|
Wu Shuang Pu
''Wu Shuang Pu'' () is a book of woodcut prints, first printed in 1694, early on in the Qing dynasty. This book contains the biographies and imagined portraits of 40 notable heroes and heroines from the Han Dynasty to the Song Dynasty, all accompanied by a brief introduction and guided by a related poem in yuefu style. The illustrations from the book were widely distributed and re-used, often as motifs on Chinese porcelain. The original book has a seal what says Nanling, that's why the book is also known as Nanling Wu Shuang Pu. A re-edition of this book from the year 1699 is kept in the National Museum of China. In January 2006, an original hand-painted book of Wu Shuang Pu was sold at the Chongyuan auction house in Shanghai for 2.86 million CNY, some 440,000 Dollar (GBP 320,000). The scholar and philologist Mao Qiling praised the book in the preface, he felt that the prose in this book formed a trinity with the poems and prints. The painter of Wu Shuang Pu is Jin Shi (ķćæÕ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xianfeng Emperor
The Xianfeng Emperor (17 July 1831 ŌĆō 22 August 1861), or by temple name Emperor Wenzong of Qing (), given name Yizhu (), was the eighth Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the seventh Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigned from 1850 to 1861. During his reign, the Qing dynasty experienced several wars and rebellions including the Taiping Rebellion, Nian Rebellion, and Second Opium War (Arrow War). He was the last Chinese emperor to have authoritarian and total executive ruling power. After his death, the Qing government was controlled by Empress Dowager Cixi. Family and early life Yizhu was born in 1831 at the Old Summer Palace, eight kilometres northwest of Beijing. He was from the Manchu Aisin Gioro clan, and was the fourth son of the Daoguang Emperor. His mother was the Noble Consort Quan, of the Manchu Niohuru clan, who was made Empress in 1834, and is known posthumously as Empress Xiaoquancheng. Yizhu was reputed to have an ability in literature and administrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Hongshou
Chen Hongshou (1598ŌĆō1652), formerly romanized as Ch'en Hung-shou, was a Chinese painter of the late Ming dynasty. Life Chen was born in Zhuji, Zhejiang province in 1598, during the Ming dynasty. His courtesy name was Zhanghou (ń½ĀõŠ»), and his pseudonyms were Laolian (ĶĆüĶÄ▓), Fuchi (Õ╝ŚĶ┐¤), Yunmenseng (õ║æķŚ©Õā¦), Huichi (µéöĶ┐¤), Chiheshang (Ķ┐¤ÕÆīÕ░Ü) and Huiseng (µéöÕā¦).Cihai: Page 431. He once trained under Lan Ying, and was skilled in painting peculiar human figures, landscapes, flower-and-bird. He utilized plump, profound brushwork and precise color, creating a unique style. He always painted illustrations and made tapestry portraits. His two masterpieces, ''Shui Hu Ye Zi'' (µ░┤µĄÆÕÅČÕŁÉ) and ''Bo Gu Ye Zi'', were the rare examples among the Ming and the Qing dynasties. He was very famous at that time, called "Chen in South and Cui in North", together with Cui Zizhong. He also was skilled in calligraphy, poetry and prose. Works His works are kept in museums and gall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dong Xian
Dong Xian ( ĶæŻ Ķ│ó) (23 BCE(?) – 1 BCE) was a Han Dynasty politician who quickly rose from obscurity as a minor official to being the most powerful official in the imperial administration of Emperor Ai within a span of a few years, and he had both the interest and the complete trust of the emperor.Hinsch, Bret. (1990) ''Passions of the Cut Sleeve''. University of California Press. Most scholars agree that Dong's quick career advancement came mostly because of his personal relationship with Emperor Ai, very likely a romantic and sexual one, rather than a demonstration of abilities. Both men were married to women, but Emperor Ai, at least, was childless. An idiomatic term for homosexuality in Chinese is ''duanxiu zhi pi'' (µ¢ĘĶó¢õ╣ŗńÖ¢, literally, "passion of the cut sleeve"), derived from an episode involving Dong and Emperor Ai. They often slept together on the same straw mat. One afternoon, after Emperor Ai woke up from a nap, Dong was still sleeping, and Emperor Ai' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sima Qian
Sima Qian (; ; ) was a Chinese historian of the early Han dynasty (206AD220). He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for his ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a general history of China covering more than two thousand years beginning from the rise of the legendary Yellow Emperor and the formation of the first Chinese polity to the reigning sovereign of Sima Qian's time, Emperor Wu of Han. As the first universal history of the world as it was known to the ancient Chinese, the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' served as a model for official history-writing for subsequent Chinese dynasties and the Chinese cultural sphere (Korea, Vietnam, Japan) up until the 20th century. Sima Qian's father Sima Tan first conceived of the ambitious project of writing a complete history of China, but had completed only some preparatory sketches at the time of his death. After inheriting his father's position as court historian in the imperial court, he was determined to fulfill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Su Wu
Su Wu (; 140 BC - 60 BC ) was a Chinese diplomat and politician of the Western Han dynasty. He is known in Chinese history for making the best of his mission into foreign territory. During his mission he was captured and then detained for nineteen years, enduring major hardship at least in the early years of his captivity. Nevertheless, he endured this treatment while remaining faithful to his mission and his homeland. According to Chinese tradition, in the early stages of his captivity, Su Wu was so deprived of food that he only survived in the cold north lands by eating his coverings, then enduring long years of servitude herding sheep, before managing to return home. He was able to return home after deceiving his captors with a story about his having sent a message back to the Western Han dynasty by means of tying a letter on the leg of a wild goose. Su's loyalty to the Western Han is emphasised by the story that during his detainment he married a wife, that he had chil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Qian
Zhang Qian (; died c. 114) was a Chinese official and diplomat who served as an imperial envoy to the world outside of China in the late 2nd century BC during the Han dynasty. He was one of the first official diplomats to bring back valuable information about Central Asia, including the Greco-Bactrian remains of the Macedonian Empire as well as the Parthian Empire, to the Han dynasty imperial court, then ruled by Emperor Wu of Han. He played an important pioneering role for the future Chinese conquest of lands west of Xinjiang, including swaths of Central Asia and even lands south of the Hindu Kush (see Protectorate of the Western Regions). This trip created the Silk Road that marked the beginning of globalization between the countries in the east and west. Zhang Qian's travel was commissioned by Emperor Wu with the major goal of initiating transcontinental trade in the Silk Road, as well as create political protectorates by securing allies. His missions opened trade routes bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
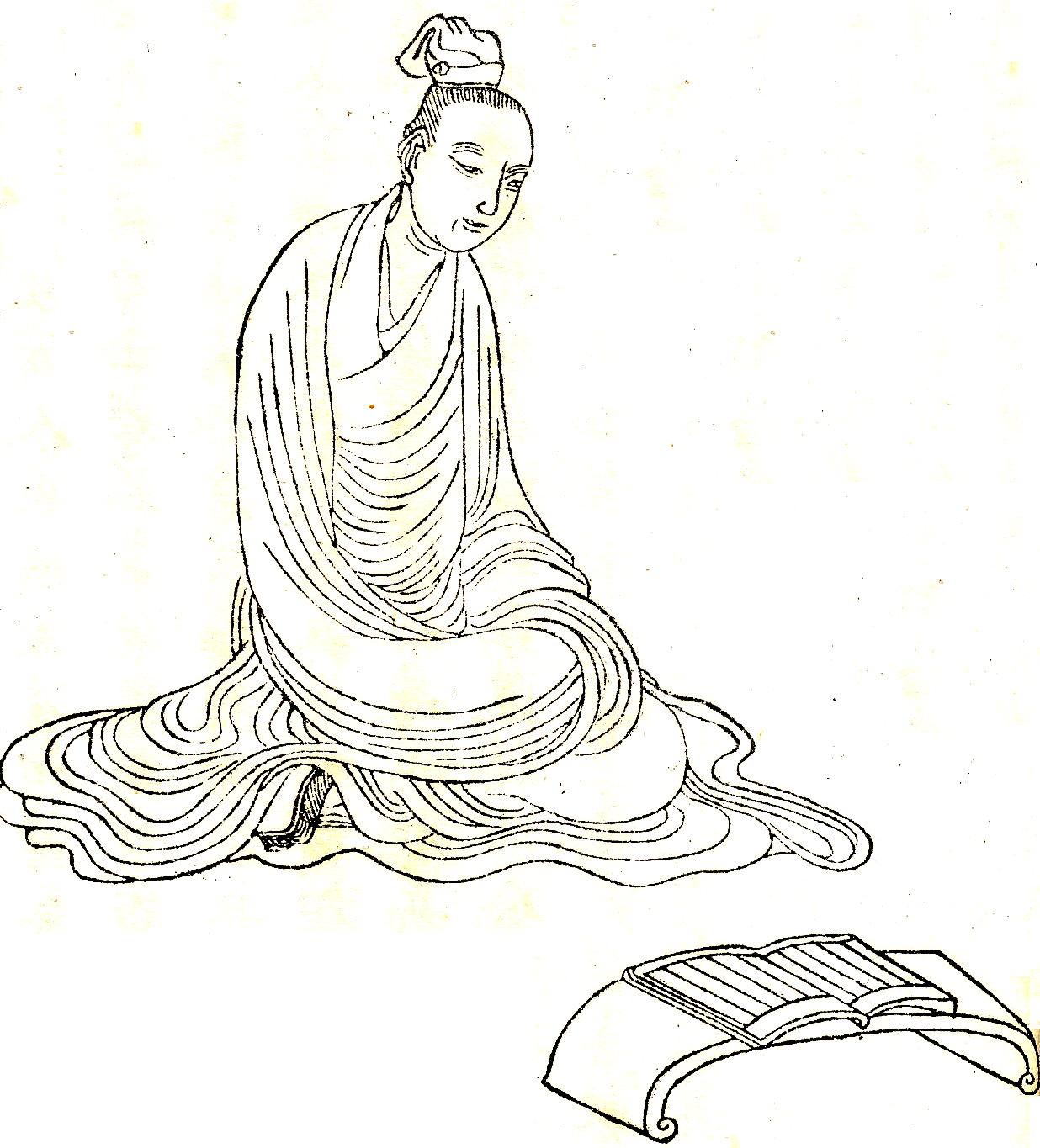
Dongfang Shuo
Dongfang Shuo (, c. 160 BCE ŌĆō c. 93 BCE) was a Han Dynasty scholar-official, ''fangshi'' ("master of esoterica"), author, and court jester to Emperor Wu (r. 141 ŌĆō 87 BCE). In Chinese mythology, Dongfang is considered a Daoist ''xian'' ("transcendent; immortal") and the spirit of Venus who incarnated as a series of ancient ministers including Laozi. Dongfang Shuo is depicted in the Wu Shuang Pu (ńäĪķøÖĶŁ£, Table of Peerless Heroes) by Jin Guliang. Names Dongfang Shuo's original Chinese surname was Zhang (Õ╝Ą meaning "stretch; spread"), which was later changed to an uncommon compound surname Dongfang (µØ▒µ¢╣ "eastern direction; the east", cf. The East Is Red). His Chinese given name was Shuo (µ£ö "new moon") and his courtesy name was Manqian (µø╝ÕĆ® "graceful handsome"). Owing to his eccentric and humorous behavior at the Han court in Chang'an, Dongfang's nickname was Huaji (µ╗æń©Į "Buffoon") and he proclaimed himself the first ''chaoyin'' (µ£ØķÜ▒ "recluse at court", p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fu Sheng (scholar)
Fu Sheng (; 268ŌĆō178 BC), also known as Master Fu (õ╝Åńö¤), was a Chinese philosopher and writer. He was a Confucian scholar of the Qin and Western Han dynasties of ancient China, famous for saving the Confucian classic ''Shangshu'' (''Book of Documents'') from the book burning of the First Emperor of Qin. Fu Sheng is depicted in the Wu Shuang Pu (ńäĪķøÖĶŁ£, Table of Peerless Heroes) by Jin Guliang. Biography Fu Sheng was a native of Jinan prefecture (µ┐¤ÕŹŚ, in present-day Zouping or Zhangqiu, Shandong province), and was said to be a descendant of the legendary ancient ruler Fu Xi. He was a ''boshi'' (ÕŹÜÕŻ½, "erudite") of the Qin dynasty. In 213 BC the First Emperor of Qin ordered the Burning of Books and killed many Confucian scholars. Risking his life, Fu Sheng hid a copy of the book in the walls of his house. He later escaped his hometown in the warfare that soon broke out and eventually ended the Qin dynasty. After the Han dynasty was established in 206 BC, Fu Sheng return ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
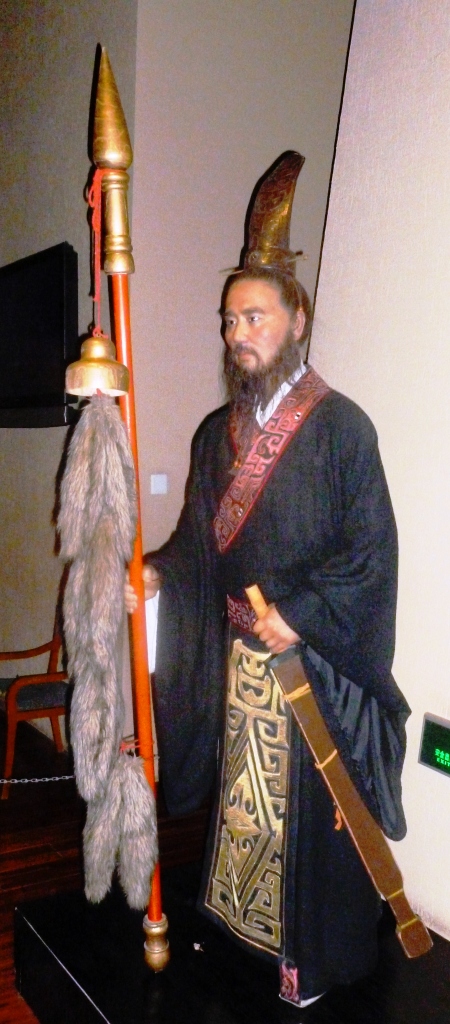
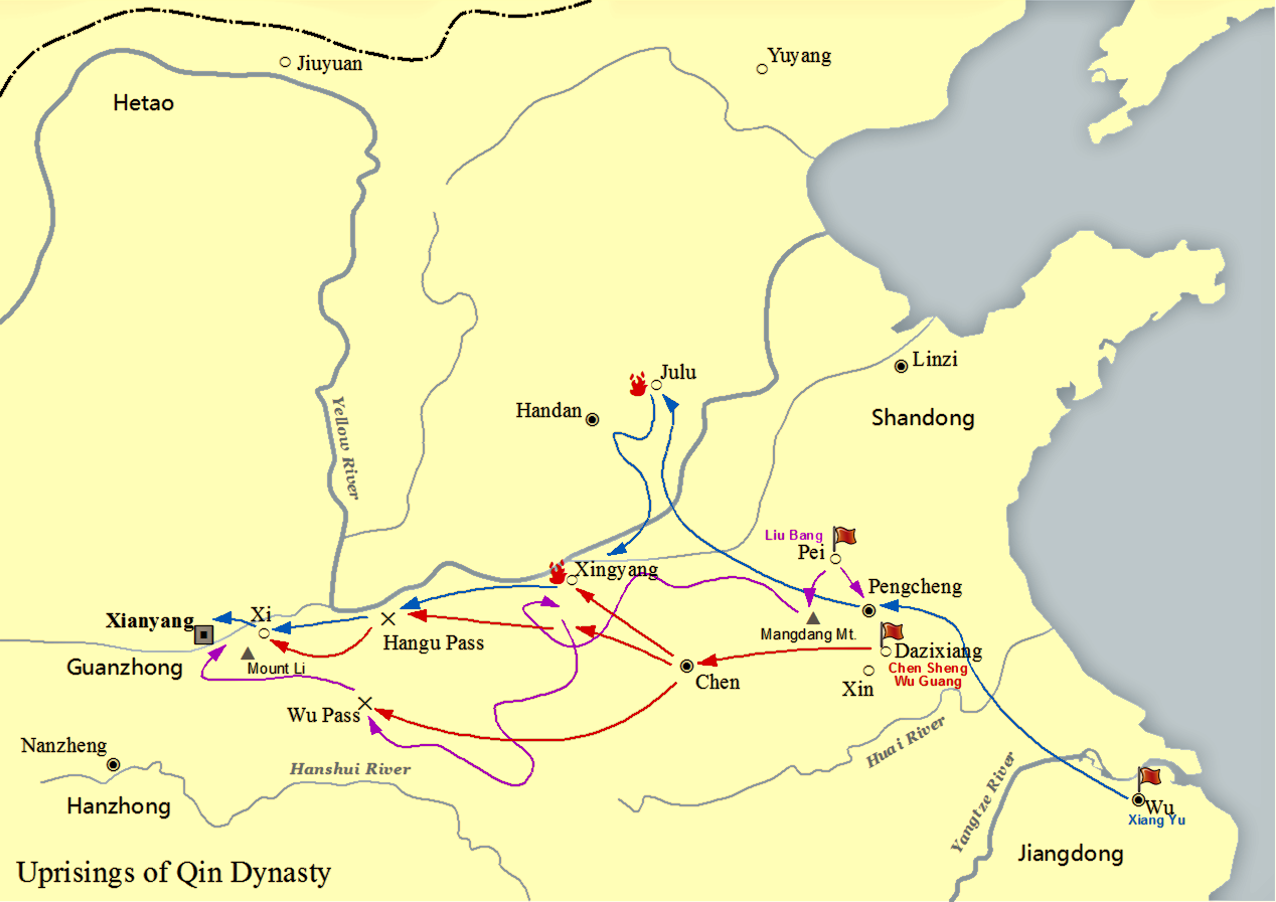
Xiang Yu
Xiang Yu (, ŌĆō202 BC), born Xiang Ji (), was the Hegemon-King (Chinese: ķ£ĖńÄŗ, ''B├Ā W├Īng'') of Western Chu during the ChuŌĆōHan Contention period (206ŌĆō202 BC) of China. A noble of the Chu state, Xiang Yu rebelled against the Qin dynasty and became a prominent warlord. He was granted the title of "Duke of Lu" () by King Huai II of the restoring Chu state in 208 BC. The following year, he led the Chu forces to victory at the Battle of Julu against the Qin armies led by Zhang Han. After the fall of Qin, Xiang Yu was enthroned as the "Hegemon-King of Western Chu" () and ruled a vast area covering modern-day central and eastern China, with Pengcheng as his capital. He engaged Liu Bang, the founding emperor of the Han dynasty, in a long struggle for power, known as the ChuŌĆōHan Contention, which concluded with his eventual defeat at the Battle of Gaixia and his suicide. Xiang Yu is depicted in the Wu Shuang Pu (, Table of Peerless Heroes) by Jin Guliang. Names and titles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Liang (Western Han)
:''Note: In this article, to distinguish between the Han state of the Warring States period and the Han dynasty, the former is referred to as "H├Īn" while "Han" is reserved for the latter.'' Zhang Liang ( 251 BC ŌĆō 186 BC), courtesy name Zifang, was a Chinese military strategist and politician who lived in the early Western Han dynasty. He is also known as one of the "Three Heroes of the early Han dynasty" (), along with Han Xin () and Xiao He. Zhang Liang contributed greatly to the establishment of the Han dynasty. After his death, he was honoured with the posthumous title "Marquis Wencheng" by Emperor Qianshao. Zhang Liang is depicted in the Wu Shuang Pu (ńäĪķøÖĶŁ£, Table of Peerless Heroes) by Jin Guliang. Early life Zhang Liang was born in Xinzheng (µ¢░ķäŁ; present-day Zhengzhou, Henan), the capital of the H├Īn state(), while his ancestral home was in Chengfu (Õ¤ÄńłČ; present-day Chengfu Town, Bozhou, Anhui). He descended from an aristocrat family in H├Īn. His grandfathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin (), often shortened to just pinyin, is the official romanization system for Standard Mandarin Chinese in China, and to some extent, in Singapore and Malaysia. It is often used to teach Mandarin, normally written in Chinese form, to learners already familiar with the Latin alphabet. The system includes four diacritics denoting tones, but pinyin without tone marks is used to spell Chinese names and words in languages written in the Latin script, and is also used in certain computer input methods to enter Chinese characters. The word ' () literally means "Han language" (i.e. Chinese language), while ' () means "spelled sounds". The pinyin system was developed in the 1950s by a group of Chinese linguists including Zhou Youguang and was based on earlier forms of romanizations of Chinese. It was published by the Chinese Government in 1958 and revised several times. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) adopted pinyin as an international standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baidu
Baidu, Inc. ( ; , meaning "hundred times") is a Chinese multinational technology company specializing in Internet-related services and products and artificial intelligence (AI), headquartered in Beijing's Haidian District. It is one of the largest AI and Internet companies in the world. The holding company of the group is incorporated in the Cayman Islands. Baidu was incorporated in January 2000 by Robin Li and Eric Xu. The Baidu search engine is currently the sixth largest website in the Alexa Internet rankings. Baidu has origins in RankDex, an earlier search engine developed by Robin Li in 1996, before he founded Baidu in 2000. Baidu offers various services, including a Chinese search engine, as well as a mapping service called Baidu Maps. Baidu offers about 57 search and community services, such as Baidu Baike (an online encyclopedia), Baidu Wangpan (a cloud storage service), and Baidu Tieba (a keyword-based discussion forum). Baidu Global Business Unit (GBU) is respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)