|
Wood Bay Formation
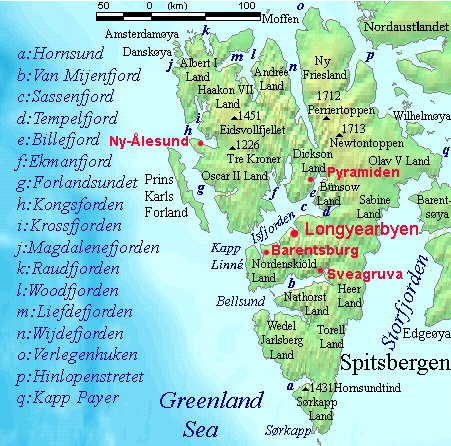
The Wood Bay Series is a geologic formation found on the island of Spitsbergen, Svalbard in Norway. It preserves fossils dating back to the Pragian–Emsian stages of the Devonian period. Fossil content Acanthodians Jawless fish Sarcopterygians See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Norway See also * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Europe ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Denmark ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Scotland See also *Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in ... References * Geologic formations of Norway Devonian System of Europe Devonian Norway {{Devonian-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation (stratigraphy)
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness (geology), thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplacanthus
''Diplacanthus'' is an extinct genus of Mid to Late Devonian fish in the class Acanthodii, known as spiny sharks. Classification The genus was named by Louis Agassiz in 1843. It was formerly regarded as belonging to the Climatiformes but recently reassigned to the Diplacanthiformes, in which it is united with, amongst others, ''Rhadinacanthu''s, '' Uraniacanthus'', and '' Culmacanthus''. Diplacanthiforms were widespread during the Middle and early Late Devonian. They are best represented in the Middle Devonian, by articulated fossils, fin spines, and abundant scales, the latter particularly from northern Europe. In a latest revision of the genus ''Diplacanthus,'' a large number of species from Europe were synonymized with earlier Scottish species, and these too were redefined. D. ''crassisimus'' was taken to have precedence over D. ''striatus'' as the name of the type specimen. ''Diplacanthus longispinus'' was reassigned to ''Rhadinacanthus longispinus'', within which we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Formations Of Norway
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of Eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fossiliferous Stratigraphic Units In Norway
See also * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Europe ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Denmark ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Scotland See also *Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Europe * Lists of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in the United Kingdom References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Scotland Scotland Scotland (, ) is a ... ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Svalbard ** List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Sweden References Bibliography * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Norway . * Norway Fossiliferous stratigraphic units ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
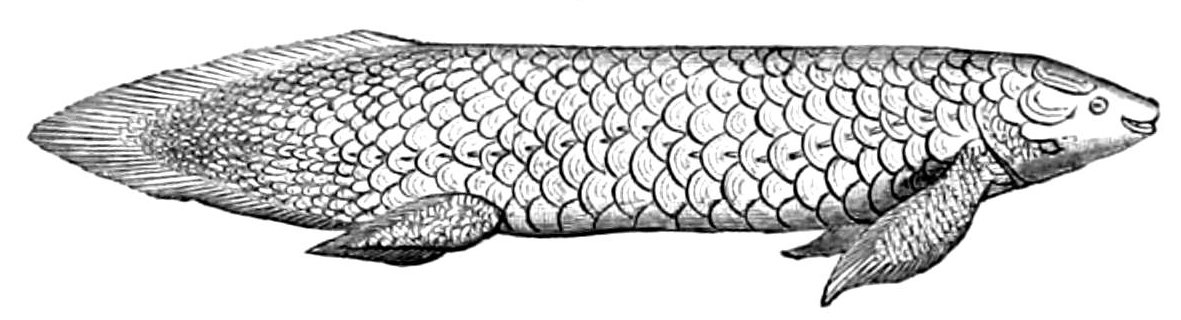
Lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, including the presence of lobed fins with a well-developed internal skeleton. Lungfish represent the closest living relatives of the tetrapods. Today there are only six known species of lungfish, living in Africa, South America, and Australia. The fossil record shows that lungfish were abundant since the Triassic. While vicariance would suggest this represents an ancient distribution limited to the Mesozoic supercontinent Gondwana, the fossil record suggests advanced lungfish had a widespread freshwater distribution and the current distribution of modern lungfish species reflects extinction of many lineages subsequent to the breakup of Pangaea, Gondwana and Laurasia. Lungfish have historically been referred to as salamanderfish, but this t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrée Land (Svalbard)
Andrée Land is the land area between Wijdefjorden and Woodfjorden on Spitsbergen, Svalbard in Arctic Norway. Limited in the south by a line from Woodfjorden through Vonbreen to Holtedahlfonna eastwards to the upper part of Abrahamsenbreen through Ruskbreen, Millarpasset, Lisbetbreen and Vestfjorddalen to Vestfjorden. The area is named after Swedish engineer and polar explorer Salomon August Andrée Salomon August Andrée (18 October 1854, in Gränna, Småland – October 1897, in Kvitøya, Arctic Norway), during his lifetime most often known as S. A. Andrée, was a Swedish engineer, physicist, aeronaut and polar explorer who died while .... References Geography of Svalbard Peninsulas of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipnoi
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, including the presence of lobed fins with a well-developed internal skeleton. Lungfish represent the closest living relatives of the tetrapods. Today there are only six known species of lungfish, living in Africa, South America, and Australia. The fossil record shows that lungfish were abundant since the Triassic. While vicariance would suggest this represents an ancient distribution limited to the Mesozoic supercontinent Gondwana, the fossil record suggests advanced lungfish had a widespread freshwater distribution and the current distribution of modern lungfish species reflects extinction of many lineages subsequent to the breakup of Pangaea, Gondwana and Laurasia. Lungfish have historically been referred to as salamanderfish, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcopterygii
Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass including amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (with mammals being the only extant group), evolved from certain sarcopterygians; under a cladistic view, tetrapods are themselves considered a subgroup within Sarcopterygii. The known extant non-tetrapod sarcopterygians include two species of coelacanths and six species of lungfishes. Characteristics Early lobe-finned fishes are bony fish with fleshy, lobed, paired fins, which are joined to the body by a single bone. The fins of lobe-finned fishes differ from those of all other fish in that each is borne on a fleshy, lobelike, scaly stalk extending from the body. The scales of sarcopterygians are true scaloids, consisting of lamellar bone sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doryaspis NT
''Doryaspis'' (from el, δόρῠ 'spear' and el, ἀσπίς 'shield') (also known by its synonym, "''Lyktaspis''") is an extinct genus of primitive jawless fish that lived in the Devonian period. Fossils have been discovered in Spitsbergen. The animals had canteen-shaped body armor and had large branchial plates that extended out and curved downward in a triangular shape, very similar to those of the pycnosteids. An element of the median oral plates (that would correspond to the lower lip or chin in gnathostomes) extends out in a long rod-shaped appendage, called the "pseudorostrum." The tail is long and slender and has large rows of thick scales. In the type species, ''D. nathorsti'', the lateral edges of the branchial plates and of the pseudorostrum are serrated. The second species, ''D. arctica'', is smaller, and lacks serrated edges. File:Doryaspis_arctica.JPG, Reconstruction of recently discovered species, ''D. arctica'' File:Doryaspis.jpg, Reconstruction of the typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doryaspis Arctica
''Doryaspis'' (from el, δόρῠ 'spear' and el, ἀσπίς 'shield') (also known by its synonym, "''Lyktaspis''") is an extinct genus of primitive jawless fish that lived in the Devonian period. Fossils have been discovered in Spitsbergen. The animals had canteen-shaped body armor and had large branchial plates that extended out and curved downward in a triangular shape, very similar to those of the pycnosteids. An element of the median oral plates (that would correspond to the lower lip or chin in gnathostomes) extends out in a long rod-shaped appendage, called the "pseudorostrum." The tail is long and slender and has large rows of thick scales. In the type species, ''D. nathorsti'', the lateral edges of the branchial plates and of the pseudorostrum are serrated. The second species, ''D. arctica'', is smaller, and lacks serrated edges. File:Doryaspis_arctica.JPG, Reconstruction of recently discovered species, ''D. arctica'' File:Doryaspis.jpg, Reconstruction of the typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |