|
Wreechener See Nature Reserve
The Wreechener See Nature Reserve (german: Naturschutzgebiet Wreechener See) is a nature reserve in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. It lies 2 kilometres south of the town of Putbus and has an area of 72 hectares. It was placed under protection on 12 September 1990 as part of the creation of the Southeast Rügen Biosphere Reserve. The purpose of its designation as a nature reserve is to preserve a lagoon-like cove (or ''bodden'') in the Bay of Greifswald as one of the last regional quiet areas for resting water birds. The Wreechener See also has areas undergoing natural silting up that support special communities and are breeding grounds for rare bird species. Adjacent wet meadows are extensively used. Nearby villages are Wreechen, immediately to the east, Krakvitz and Neukamp. The cove is linked to the Bay of Greifswald by a short narrow channel spanned by a wooden road bridge. The condition of the reserve is only classed as satisfactory, because the water c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wreechen
Wreechen is a village in the borough of Putbus on the German Baltic Sea island of Rügen. Location The village lies in picturesque countryside between the lake of Wreecher See to the west and the Baltic Sea bay of Rügischer Bodden to the east. It lies strung out along the roughly north–south running road from Putbus to Neukamp. Northwest of the village is the farmstead of the former Wreechen Watermill which now houses a small exhibition of sculptures and email art. History Wreechen was first mentioned in 1318.Hanswilhelm Haefs, Ortsnamen und Ortsgeschichten auf Rügen mitsamt Hiddensee und Mönchgut, BoD, Books on Demand, 2003, , page 101 The name may be derived from the Slavic ''Vrechy'', which means "nut", suggesting that it was originally a settlement with a number of nut trees. As early as the 14th century the settlement had been divided into Groß and Klein Wreechen ("Great Wreechen" and "Little Wreechen"). Klein Wreechen covered the land around the watermill at Wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Protection Area
A Special Protection Area (SPA) is a designation under the European Union Directive on the Conservation of Wild Birds. Under the Directive, Member States of the European Union (EU) have a duty to safeguard the habitats of migratory birds and certain particularly threatened birds. Together with Special Areas of Conservation (SACs), the SPAs form a network of protected sites across the EU, called Natura 2000. Each SPA has an EU code – for example the North Norfolk Coast SPA has the code ''UK9009031''. In the United Kingdom As at 21 September 2006, there were 252 classified SPAs and 12 proposed SPAs in England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The Conservation (Natural Habitats etc.) Regulations 1994 implement the terms of the Directive in Scotland, England and Wales. In Great Britain, SPAs (and SACs) designated on land or in the intertidal area are normally also notified as Sites of Special Scientific Interest (SSSIs), and in Northern Ireland as Areas of Special Scientific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
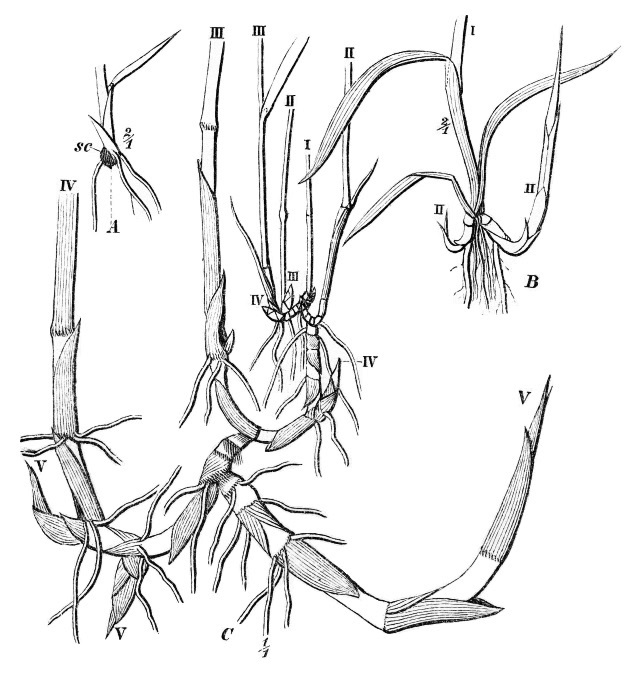
Tule
''Schoenoplectus acutus'' ( syn. ''Scirpus acutus, Schoenoplectus lacustris, Scirpus lacustris'' subsp. ''acutus''), called tule , common tule, hardstem tule, tule rush, hardstem bulrush, or viscid bulrush, is a giant species of sedge in the plant family Cyperaceae, native to freshwater marshes all over North America. The common name derives from the Nāhuatl word ''tōllin'' , and it was first applied by the early settlers from New Spain who recognized the marsh plants in the Central Valley of California as similar to those in the marshes around Mexico City. Tules once lined the shores of Tulare Lake in California, formerly the largest freshwater lake in the western United States. It was drained by land speculators in the 20th century. The expression "out in the tules" is still common, deriving from the dialect of old Californian families and meaning "where no one would want to live", with a touch of irony. The phrase is comparable to "out in the boondocks". ''Schoenoplectus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Softstem Bulrush
''Schoenoplectus tabernaemontani'' (syn. ''Scirpus validus'') is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family known by the common names softstem bulrush, grey club-rush, and great bulrush. It can be found throughout much of the world; it has been reported from every state in the United States (including Hawaii), and from every province and territory in Canada except Nunavut. It grows in moist and wet habitat, and sometimes in shallow water. ''Schoenoplectus tabernaemontani'' is quite variable in appearance, thus explaining the long list of synonyms that have been created over the years. It is a perennial herb producing dense stands of many narrow erect stems reaching 1–3 m (33–100 inches) in height. It grows from a long rhizome system. The leaves are mostly basal and have wide sheaths around the stems. The inflorescence is generally a panicle of spikelets on long, thin branches which spread, arch, or droop. The spikelets vary in color. There is usually a long, stiff bract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Aster
''Tripolium pannonicum'', called sea aster or seashore aster and often known by the synonyms ''Aster tripolium'' or ''Aster pannonicus'', is a flowering plant, native to Eurasia and northern Africa, that is confined in its distribution to salt marshes, estuaries and occasionally to inland salt works. It is a perennial growing up to 50 cm tall with fleshy lanceolate leaves and purple ray florets flowering from July to September. The plants tend to be short-lived and populations need significant new recruitment each year from new seedlings. There are rayed as well as rayless varieties and only the former have long blue or white florets. The rayless form is yellow. The plant flowers well into autumn and hence provides a valuable source of nectar for late-flying butterflies such as painted lady and red admiral. Young leaves of this plant are edible and are collected for consumption on the floodplains of the Dutch province of Zeeland , nl, Ik worstel en kom boven("I stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saltmarsh Rush '', native to the Southeastern United States and Caribbean
{{Plant common name ...
Saltmarsh rush or salt marsh rush is a common name for several plants and may refer to: *''Juncus gerardii'', native to the Northern North America and Europe *''Juncus kraussii'', native to the Southern hemisphere *''Juncus roemerianus ''Juncus roemerianus'' is a species of flowering plant in the rush family known by the common names black rush, needlerush, and black needlerush. It is native to North America, where its main distribution lies along the coastline of the southeas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmites
''Phragmites'' () is a genus of four species of large perennial reed grasses found in wetlands throughout temperate and tropical regions of the world. Taxonomy The World Checklist of Selected Plant Families, maintained by Kew Garden in London, accepts the following four species: * ''Phragmites australis'' ( Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. – cosmopolitan * ''Phragmites japonicus'' Steud. – Japan, Korea, Ryukyu Islands, Russian Far East * ''Phragmites karka'' ( Retz.) Trin. ex Steud. – tropical Africa, southern Asia, Australia, some Pacific Islands, invasive in New Zealand * ''Phragmites mauritianus'' Kunth – central + southern Africa, Madagascar, Mauritius The cosmopolitan common reed has the generally accepted botanical name ''Phragmites australis''. (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. About 130 other synonyms have been proposed. Examples include ''Phragmites communis'' Trin., ''Arundo phragmites'' L., and ''Phragmites vulgaris'' (Lam.) Crép. (illegitimate name). Wildlife in reed beds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Rügen (1678)
The invasion of Rügen of 22 to 24 September 1678 was a military operation in the Swedish-Brandenburg War, or Scanian War, that ended with the annexation of the Swedish-ruled island of Rügen by the Allies – Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark – for just under a year before it was restored by treaty to Sweden. The operation was a prelude to the long-planned Siege of Stralsund that followed shortly thereafter. Background The first invasion of Rügen in this war took place on 17 September 1677, when the Danes landed and succeeded, after the Battle of Bergen, in expelling the Swedes from the entire island. Soon after, the Swedes under the command of Field Marshal Otto Wilhelm von Konigsmark began moves to recapture the island, which proved successful when they won the Battle of Warksow on 18 January 1678. The island was not safe for long in spite of this Swedish victory, mainly because the Danes made several raids on Rügen over the summer. The possession of the island of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Stone Age
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring Fen
A fen is a type of peat-accumulating wetland fed by mineral-rich ground or surface water. It is one of the main types of wetlands along with marshes, swamps, and bogs. Bogs and fens, both peat-forming ecosystems, are also known as mires. The unique water chemistry of fens is a result of the ground or surface water input. Typically, this input results in higher mineral concentrations and a more basic pH than found in bogs. As peat accumulates in a fen, groundwater input can be reduced or cut off, making the fen ombrotrophic rather than minerotrophic. In this way, fens can become more acidic and transition to bogs over time. Fens can be found around the world, but the vast majority are located at the mid to high latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere. They are dominated by sedges and mosses, particularly graminoids that may be rarely found elsewhere, such as the sedge species '' Carex exilis''. Fens are highly biodiverse ecosystems and often serve as habitats for endange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valley Bog
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; alkaline mires are called fens. A baygall is another type of bog found in the forest of the Gulf Coast states in the United States.Watson, Geraldine Ellis (2000) ''Big Thicket Plant Ecology: An Introduction'', Third Edition (Temple Big Thicket Series #5). University of North Texas Press. Denton, Texas. 152 pp. Texas Parks and Wildlife. Ecological Mapping systems of Texas: West Gulf Coastal Plain Seepage Swamp and Baygall'. Retrieved 7 July 2020 They are often covered in heath or heather shrubs rooted in the sphagnum moss and peat. The gradual accumulation of decayed plant material in a bog functions as a carbon sink. Bogs occur where the water at the ground surface is acidic and low in nutrients. In contrast to fens, they derive most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graded Shoreline
A graded shoreline is a stage in the cycle of coastal development characterised by a flat and straight coastline. It is formed under the influence of wind and water from the original bays, islands, peninsulas and promontories. Sand and gravel is carried away and dumped at other locations depending on the direction and strength of sea currents. Typical of graded shorelines are the formation of dunes, wide sandy beaches and sometimes a lagoon or a spit. Where two graded shorelines meet, a headland may form with a sandy reef in the sea beyond it. Parallel to the graded shoreline sandbanks may form as a result of sediments transported away from the shore. Examples *Long stretches of the southern Baltic Sea coast in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, in Poland, Russia, Lithuania and Latvia. *The North Sea coast from Belgium, along the outer edge of the Wadden Sea islands in the Netherlands and Germany, to the west coast and northeast coast of Jutland in Denmark. *On the hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |