|
Wuwei Bronze Cannon
The Wuwei Bronze Cannon (武威銅火炮 — Wǔwēi tóng huǒpào) or Xi Xia Bronze cannon (西夏铜火炮 — Xīxià tóng huǒpào)Kelly DeVries, John France, Clifford J. Rogers (October 2015). Journal of Medieval Military History'. 13: 251. was discovered in 1980 and is probably the oldest and largest cannon dated to the 13th century. This 100 centimeter long, 108 kilogram bronze cannon was discovered in a cellar in Wuwei, Gansu Province. It bears no inscription, but has been dated by historians to the late Western Xia period between 1214 and 1227 through contextual evidence. The gun contained an iron ball about nine centimeters in diameter, which is smaller than the muzzle diameter at twelve centimeters, and 0.1 kilograms of gunpowder in it when discovered, meaning that the projectile might have been another co-viative. Ben Sinvany and Dang Shoushan believe that the ball used to be much larger prior to its highly corroded state at the time of discovery. While large in siz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuwei, Gansu
Wuwei () is a prefecture-level city in northwest central Gansu province. In the north it borders Inner Mongolia, in the southwest, Qinghai. Its central location between three western capitals, Lanzhou, Xining, and Yinchuan makes it an important business and transportation hub for the area. Because of its position along the Hexi Corridor, historically the only route from central China to western China and the rest of Central Asia, many major railroads and national highways pass through Wuwei. History In ancient times, Wuwei was called Liangzhou (—the name retained by today's Wuwei's central urban district) and is the eastern terminus of the Hexi Corridor. People began settling here about 5,000 years ago. It was a key link for the Northern Silk Road, and a number of important archaeological finds were uncovered from Wuwei, including ancient copper carts with stone animals. The motifs and types of objects in the Wuwei graves, as well as their earthenware, lacquer, and bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gansu Province
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province. The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibetan and Loess plateaus and borders Mongolia ( Govi-Altai Province), Inner Mongolia and Ningxia to the north, Xinjiang and Qinghai to the west, Sichuan to the south and Shaanxi to the east. The Yellow River passes through the southern part of the province. Part of Gansu's territory is located in the Gobi Desert. The Qilian mountains are located in the south of the Province. Gansu has a population of 26 million, ranking 22nd in China. Its population is mostly Han, along with Hui, Dongxiang and Tibetan minorities. The most common language is Mandarin. Gansu is among the poorest administrative divisions in China, ranking 31st, last place, in GDP per capita as of 2019. The State of Qin originated in what is now southeastern Gansu a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Xia
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia (), officially the Great Xia (), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as ''Mi-nyak''Stein (1972), pp. 70–71. to the Tanguts and Tibetans, was a Tangut-led Buddhist imperial dynasty of China that existed from 1038 to 1227. At its peak, the dynasty ruled over the modern-day northwestern Chinese provinces of Ningxia, Gansu, eastern Qinghai, northern Shaanxi, northeastern Xinjiang, and southwest Inner Mongolia, and southernmost Outer Mongolia, measuring about . Its capital was Xingqing (modern Yinchuan), until its destruction by the Mongols in 1227. Most of its written records and architecture were destroyed, so the founders and history of the empire remained obscure until 20th-century research in China and the West. The Western Xia occupied the area around the Hexi Corridor, a stretch of the Silk Road, the most important trade route between northern China and Central Asia. They made significant achievements in literature, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongols, Mongol-led Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the Mongol Empire, its division. It was established by Kublai Khan, Kublai, the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan had been enthroned with the Han Chinese, Han-style title of Emperor of China, Emperor in 1206 and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day Northern and southern China, northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in the Battle of Yamen. His realm was, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanadu Gun
The oldest extant gun bearing a date of production is the Xanadu Gun, so called because it was discovered in the ruins of Xanadu (Shangdu), the summer palace of the Yuan dynasty in Inner Mongolia, China. The Xanadu Gun is 34.7 cm in length and weighs 6.21 kg, its muzzle is flared outwards, slightly bowl-shape, and called by Chinese as 碗口铳 ( Wǎn kǒu chòng). Its dating is based on archaeological context and a straightforward inscription containing an era name and year that correspond with the Gregorian Calendar at 1298. Not only does the inscription contain the era name and date, it also includes a serial number and manufacturing information which suggests that gun production had already become systematized, or at least become a somewhat standardized affair by the time of its fabrication. The design of the gun includes axial holes in its rear which some speculate could have been used in a mounting mechanism. Like most early guns with the possible exception of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heilongjiang Hand Cannon
The Heilongjiang hand cannon or hand-gun is a bronze hand cannon manufactured no later than 1288 and is the world's oldest confirmed surviving firearm. It weighs 3.55 kg (7.83 pounds) and is 34 centimeters (13.4 inches) long. The Heilongjiang hand cannon was excavated during the 1970s in Banlachengzi, a village in Acheng District, Heilongjiang province, China. It was found alongside other bronze artifacts made in the style of the Jurchen Jin Dynasty (12th–13th century). The hand cannon was probably used in battles fought nearby in Banlachengzi in 1287 and 1288. The ''History of Yuan'' states that a Jurchen commander by the name of Li Ting led a group of soldiers equipped with hand cannons into a military camp in 1288, as part of an anti-rebellion campaign for the Yuan dynasty. The cannon currently resides at the Heilongjiang Provincial Museum in Harbin, China. Description The Heilongjiang hand cannon is long without a handle and weighs . The diameter of the interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Needham
Noel Joseph Terence Montgomery Needham (; 9 December 1900 – 24 March 1995) was a British biochemist, historian of science and sinologist known for his scientific research and writing on the history of Chinese science and technology, initiating publication of the multivolume '' Science and Civilisation in China''. He was elected a fellow of the Royal Society in 1941 and a fellow of the British Academy in 1971. In 1992, Queen Elizabeth II conferred on him the Companionship of Honour, and the Royal Society noted he was the only living person to hold these three titles. Early life Needham's father, Joseph was a doctor, and his mother, Alicia Adelaïde, née Montgomery (1863–1945), was a music composer from Oldcastle, County Meath, Ireland. His father, born in East London, then a poor section of town, rose to became a Harley Street physician, but frequently battled with Needham's mother. The young Needham often mediated. In his early teens, he was taken to hear the Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hu Dun Pao
''Hu dun pao'' (虎蹲砲) is the name of two different missile weapons in Chinese history. In the Song dynasty (960–1279), it was a trebuchet and its name is translated into English as Crouching Tiger Trebuchet; in the Ming dynasty (1368–1644), the name was given to a type of bombard and it is known in English as Crouching Tiger Cannon. Trebuchet According to the Song dynasty military compendium ''Wujing Zongyao'' (published 1044), the ''hu dun pao'' is depicted as a traction trebuchet with a triangular frame. It is operated by a dedicated corps of 70 haulers, who took turns pulling the ropes attached to the trebutchet arm to send the projectile, a stone or bomb, into flight. It has a range of . The '' Annales ianuenses'', the official history of Genoa, carries drawings of ''trabuchium'', a counterweighted trebuchet with triangular supporting trusses, that Sinologist Joseph Needham considers to be derived from or related to the Chinese "Crouching Tiger Trebuchet". Similar tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huochong
''Huochong'' () was the Chinese name for hand cannons. The oldest confirmed metal ''huochong'', also the first cannon, is a bronze hand cannon bearing an inscription dating it to 1298 (see Xanadu Gun, Xanadu gun). By the time of the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644) two types of ''huochong'' were in use. One was a hand held version with a wooden shaft known as a '' shouchong'' () whilst the larger ''Wankouchong'' ( — bowl-mouthed cannon) or ''Zhankouchong'' ( — cup-mouthed cannon) rested on a supporting wooden frame.''History of Ming'' Army Records Chapter Four It was invented presumably as an advance in warfare, a new way to fight. Gallery File:上都火銃.jpg, The Xanadu gun, 1298, is an example of a Wankouchong () File:Bronze cannon of 1332.jpg, Bronze cannon with inscription dated the 3rd year of the Zhiyuan era (1332) of the Yuan Dynasty (1271–1368); it was discovered at the Yunju Temple of Fangshan District, Beijing in 1935. It is similar to Xanadu gun. File:Ming 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunpowder Weapons In The Song Dynasty
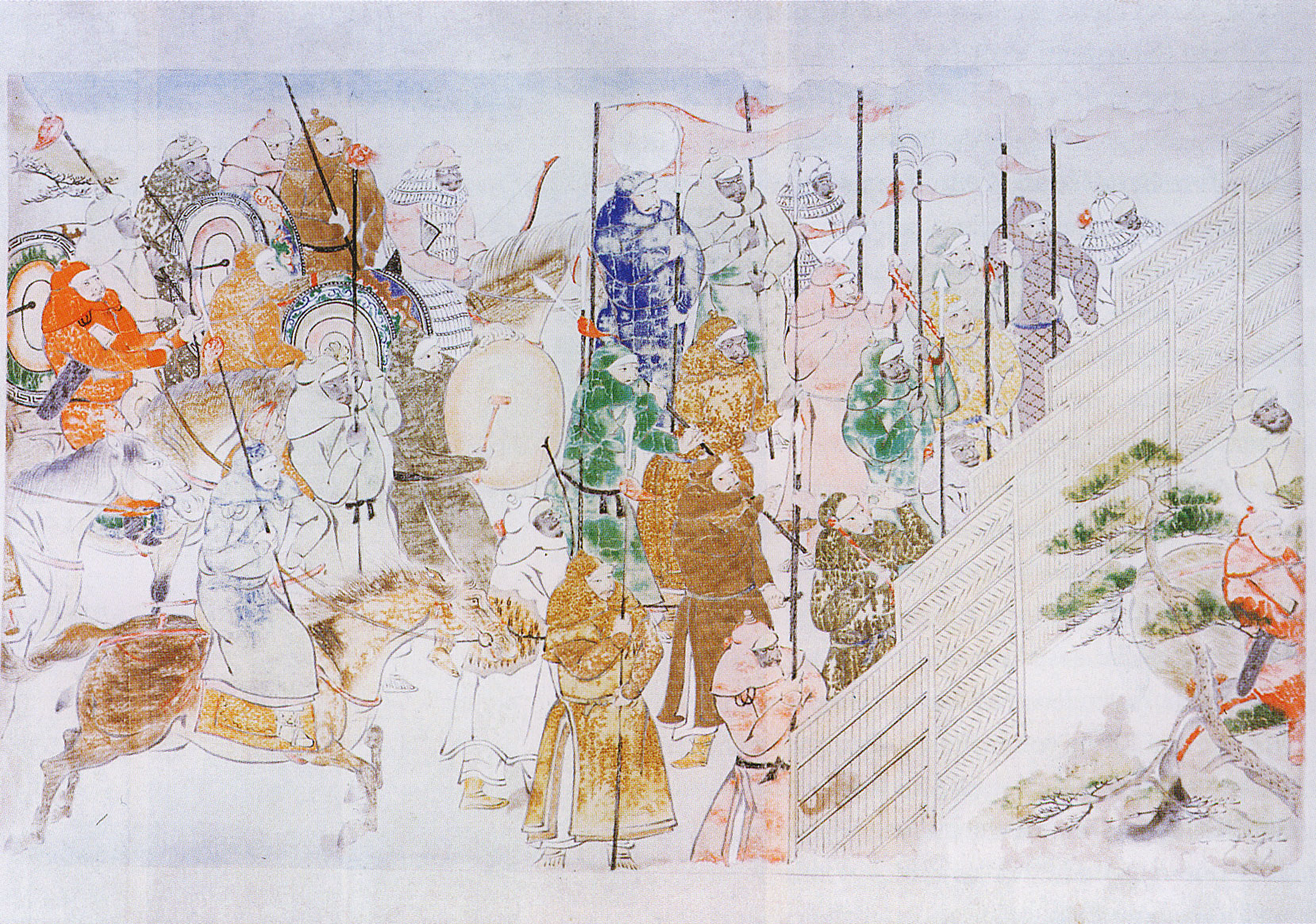
Gunpowder weapons in the Song dynasty included fire arrows, gunpowder lit flamethrowers, soft shell bombs, hard shell iron bombs, fire lances, and possibly early cannons known as "eruptors". The eruptors, such as the "multiple bullets magazine eruptors" (bǎi-zi lián zhū pào, 百子連珠炮), consisting of a tube of bronze or cast iron that was filled with about 100 lead balls,Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, 263-364. and the "flying-cloud thunderclap eruptor" (fēi yún pī-lì pào, 飛雲霹靂炮), were early cast-iron proto-cannons that did not include single shots that occluded the barrel (thus called "co-viative" weapons). The use of proto-cannon, and other gunpowder weapons, enabled the Song dynasty to ward off its generally militarily superior enemies—the Khitan led Liao, Tangut led Western Xia, and Jurchen led Jin—until its final collapse under the onslaught of the Mongol forces of Kublai Khan and his Yuan dynasty in the late 13th century. History Fire arrow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Of The Yuan Dynasty
The military of the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368) were the armed forces of the Yuan dynasty, a fragment of the Mongol Empire created by Kublai Khan in China. The forces of the Yuan were based on the troops that were loyal to Kublai after the Division of the Mongol Empire in 1260. At first this ''Tamma'', a frontier army drawn from all Mongol tribes for conquest of China, had no central organisation but was rather a loose collection of local warlords and Mongol princely armies. However the army was gradually reformed by Kublai Khan into a more systematic force. Army Organisation Unlike previous Chinese dynasties that strictly separated military and civilian power, the Yuan administration of military and civil affairs tended to overlap, as a result of traditional Mongol favour for military matters. This was harshly criticised by the Chinese scholar officials at the time. Military officers were allowed to pass on their positions to their sons or grandsons after death, retirement or some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |