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Locomotive Class WAP-1
The Indian locomotive class WAP-1 is a class of 25 kV AC electric locomotives that was developed in 1980 by Chittaranjan Locomotive Works for Indian Railways. The model name stands for broad gauge (W), AC Current (A), Passenger traffic (P) engine, 1st generation (1). They entered service in late 1981. A total of 65 WAP-1 were built at CLW between 1980 and 1996, which made them the most numerous class of mainline electric passenger locomotive until its successor, the WAP-4. The WAP-1 is India's first dedicated electric passenger locomotive of Indian Railways serving passenger trains for over 42 years. This class provided the basic design for a number of other locomotives like WAP-3 and WAP-4 models. However, with the advent of new 3-phase locomotives like WAP-5 and WAP-7, the WAP-1 locomotives were relegated to hauling smaller express and passenger trains and now the aging fleet the WAP-1 locomotives are being slowly withdrawn from mainline duties and scrapped. As of June 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Loco Shed, Bhusawal
Electric Loco Shed, Bhusawal is a motive power depot performing locomotive maintenance and repair facility for electric locomotives of the Indian Railways, located at Bhusawal of the Central Railway in Maharashtra, India. It is one of the three electric locomotive sheds of the Central Railway, the others being at Kalyan (KYN) and Ajni. As of 1 August 2020 there are 203 locomotives in the shed. History Steam locomotive sheds used to exist at Bhusawal until the late 1960s. Bhusawal used to be the largest steam shed (after World War II). After Central Railway set a deadline to eliminate all steam locomotive operations by 1990, a push was given towards establishing electric locomotion as the primary motive power, and the Steam locomotive sheds was decommissioned. To meet the needs of exponentially increasing rail traffic on the new continuous broad-gauge lines from Delhi to rest of India with the completion of gauge conversion, the Bhusawal was selected by Indian railways for a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Loco Shed, Samastipur
Diesel & Electric Loco Shed, Samastipur is an engine shed located in Samastipur, in the Indian state of Bihar. Located east of , it falls under the Samastipur railway division. It is the smallest of the three locomotive sheds in the East Central Railway zone. It is exceeded by and , the two largest in the country. History The Railway Board sanctioned construction of Diesel Loco Shed, Samastipur in the year 1996–97. Construction began in 1999. The initial holding capacity was 20 locomotives, which were transferred from the Diesel Loco shed, Gonda. Continuation Major and minor maintenance schedules of locomotives are carried out. The shed is ISO 9001:2000, ISO 14001:2004 and OHSAS 18001:2007 certified as or 2009. The shed is divided into Light Schedule Repair Section, Heavy Schedule Repair Section, Heavy Repair (Mechanical), Heavy Repair (Electrical), Bogie Section, Machine Shop and Training Centre. Locomotives References External links * Central Railway - O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughalsarai Junction Railway Station
Mughalsarai Junction, officially known as Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Junction, (station code: DDU, formerly MGS) is a railway station in the town of Mughalsarai in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The station contains the largest railway marshaling yard in Asia. Mughalsarai yard cater to around 450–500 trains in a month. All trains including premium category east bound Rajdhani trains and Duronto trains halt (makes it unique in entire Indian Railway Network; which distinguishes it from other major railway stations like Prayagraj junction, Bhopal junction, Agra Cantt, Gwalior junction, Kharagpur, Nagpur etc.) at this station. Major installations in Mughalsarai include electric locomotive shed holding 147 locomotives, diesel locomotive shed holding 53 locomotives, wagon ROH shed and a 169-bed divisional hospital. History The East Indian Railway Company started connecting Delhi and Howrah from the mid nineteenth century. This was the second biggest railway station after Gadd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erode
Erode () is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Erode is the seventh largest urban agglomeration in the state, after Chennai, Coimbatore, Madurai, Tiruchirapalli, Tiruppur and Salem. It is also the administrative headquarters of the Erode district. Administered by a city municipal corporation since 2008, Erode is a part of Erode Lok Sabha constituency that elects its member of parliament. Located on the banks of River Kaveri, it is situated centrally on South Indian Peninsula, about southwest of its state capital Chennai, south of Bengaluru, east of Coimbatore and east of Kochi. Erode is an agricultural, textile and a BPO hub and among the largest producers of turmeric, hand-loom and knitwear, and food products. History Etymology of Erode might have its origin in the Tamil phrase ''Eeru Odai'' meaning ''two streams'' based on presence of two water courses of Perumpallam and Pichaikaranpallam Canal. Alternatively, it might have been derived from Tamil phras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arakkonam Junction Railway Station
Arakkonam () is a railway town and suburb of Chennai within Chennai Metropolitan Area limit, in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, with a population of 78,395 per the census 2011. It is in the newly created Ranipet district, about from Ranipet headquarters and about from the state capital of Chennai. On October 2022 Arakkonam is a part of Chennai Metropolitan Area. Arakkonam is one of the hottest towns in India, where the temperature can exceed 43 °C (110 °F) for several peak days in summer. The name 'Arakkonam' was derived from the word "Arunthamizhkundram" also later called "Aarukonam", meaning 'hexagon' which connects six important places around. History The ancient name of the town was "''Arumthamizh kundram''" ("''Arumtamil kunram''") which is believed to have been derived from the Tamil words ''aaru konam'' meaning "six angles" or hexagon, based on the fact that six important places exist on the town's six sides, namely Kanchipuram, Thakkolam, Manavur, Thiruvalan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Locomotive Class WAP-5
The Indian locomotive class WAP-5 is the name of a class of "High Speed" electric locomotives produced and used by Indian Railways. The first 10 locomotives were imported from ABB in Switzerland in 1995. They are supposed to be a variant of the Swiss Lok 2000 (Design concept) and German DB Class 120 (mechanical chassis). One of the notable features of WAP-5 is regenerative braking. Other notable features of this loco are the provision of taps from the main loco transformer for hotel load, pantry loads, flexible gear coupling, wheel-mounted disc brakes, and a potential for speed enhancement to . Braking systems include regenerative brakes, loco disc brakes, automatic train air brakes, and a charged spring parking brake. On 3 July 2014, a WAP-5 set an Indian speed record by hauling a train from Delhi to Agra within 90 minutes at a speed of . The Gatimaan Express and Bhopal Shatabdi trains hauled by WAP-5 locomotives travel at and respectively in the New Delhi - Agra Cantt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Central Railway Zone
The East Central Railway (abbreviated ECR) is one of the 19 railway zones in India. It is headquartered at Hajipur and comprises Sonpur, Samastipur, Danapur, Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhyaya, and Dhanbad divisions. History First set up on 8 September 1996 with headquarters at Hajipur, Bihar, East Central Railway became operational on 1 October 2002 by carving out areas from Eastern and North Eastern Railway zones currently consists of the divisions viz. Dhanbad, Danapur, Mughalsarai of Eastern Railway and Sonpur and Samastipur of North Eastern Railway. The last 13 years of its existence has been full of challenges and every obstacle was dealt in a dedicated manner despite constraints of work force and infrastructure. ECR, has a vast network of 5402.693 track kilometers and 3707.988 route kilometers encompassing the states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh. Out of the route, have been electrified. ECR has been lifeline for the people in its expanse and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Railway Zone
The Eastern Railway (abbreviated ER) is among the 19 zones of the Indian Railways. Its headquarters is at Fairley Place, Kolkata and comprises four divisions: , , , and . Each division is headed by a Divisional Railway Manager (DRM). The name of the division denotes the name of the city where the divisional headquarters is located. Eastern Railway oversees the largest and second largest rail complexes in the country, Howrah Junction and Sealdah railway station, and also contains the highest number of A1 and A Category Stations like , , , , Kolkata, , Barddhaman, Rampurhat Junction, , Jasidih, Bandel and Naihati. Eastern Railways operates India's oldest train, Kalka Mail. History The East Indian Railway (EIR) Company was incorporated in 1845 to connect eastern India with Delhi. The first train ran here between and on 15 August 1854. The train left Howrah station at 8:30 a.m. and reached Hooghly in 91 minutes. The management of the East Indian Railway was taken over by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |