|
Wooden Tserkvas Of The Carpathian Region In Poland And Ukraine
The Wooden ''Tserkvas'' of the Carpathian Region in Poland and Ukraine (; ) are a group of wooden Orthodox (and some Eastern Catholic) churches (in Ukrainian, церкви ''tserkvy'') located in Poland and Ukraine which were inscribed in 2013 on the UNESCO World Heritage List which explains: Inscribed Tserkvas See also * Vernacular architecture of the Carpathians * Carpathian Wooden Churches * Wooden churches of Southern Lesser Poland * Wooden churches in Ukraine * Wooden churches of the Slovak Carpathians * Wooden churches of Maramureș The wooden churches of Maramureș in the Maramureș region of northern Transylvania are a group of almost one hundred Orthodox churches, and occasionally Greek-Catholic ones, of different architectural solutions from different periods and areas. Th ... References {{World Heritage Sites in Ukraine * World Heritage Sites in Poland World Heritage Sites in Ukraine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpathian Region
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretches from the far eastern Czech Republic (3%) and Austria (1%) in the northwest through Slovakia (21%), Poland (10%), Ukraine (10%), Romania (50%) to Serbia (5%) in the south. "The Carpathians" European Travel Commission, in The Official Travel Portal of Europe, Retrieved 15 November 2016 The Carpathian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matkiv
Matkiv ( ua, Матків, pl, Matków) is a village (''selo'') in Stryi Raion, Lviv Oblast, in south-west Ukraine. It belongs to Kozova rural hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. The village was probably established in the 15th century but was first mentioned in the first half of the 16th century. In the interwar period the village had around 1,500 inhabitants, 70% of them were Poles. The village boasts the St. Dmytro's Church, built in 1838, in 2013 inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List together with other wooden tserkvas of Carpathian region in Poland and Ukraine. Until 18 July 2020, Matkiv belonged to Turka Raion. The raion was abolished in July 2020 as part of the administrative reform of Ukraine, which reduced the number of raions of Lviv Oblast to seven. The area of Turka Raion was merged into Sambir Raion Sambir Raion ( uk, Самбірський район) is a raion in Lviv Oblast in western Ukraine. Its administrative center is Sambir. Population: . It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wooden Tserkvas Of Carpathian Region In Poland And Ukraine
The Wooden ''Tserkvas'' of the Carpathian Region in Poland and Ukraine (; ) are a group of wooden Orthodox (and some Eastern Catholic) churches (in Ukrainian, церкви ''tserkvy'') located in Poland and Ukraine which were inscribed in 2013 on the UNESCO World Heritage List which explains: Inscribed Tserkvas See also * Vernacular architecture of the Carpathians * Carpathian Wooden Churches * Wooden churches of Southern Lesser Poland * Wooden churches in Ukraine * Wooden churches of the Slovak Carpathians * Wooden churches of Maramureș The wooden churches of Maramureș in the Maramureș region of northern Transylvania are a group of almost one hundred Orthodox churches, and occasionally Greek-Catholic ones, of different architectural solutions from different periods and areas. ... References {{World Heritage Sites in Ukraine * World Heritage Sites in Poland World Heritage Sites in Ukraine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
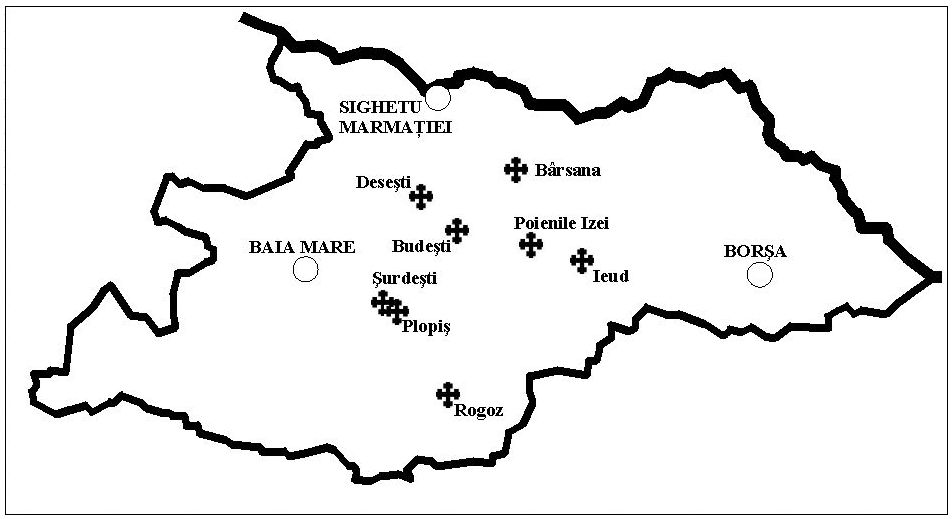
Wooden Churches Of Maramureș
The wooden churches of Maramureș in the Maramureș region of northern Transylvania are a group of almost one hundred Orthodox churches, and occasionally Greek-Catholic ones, of different architectural solutions from different periods and areas. The Maramureș churches are high timber constructions with characteristic tall, slim bell towers at the western end of the building. They are a particular vernacular expression of the cultural landscape of this mountainous area of northern Romania. Maramureș is one of the better-known regions of Romania, with autonomous traditions since the Middle Ages. Its well-preserved wooden villages and churches, its traditional lifestyle, and the local colourful dresses still in use make Maramureș as near to a living museum as can be found in Europe. The wooden churches of the region that still stand were built starting from the 17th century all the way to 19th century. Some were erected on the place of older churches. They were a response to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wooden Churches In Ukraine
Wooden church architecture in Ukraine dates from the beginning of Christianity in the area and comprises a set of unique styles and forms specific to many sub-regions of the country. As a form of vernacular culture, construction of the churches in specific styles is passed on to subsequent generations. The architectural styles vary from very simple to complicated, involving a high degree of carpentry and wood-cutting artistry. Aside from ''tserkvas'' (Greek Catholic or Eastern Orthodox churches), there are quite a few ''kosciols'' (Latin Catholic churches) that are preserved in Western Ukraine. Some of these churches remain in active use. General overview Nearly 1,900 wooden churches have been identified in Ukraine . When Ukrainians emigrated to the New World in the late 19th century, many used these stylistic forms but adapted their construction to the new materials and new environmental conditions (see for example the Holy Trinity Cathedral in Chicago, Illinois). According to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wooden Churches Of Southern Lesser Poland
The wooden churches of southern Lesser Poland () of the UNESCO inscription are located in Binarowa, Blizne, Dębno, Nowy Targ County, Dębno, Haczów, Lipnica Murowana, and Sękowa (Lesser Poland Voivodeship or Małopolska). There are in fact many others of the region which fit the description: "The wooden churches of southern Little Poland represent outstanding examples of the different aspects of medieval church-building traditions in Roman Catholic Culture, Catholic culture. Built using the horizontal log technique, common in eastern and northern Europe since the Middle Ages..." The wooden church style of the region originated in the late Medieval, the late sixteenth century, and began with Gothic architecture, Gothic ornament and polychrome detail, but because they were timber construction, the structure, general form, and feeling is entirely different from the gothic architecture or Polish Gothic (in stone or brick). Later construction show Rococo and Baroque ornamental influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
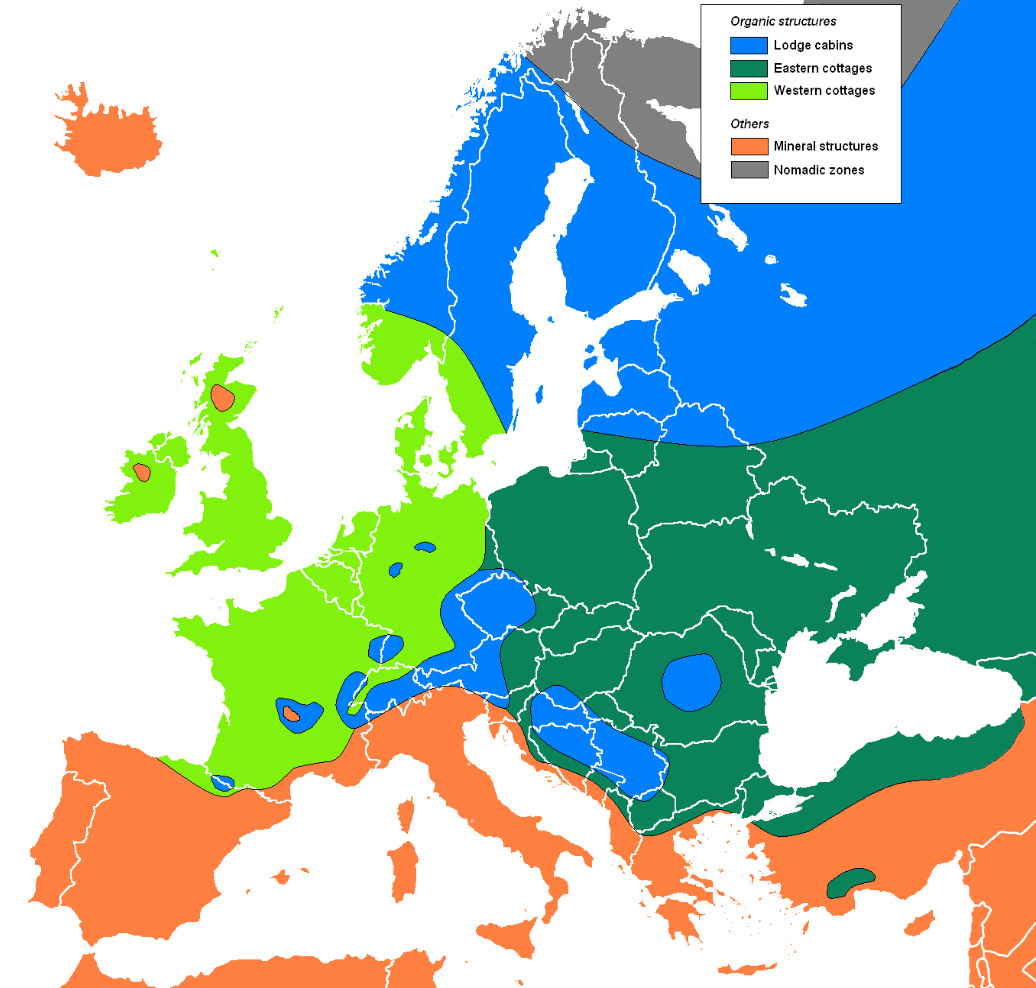
Vernacular Architecture Of The Carpathians
The vernacular architecture of the Carpathians draws on environmental and cultural sources to create unique designs. Vernacular architecture refers to non-professional, folk architecture, including that of the peasants. In the Carpathian Mountains and the surrounding foothills, wood and clay are the primary traditional building materials. Effect of culture and religion Eastern Christianity Because most Ukrainian, Rusyn, and Romanian people are Eastern Christians, their building techniques have traditionally incorporated religious considerations into their buildings that are distinct from their Western Christian and Jewish neighbours. Firstly, all churches are divided into three parts (the narthex, the nave, and the sanctuary) and include an iconostasis (a wall of icons). The outer shape is often cruciform (cross shaped), but will always include a central dome and often several other domes. Parishioners face east during worship and there are no pews. The main door and wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yasinia
Yasinia ( uk, Ясіня, hu, Körösmező, sk, Jasiňa) is an urban-type settlement in Rakhiv Raion of Zakarpattia Oblast in Ukraine. Population: . It was the site of the Hutsul Republic after World War I, and the birthplace of several prominent Ukrainians declaring independence from Kingdom of Hungary. This republic was ended by Romanian troops on June 11, 1919. Yasinia was shortly reoccupied by Hungary in July 1919 and passed to Czechoslovakia according to the Treaty of Trianon. During 1919-39, it was that country's easternmost settlement. Hungary again occupied and annexed it as part of Carpathian Ruthenia in 1939 and held it until the end of the war. It was given to the Soviet Union in 1945. The wooden church in Yasinia appears on several stamps of the area, including the first stamp of Carpatho-Ukraine. People from Yasinia * Daniel Ivancho * Stepan Klochurak * Orest Klympush See also * Kobyletska Poliana and Velykyi Bychkiv Velykyi Bychkiv ( uk, Вели� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rohatyn
Rohatyn ( uk, Рогатин, pl, Rohatyn) is a city located on the Hnyla Lypa River in Ivano-Frankivsk Raion, Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast, in western Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Rohatyn urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: . Prior to World War II the town was located in Poland. Name It was first mentioned in historical documents in 1184 as a part of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia. Its name seems to be derived from Ruthenia, the name of the region of the location. However, the town emblem has a horn of a deer which gives the first part of the Slavic name of Rohatyn or Rogatyn – "Rog" ("Horn"). The second part "Tyn" can be connected with a word which means " Stacket". Together these two words give us "Horn Stacket". Also, there is a legend connected with the image of the deer horn of the town emblem. It is said that a wife of the Duke Jaroslav Osmomysl, being lost in a forest, met a deer. She survived by following the deer out of the forest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |