|
Wreath Valley
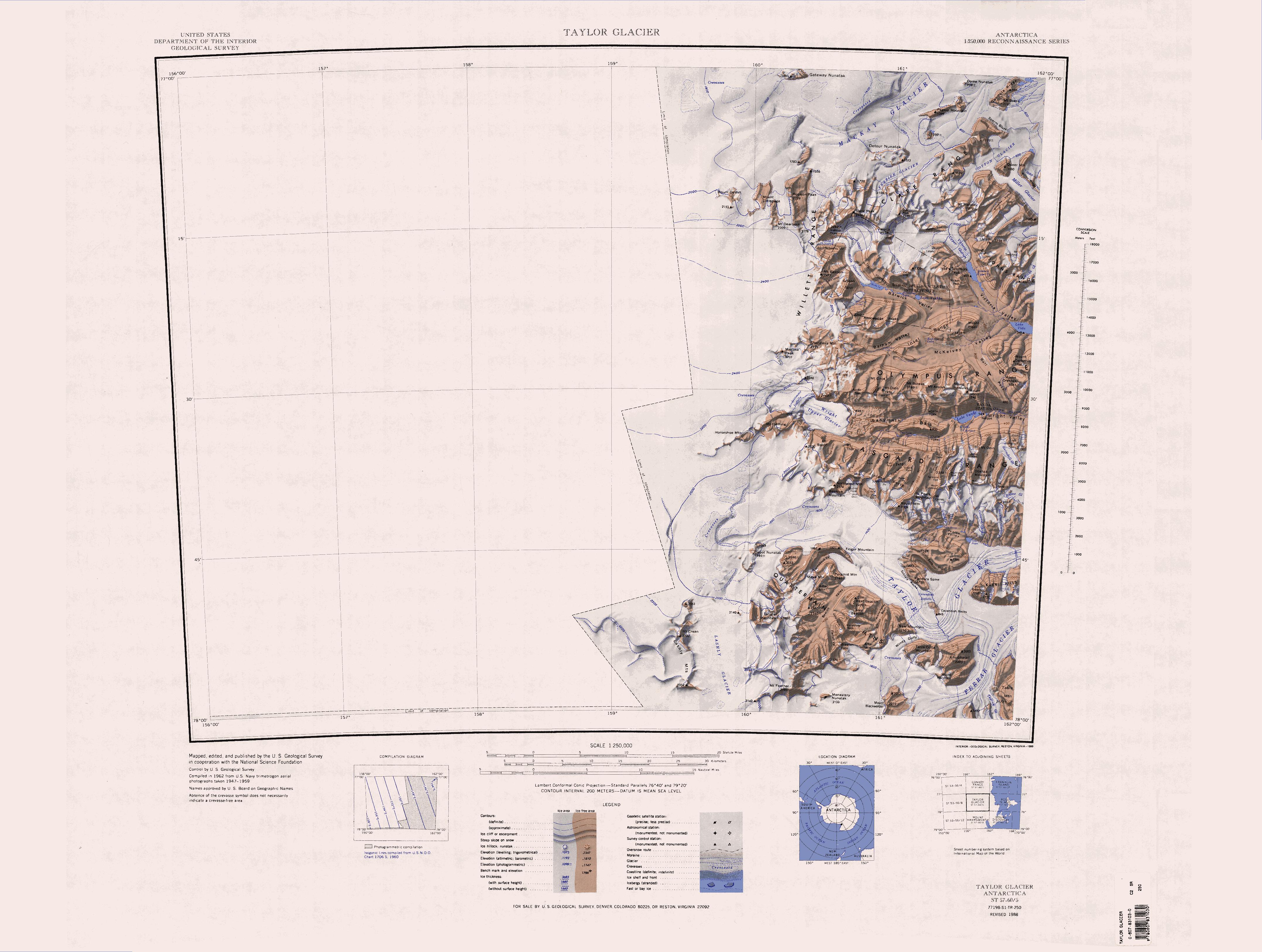
The Apocalypse Peaks () are a group of peaks with a highest point of , standing east of Willett Range and between Barwick Valley and Balham Valley, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. Name The Apocalypse Peaks were so named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (1958–59) because the peaks are cut by talus slopes which gives them the appearance of the "Riders of the Apocalypse." Location The Apocalypse Peaks are bounded by the Barwick Valley to the northeast and the Balham Valley to the southeast. The Willett Range lies to the west, the Cruzen Range (formerly part of the Clare Range) to the north, the Insel Range to the southeast and the Olympus Range to the south. Southern features Features of the south of the peaks include, from west to east, Edbrooke Hill . A hill, high, at the extreme west end of the Apocalypse Peaks. The hill rises high above the adjacent plateau ice, which diverges at the hill to the east-northeast-flowing Haselton Glacier an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olympus Range
Olympus Range () is a primarily ice-free mountain range of Victoria Land, Antarctica, with peaks over , between Victoria and McKelvey Valleys on the north and Wright Valley on the south. It was mapped by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition, 1958–59, and named for the mythological home of the Greek gods. Peaks in the range are named for figures in Greek mythology. Further reading * I.B. Campbell, G.G.C. ClaridgeAntarctica: Soils, Weathering Processes and Environment PP 30 - 32 * Vivien GornitzRising Seas: Past, Present, Future P 64 * A.R. Lewis, D.R. Marchant, A.C. Ashworth, S.R. Hemming, M.L. MachlusMajor middle Miocene global climate change: Evidence from East Antarctica and the Transantarctic Mountains* Adam R. Lewis, David R. Marchant, Allan C. Ashworth, Lars Hedenäs, Sidney R. Hemming, Jesse V. Johnson, Melanie J. Leng, Malka L. Machlus, Angela E. Newton, J. Ian Raine, Jane K. Willenbring Jane Kathryn Willenbring is an American geomorphologist an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson Piedmont Glacier
Wilson Piedmont Glacier () is a large piedmont glacier extending from Granite Harbour to Marble Point on the coast of Victoria Land. Scheuren Stream takes meltwater from the glacier into the Bay of Sails, while South Stream flows southeastward to Bernacchi Bay. Discovered by the ''Discovery'' expedition, 1901–04. The British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, named the feature for Dr. Edward A. Wilson, surgeon and artist with Scott's first expedition and chief of the scientific staff with the second. Wilson lost his life on the way back from the South Pole with Scott. See also * Ball Stream *King Pin King Pin () is a nunatak, high, rising above the Wilson Piedmont Glacier, Antarctica, about midway between Mount Doorly and Hogback Hill. It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition, 1958–59, after the American h ... Glaciers of Scott Coast {{ScottCoast-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mackay Glacier
Mackay Glacier () is a large glacier in Victoria Land, descending eastward from the Antarctic polar plateau, between the Convoy Range and Clare Range, into the southern part of Granite Harbour. It was discovered by the South Magnetic Pole party of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1907–09, and named for Alistair F. Mackay, a member of the party. The glacier's tongue The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste ... is called Mackay Glacier Tongue. First mapped by the British Antarctic Expedition (1910–13) and named in association with Mackay Glacier. Cuff Cape emerges from the icy coast immediately south of Mackay Glacier. References Glaciers of Victoria Land Scott Coast {{ScottCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Johns Range
Saint Johns Range () is a crescent-shaped mountain range about long, in Victoria Land. It is bounded on the north by the Cotton, Miller and Debenham Glaciers, and on the south by Victoria Valley and the Victoria Upper Glacier, Victoria Upper and Victoria Lower Glaciers. Its eastern end is formed by a spur called Lizards Foot. Named by the New Zealand Northern Survey Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition, 1956–58, which surveyed peaks in the range in 1957. Named for St John's College, Cambridge, St. John's College at Cambridge, England, with which several members of the Terra Nova Expedition, British Antarctic Expedition (1910–13) were associated during the writing of their scientific reports, and in association with the adjacent Gonville and Caius Range. Kuivinen Ridge Kuivinen Ridge () is a transverse ridge extending southwest–northeast across the Saint Johns Range between an unnamed glacier and the Ringer Glacier in Victoria Land. The ridge is long and rises ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Valley
Victoria Valley is one of the larger McMurdo Dry Valleys in Antarctica. Lake Vida is the largest lake of the valley. The Victoria River drains the Victoria Upper Glacier, with Upper Victoria Lake just below it and northwest of Lake Vida, into Vida Lake on its western side. Lake Thomas Lake Thomas is a meltwater lake that is circumscribed on the northwest and northeast sides by Robertson Ridge and Clark Glacier (Antarctica), Clark Glacier, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for ... is east of Lake Vida. See also * Dry Valleys Geology Valleys of Victoria Land McMurdo Dry Valleys {{McMurdoDryValleys-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asgard Range
The Asgard Range is a mountain range in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It divides Wright Valley from Taylor Glacier and Taylor Valley, and was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (1958–59) after Asgard, the home of the Norse gods. Geography The Asgard Range contains numerous named features such as peaks, valleys, and glaciers, and even some sub-ranges. Many are named after Norse gods and mythological figures, in keeping with the name of the range itself. Mountains * Ball Peak * Mount Beowulf * Bromley Peak * Brunhilde Peak * Mount Carnes * Mount Darby * Mount Feola * Mount Freya * Mount Holm-Hansen * Mount Grendal * Mount Hall * Harp Hill * Harris Peak * Hetha Peak * Hind Turret * Hoehn Peak * Hoffman Peak * Idun Peak * Mount Irvine * Mount Jord * Mount Knox * Mount Loke * Lyons Cone * Matterhorn * Mattox Bastion * Mount Newall * Obelisk Mountain * Mount Odin * Oliver Peak * Panorama Peak * Perk Summit * Ponder Peak * Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernandez Valley
Barwick Valley is an ice-free valley north of Apocalypse Peaks, extending from Webb Glacier to Victoria Valley in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) for R.E. Barwick, summer biologist with the New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58) who worked in this area in 1957–58 and as a member of the VUWAE, 1958–59. Antarctic Specially Protected Area An area of 480 km2, comprising parts of both Barwick Valley and the adjacent Balham Valley, is protected under the Antarctic Treaty System as Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.123 because it is one of the least disturbed or contaminated of the McMurdo Dry Valleys. It is consequently important as a reference base for measuring changes in the similar polar desert ecosystem An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. Thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Valley
Barwick Valley is an ice-free valley north of Apocalypse Peaks, extending from Webb Glacier to Victoria Valley in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) for R.E. Barwick, summer biologist with the New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58) who worked in this area in 1957–58 and as a member of the VUWAE, 1958–59. Antarctic Specially Protected Area An area of 480 km2, comprising parts of both Barwick Valley and the adjacent Balham Valley, is protected under the Antarctic Treaty System as Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.123 because it is one of the least disturbed or contaminated of the McMurdo Dry Valleys. It is consequently important as a reference base for measuring changes in the similar polar desert ecosystem An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. Thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papitashvili Valley
Barwick Valley is an ice-free valley north of Apocalypse Peaks, extending from Webb Glacier to Victoria Valley in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) for R.E. Barwick, summer biologist with the New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58) who worked in this area in 1957–58 and as a member of the VUWAE, 1958–59. Antarctic Specially Protected Area An area of 480 km2, comprising parts of both Barwick Valley and the adjacent Balham Valley, is protected under the Antarctic Treaty System as Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.123 because it is one of the least disturbed or contaminated of the McMurdo Dry Valleys. It is consequently important as a reference base for measuring changes in the similar polar desert ecosystem An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. Thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Geographic Board
The New Zealand Geographic Board Ngā Pou Taunaha o Aotearoa (NZGB) was established by the New Zealand Geographic Board Act 1946, which has since been replaced by the New Zealand Geographic Board (Ngā Pou Taunaha o Aotearoa) Act 2008. Although an independent institution, it is responsible to the Minister for Land Information. The board has authority over geographical and hydrographic names within New Zealand and its territorial waters. This includes the naming of small urban settlements, localities, mountains, lakes, rivers, waterfalls, harbours and natural features and may include researching local Māori names. It has named many geographical features in the Ross Sea region of Antarctica. It has no authority to alter street names (a local body responsibility) or the name of any country. The NZGB secretariat is part of Toitū Te Whenua Land Information New Zealand (LINZ) and provides the board with administrative and research assistance and advice. The New Zealand Geograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insel Range
The Insel Range () is a series of ice-free flat-topped peaks resembling islands which rise above the surrounding terrain and separate McKelvey Valley from Balham Valley, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was so named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (1958–59) because of the resemblance to islands. Features Geographical features include: * Balham Valley * Bullseye Lake * Canfield Mesa * Green Mesa * Halzen Mesa * McKelvey Valley * Mount Insel References Mountain ranges of Victoria Land McMurdo Dry Valleys {{McMurdoDryValleys-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |