|
Wurfbainia Villosa
''Wurfbainia villosa'', also known by its basionym ''Amomum villosum'', (Chinese: (Chinese: 砂仁; pinyin: shārén) is a plant in the ginger family that is grown throughout Southeast Asia and in South China. Similar to cardamom, the plant is cultivated for its fruits, which dry into pods when mature and contain strongly aromatic seeds. ''W. villosa'' is an evergreen plant in the ginger family, grow in the shade of the tree, 1.5 to 3.0 m high, whose branches and leaves are similar to ginger's. ''W. villosa'' has a characteristic that flowers spread on the ground can bear fruit while flowers on the branches can not. Its flowers bloom in March and April and are the colour of white jade. Use in cuisine The ''Wurfbainia villosa'' seed is used as a spice, including some versions of five-spice powder in Chinese cooking. The pods are used in Chinese cuisine for flavour. Since the Tang dynasty, many ancient books, such as the Compendium of Materia Medica, say ''W. villosa'' tastes ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basionym
In the scientific name of organisms, basionym or basyonym means the original name on which a new name is based; the author citation of the new name should include the authors of the basionym in parentheses. The term "basionym" is used in both botany and zoology. In zoology, alternate terms such as original combination or protonym are sometimes used instead. Bacteriology uses a similar term, basonym, spelled without an ''i''. Although "basionym" and "protonym" are often used interchangeably, they have slightly different technical definitions. A basionym is the ''correct'' spelling of the original name (according to the applicable nomenclature rules), while a protonym is the ''original'' spelling of the original name. These are typically the same, but in rare cases may differ. Use in botany The term "basionym" is used in botany only for the circumstances where a previous name exists with a useful description, and the '' International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compendium Of Materia Medica
The ''Bencao gangmu'', known in English as the ''Compendium of Materia Medica'' or ''Great Pharmacopoeia'', is an encyclopedic gathering of medicine, natural history, and Chinese herbology compiled and edited by Li Shizhen and published in the late 16th century, during the Ming dynasty. Its first draft was completed in 1578 and printed in Nanjing in 1596. The ''Compendium'' lists the '' materia medica'' of traditional Chinese medicine known at the time, including plants, animals, and minerals that were believed to have medicinal properties. Over the centuries it was reprinted, translated, and cited widely. In the twentieth century was adopted as a basis for Traditional Chinese Medicine. Li compiled his entries not only from hundreds of earlier works in the ''bencao'' medical tradition, but from literary and historical texts. He reasoned that a poem might have better value that a medical work and that a tale of the strange could illustrate a drug's effects. Name The title, tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wurfbainia
''Wurfbainia''Giseke PD (1792) ''Prael. Ord. Nat. Pl.'' 199, 206. is an Asian genus of plants in the family Zingiberaceae. Species have been recorded from the Himalayas, S. China, Indo-China and W. & Central Malesia. It has previously been placed as a synonym of ''Amomum''. Species ''Plants of the World Online'' currently includes: * '' Wurfbainia aromatica'' (Roxb.) Skornick. & A.D.Poulsen * '' Wurfbainia bicorniculata'' (K.Schum.) Skornick. & A.D.Poulsen * '' Wurfbainia biflora'' (Jack) Skornick. & A.D.Poulsen * '' Wurfbainia blumeana'' (Valeton) Skornick. & A.D.Poulsen * '' Wurfbainia compacta'' (Sol. ex Maton) Skornick. & A.D.Poulsen * '' Wurfbainia elegans'' (Ridl.) Skornick. & A.D.Poulsen * '' Wurfbainia glabrifolia'' (Lamxay & M.F.Newman) Skornick. & A.D.Poulsen * '' Wurfbainia gracilis'' (Blume) Skornick. & A.D.Poulsen * '' Wurfbainia graminea'' (Wall. ex Baker) Skornick. & A.D.Poulsen * '' Wurfbainia hedyosma'' (I.M.Turner) Skornick. & A.D.Poulsen * '' Wurfbainia jain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
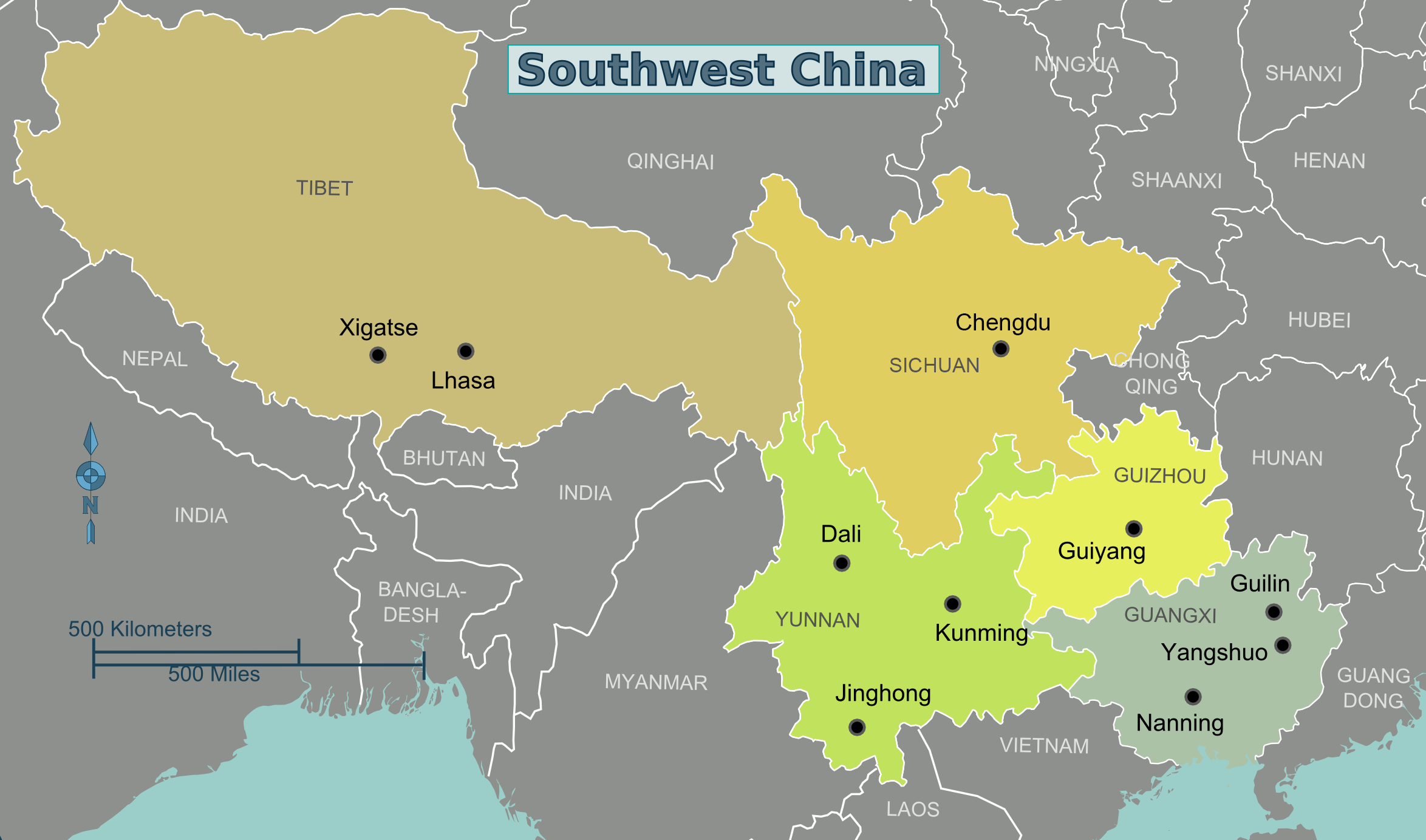
Southwest China
Southwest China () is a region in the south of the People's Republic of China. Geography Southwest China is a rugged and mountainous region, transitioning between the Tibetan Plateau to the west and the Chinese coastal hills (东南丘陵) and plains to the east. Key geographic features in the region include the Hengduan Mountains in the west, the Sichuan Basin in the northeast, and the karstic Yungui Plateau in the east. The majority of the region is drained by the Yangtze River which forms the Three Gorges in the northeast of the region. The narrowest concept of Southwest China consists of Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, and Guizhou, while wider definitions often include Guangxi and western portions of Hunan. The official government definition of Southwest China includes the core provinces of Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, and Guizhou, in addition to the Tibet Autonomous Region. History Portions of Southwest China were incorporated in the 3nd century BCE into the Qin dynast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) across a total area of about , Guangdong is the most populous province of China and the 15th-largest by area as well as the second-most populous country subdivision in the world (after Uttar Pradesh in India). Its economy is larger than that of any other province in the nation and the fifth largest sub-national economy in the world with a GDP (nominal) of 1.95 trillion USD (12.4 trillion CNY) in 2021. The Pearl River Delta Economic Zone, a Chinese megalopolis, is a core for high technology, manufacturing and foreign trade. Located in this zone are two of the four top Chinese cities and the top two Chinese prefecture-level cities by GDP; Guangzhou, the capital of the province, and Shenzhen, the first special economic zone in the count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in Southwest China, the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces of Guizhou, Sichuan, autonomous regions of Guangxi, and Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet as well as Southeast Asian countries: Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar. Yunnan is China's fourth least developed province based on disposable income per capita in 2014. Yunnan is situated in a mountainous area, with high elevations in the northwest and low elevations in the southeast. Most of the population lives in the eastern part of the province. In the west, the altitude can vary from the mountain peaks to river valleys by as much as . Yunnan is rich in natural resources and has the largest diversity of plant life in China. Of the approximately 30,000 species of Vascular plant, higher plants in China, Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubber Tree
''Hevea brasiliensis'', the Pará rubber tree, ''sharinga'' tree, seringueira, or most commonly, rubber tree or rubber plant, is a flowering plant belonging to the spurge family Euphorbiaceae originally native to the Amazon basin, but is now pantropical in distribution due to introductions. It is the most economically important member of the genus '' Hevea'' because the milky latex extracted from the tree is the primary source of natural rubber. Description ''H. brasiliensis'' is a tall deciduous tree growing to a height of up to in the wild, but cultivated trees are usually much smaller because drawing off the latex restricts the growth of the tree. The trunk is cylindrical and may have a swollen, bottle-shaped base. The bark is some shade of brown, and the inner bark oozes latex when damaged. The leaves have three leaflets and are spirally arranged. The inflorescence include separate male and female flowers. The flowers are pungent, creamy-yellow and have no petals. The fru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slash-and-burn
Slash-and-burn agriculture is a farming method that involves the cutting and burning of plants in a forest or woodland to create a field called a swidden. The method begins by cutting down the trees and woody plants in an area. The downed vegetation, or "slash", is then left to dry, usually right before the rainiest part of the year. Then, the biomass is burned, resulting in a nutrient-rich layer of ash which makes the soil fertile, as well as temporarily eliminating weed and pest species. After about three to five years, the plot's productivity decreases due to depletion of nutrients along with weed and pest invasion, causing the farmers to abandon the field and move to a new area. The time it takes for a swidden to recover depends on the location and can be as little as five years to more than twenty years, after which the plot can be slashed and burned again, repeating the cycle. In Bangladesh and India, the practice is known as jhum or jhoom. Slash-and-burn is a type of shif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications may include dehydration. The cause of dysentery is usually the bacteria from genus ''Shigella'', in which case it is known as shigellosis, or the amoeba ''Entamoeba histolytica''; then it is called amoebiasis. Other causes may include certain chemicals, other bacteria, other protozoa, or parasitic worms. It may spread between people. Risk factors include contamination of food and water with feces due to poor sanitation. The underlying mechanism involves inflammation of the intestine, especially of the colon. Efforts to prevent dysentery include hand washing and food safety measures while traveling in areas of high risk. While the condition generally resolves on its own within a week, drinking sufficient fluids such as oral rehydration s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Zhou dynasty (690–705), Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Language
Chinese (, especially when referring to written Chinese) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and many minority ethnic groups in Greater China. About 1.3 billion people (or approximately 16% of the world's population) speak a variety of Chinese as their first language. Chinese languages form the Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages family. The spoken varieties of Chinese are usually considered by native speakers to be variants of a single language. However, their lack of mutual intelligibility means they are sometimes considered separate languages in a family. Investigation of the historical relationships among the varieties of Chinese is ongoing. Currently, most classifications posit 7 to 13 main regional groups based on phonetic developments from Middle Chinese, of which the most spoken by far is Mandarin (with about 800 million speakers, or 66%), followed by Min (75 million, e.g. Southern Min), Wu (74 million, e.g. Shangh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Cuisine
Chinese cuisine encompasses the numerous cuisines originating from China, as well as overseas cuisines created by the Chinese diaspora. Because of the Chinese diaspora and historical power of the country, Chinese cuisine has influenced many other cuisines in Asia and beyond, with modifications made to cater to local palates. Chinese food staples such as rice, soy sauce, noodles, tea, chili oil, and tofu, and utensils such as chopsticks and the wok, can now be found worldwide. The preferences for seasoning and cooking techniques of Chinese provinces depend on differences in historical background and ethnic groups. Geographic features including mountains, rivers, forests, and deserts also have a strong effect on the local available ingredients, considering that the climate of China varies from tropical in the south to subarctic in the northeast. Imperial royal and noble preference also plays a role in the change of Chinese cuisine. Because of imperial expansion and trading, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |