|
Worcester Basin
The Worcester Basin or Worcester Graben is a sedimentary basin in central England, filled with mainly Permian and Triassic rocks. It trends roughly north-south and lies between the East Malverns Fault in the west and the Inkberrow Fault in the east. It forms part of a series of Permo-Triassic basins that stretch north-south across England, including the Cheshire Basin, Stafford Basin and the East Irish Sea Basin. These basins resulted from a regional rifting event that affected parts of North-West Europe, eastern North America and East Greenland. Fill The oldest part of the sedimentary fill in the Worcester Basin is the Cisuralian (Early Permian) Bridgnorth Sandstone Formation, deposited in an aeolian environment. Unconformably above this is the Early Triassic Kidderminster Formation of pebble conglomerates and sandstones, deposited in a fluvial environment. The succession continues with the Early Triassic Wildmoor Sandstone Formation, followed by the Anisian (Middle Triassic) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Basin
Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock. They form when long-term subsidence creates a regional depression that provides accommodation space for accumulation of sediments. Over millions or tens or hundreds of millions of years the deposition of sediment, primarily gravity-driven transportation of water-borne eroded material, acts to fill the depression. As the sediments are buried, they are subject to increasing pressure and begin the processes of compaction and lithification that transform them into sedimentary rock. Sedimentary basins are created by deformation of Earth's lithosphere in diverse geological settings, usually as a result of plate tectonic activity. Mechanisms of crustal deformation that lead to subsidence and sedimentary basin formation include the thinning of underlying crust; depression of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidmouth Mudstone Formation
The Mercia Mudstone Group is an early Triassic lithostratigraphic group (a sequence of rock strata) which is widespread in Britain, especially in the English Midlands – the name is derived from the ancient kingdom of Mercia which corresponds to that area. It is frequently encountered in older literature as the Keuper Marl or Keuper Marl Series. The Mercia Mudstone Group is now divided into five formations recognised and mappable across its entire outcrop and subcrop. The formations are a mix of mudstones, siltstones, sandstones and halites. Historically this sequence of rocks has been subdivided in different ways with different names in each of the basinal areas in which it is found. Increasing knowledge of the sequences and the more recent development of seamless electronic mapping by the British Geological Survey (BGS) necessitated a reappraisal of these divisions. A report published by BGS in 2008 recommended the abandonment of previous divisions and naming schemes in favour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitby Mudstone Formation
The Whitby Mudstone is a Toarcian (Early Jurassic; ''Falciferum''-''Bifrons'' in regional chronostratigraphy) geological formation in Yorkshire and Worcestershire, England.Whitby Mudstone at .org The formation, part of the , is present in the and |
Marlstone Rock Formation
The Marlstone Rock Formation is a geological formation in England. It dates to the Early Jurassic, it consists of "Sandy, shell-fragmental and ooidal ferruginous limestone interbedded with ferruginous calcareous sandstone, and generally subordinate ferruginous mudstone beds", with ironstone. References {{reflist Geologic formations of England Jurassic England Early Jurassic Europe Pliensbachian Stage Toarcian Stage Formations Jurassic System of Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyrham Formation
The Dyrham Formation is a geologic formation in England. It preserves fossils dating back to the early part of the Jurassic period (Pliensbachian). See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in England See also * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Europe * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in the United Kingdom References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Fossiliferous stratigraphic units in England England United Kingdom geology-rel ... References * Jurassic England Pliensbachian Stage Jurassic System of Europe {{England-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
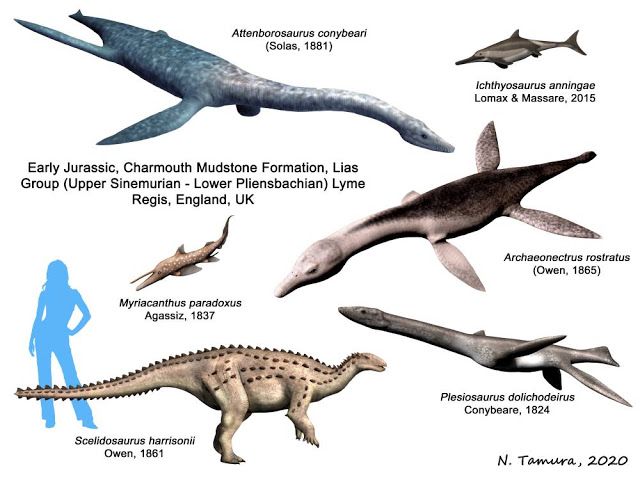
Charmouth Mudstone Formation
The Charmouth Mudstone Formation is a geological formation in England. It preserves fossils dating back to the early part of the Jurassic period (Sinemurian–Pliensbachian). It forms part of the lower Lias Group. It is most prominently exposed at its type locality in cliff section between Lyme Regis and Charmouth (alongside the underlying Blue Lias) but onshore it extends northwards to Market Weighton, Yorkshire, and in the subsurface of the East Midlands Shelf and Wessex Basin. The formation is notable for its fossils, including those of ammonites and marine reptiles and rare dinosaur remains. The formation played a prominent role in the history of early paleontology, with its Lyme Regis-Charmouth exposure being frequented by fossil collectors including Mary Anning. Stratigraphy Shales With Beef Member The Shales With Beef Member is around 28–30 metres thick in the Lyme Regis-Charmouth region and predominantly consists of thinly bedded medium to dark grey mudstone, block ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Lias Formation
The Blue Lias is a geological formation in southern, eastern and western England and parts of South Wales, part of the Lias Group. The Blue Lias consists of a sequence of limestone and shale layers, laid down in latest Triassic and early Jurassic times, between 195 and 200 million years ago. The Blue Lias is famous for its fossils, especially ammonites. Its age corresponds to the Rhaetian to lower Sinemurian stages of the geological timescale, thus fully including the Hettangian stage. It is the lowest of the three divisions of the Lower Jurassic period and, as such, is also given the name ''Lower Lias''. Stratigraphically it can be subdivided into three members: the Wilmcote Limestone, Saltford Shale and Rugby Limestone. Lithology and facies The Blue Lias comprises decimetre scale alternations of argillaceous limestone and mudstone. These alternations are caused by short-term climatic variations during the Early Jurassic attributed to orbital forcing (Milankovitch cycles). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lias Group
The Lias Group or Lias is a lithostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) found in a large area of western Europe, including the British Isles, the North Sea, the Low Countries and the north of Germany. It consists of marine limestones, shales, marls and clays. ''Lias'' is a Middle English term for hard limestone, used in this specific sense by geologists since 1833. In the past, geologists used ''Lias'' not only for the sequence of rock layers, but also for the timespan during which they were formed. It was thus an alternative name for the Early Jurassic epoch of the geologic timescale. It is now more specifically known that the Lias is Rhaetian to Toarcian in age (over a period of 20 million years between ) and thus also includes a part of the Triassic. The use of the name "Lias" for a unit of time is therefore slowly disappearing. Subdivisions In southern England, the Lias Group is often divided into Lower, Middle and Upper subgroups. In Southern England the Lias is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penarth Group
The Penarth Group is a Rhaetian age (Triassic) lithostratigraphic group (a sequence of rock strata) which is widespread in Britain. It is named from the seaside town of Penarth near Cardiff in south Wales where strata of this age are exposed in coastal cliffs southwards to Lavernock Point. This sequence of rocks was previously known as the Rhaetic or Rhaetic Beds. Stratigraphy It includes the Lilstock Formation and the underlying Westbury Formation. The Langport and Cotham Members, grey limestones of marine origin with associated mudstones, are recognised within the Lilstock Formation, itself named from Lilstock in west Somerset. The Westbury Formation is named from Westbury-on-Severn in Gloucestershire. Ireland In 1999, the discovery of an ichthyosaur from Langport Member mudstones exposed at Waterloo Bay, Larne provided the most complete example of this in Northern Ireland Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label=Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
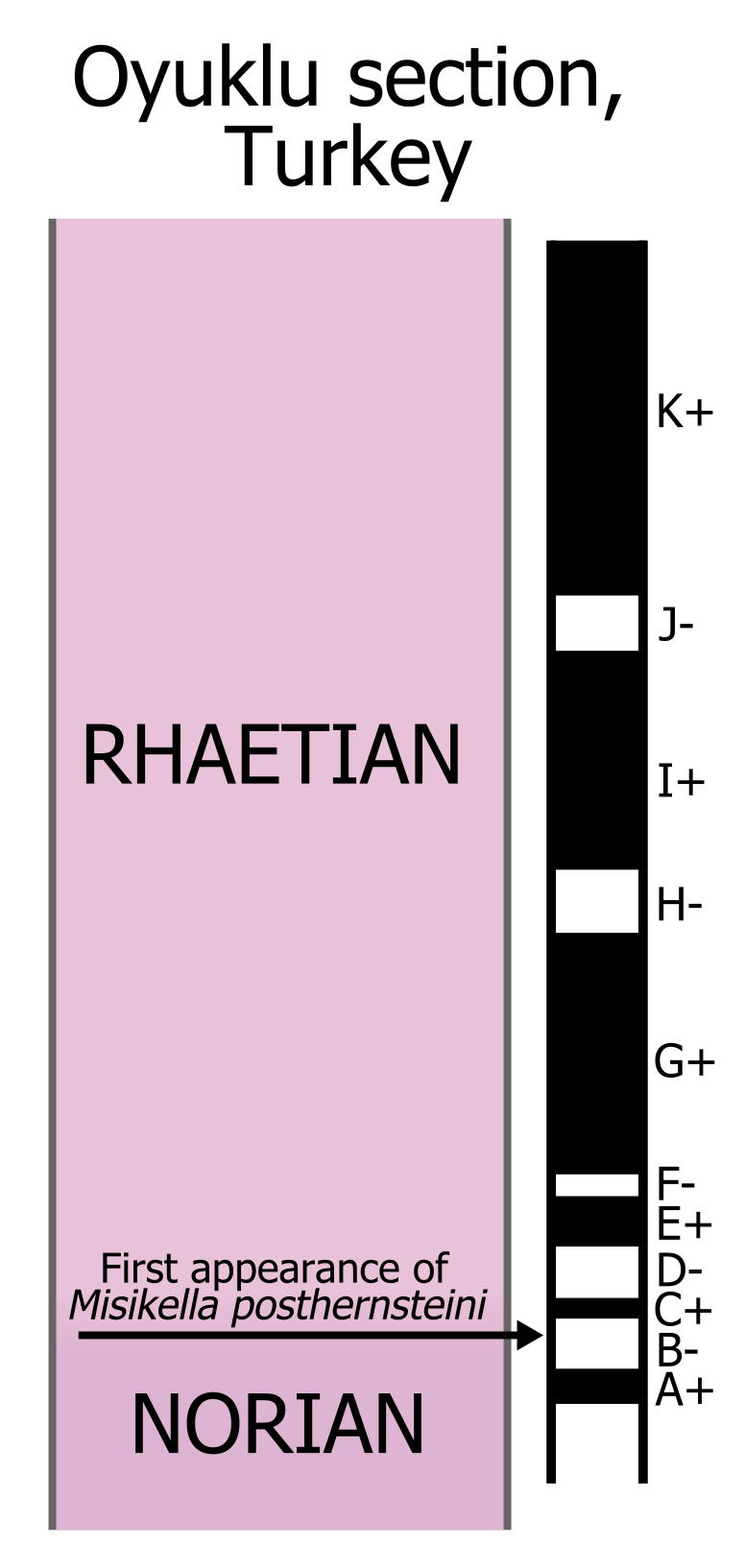
Rhaetian
The Rhaetian is the latest age of the Triassic Period (in geochronology) or the uppermost stage of the Triassic System (in chronostratigraphy). It was preceded by the Norian and succeeded by the Hettangian (the lowermost stage or earliest age of the Jurassic). The base of the Rhaetian lacks a formal GSSP, though candidate sections include Steinbergkogel in Austria (since 2007) and Pignola-Abriola in Italy (since 2016). The end of the Rhaetian (and the base of the overlying Hettangian Stage) is more well-defined. According to the current ICS (International Commission on Stratigraphy) system, the Rhaetian ended ± 0.2 Ma ( million years ago). In 2010, the base of the Rhaetian (i.e. the Norian-Rhaetian boundary) was voted to be defined based on the first appearance of '' Misikella posthernsteini'', a marine conodont. However, there is still much debate over the age of this boundary, as well as the evolution of ''M. posthernsteini''. The most comprehensive source of precise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Anchor Formation
The Mercia Mudstone Group is an early Triassic lithostratigraphic group (a sequence of rock strata) which is widespread in Britain, especially in the English Midlands – the name is derived from the ancient kingdom of Mercia which corresponds to that area. It is frequently encountered in older literature as the Keuper Marl or Keuper Marl Series. The Mercia Mudstone Group is now divided into five formations recognised and mappable across its entire outcrop and subcrop. The formations are a mix of mudstones, siltstones, sandstones and halites. Historically this sequence of rocks has been subdivided in different ways with different names in each of the basinal areas in which it is found. Increasing knowledge of the sequences and the more recent development of seamless electronic mapping by the British Geological Survey (BGS) necessitated a reappraisal of these divisions. A report published by BGS in 2008 recommended the abandonment of previous divisions and naming schemes in favour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolomite (mineral)
Dolomite () is an anhydrous carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate, ideally The term is also used for a sedimentary carbonate rock composed mostly of the mineral dolomite. An alternative name sometimes used for the dolomitic rock type is dolostone. History As stated by Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure the mineral dolomite was probably first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1768. In 1791, it was described as a rock by the French naturalist and geologist Déodat Gratet de Dolomieu (1750–1801), first in buildings of the old city of Rome, and later as samples collected in the mountains now known as the Dolomite Alps of northern Italy. Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure first named the mineral (after Dolomieu) in March 1792. Properties The mineral dolomite crystallizes in the trigonal-rhombohedral system. It forms white, tan, gray, or pink crystals. Dolomite is a double carbonate, having an alternating structural arrangement of calcium and magnesium ions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |