|
Wonderful Bridges
The Marvelous Bridges or Wonderful Bridges ( bg, Чудни[те] мостове, ''Chudni[te] mostove'') are natural arches in the Rhodope Mountains of southern Bulgaria. They are located in the karst valley of the Erkyupriya River in the Western Rhodopes at metres above sea level, at the foot of Persenk Peak. Description The "bridges" were formed by the erosion, erosive activity of the once larger Erkyupryia River. It transformed the marble clefts into a deep-water cave, the ceiling of which eroded through time and collapsed, possibly during an earthquake. Geologists suggest that the water carried the debris away. As a result, the two remaining bridge-shaped outcrops remained. The larger one (upstream) is 15 metres at its widest and 96 metres long, and shaped by three vaulted arches, the largest of which is 45 metres high and 40 metres wide. The river flows under the middle-sized arch. The larger Wonderful Bridge is passable under the vaults, where birds nest in the marble cleft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Arch
A natural arch, natural bridge, or (less commonly) rock arch is a natural landform where an arch has formed with an opening underneath. Natural arches commonly form where inland cliffs, coastal cliffs, fins or stacks are subject to erosion from the sea, rivers or weathering ( subaerial processes). Most natural arches are formed from narrow fins and sea stacks composed of sandstone or limestone with steep, often vertical, cliff faces. The formations become narrower due to erosion over geologic time scales. The softer rock stratum erodes away creating rock shelters, or alcoves, on opposite sides of the formation beneath the relatively harder stratum, or caprock, above it. The alcoves erode further into the formation eventually meeting underneath the harder caprock layer, thus creating an arch. The erosional processes exploit weaknesses in the softer rock layers making cracks larger and removing material more quickly than the caprock; however, the caprock itself continues to er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
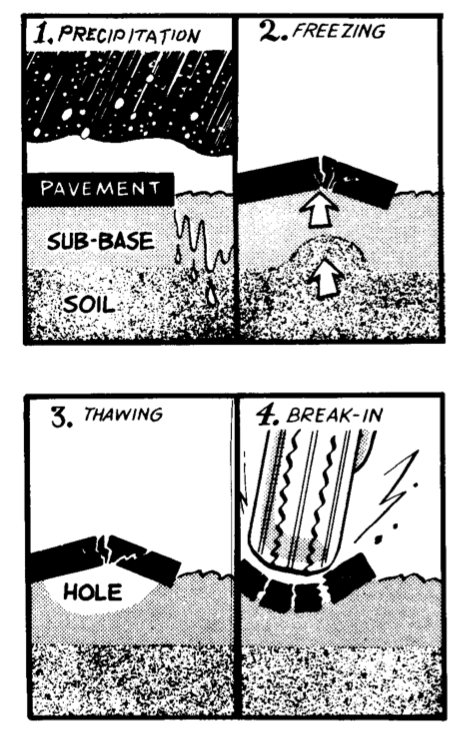
Pothole
A pothole is a depression in a road surface, usually asphalt pavement, where traffic has removed broken pieces of the pavement. It is usually the result of water in the underlying soil structure and traffic passing over the affected area. Water first weakens the underlying soil; traffic then fatigues and breaks the poorly supported asphalt surface in the affected area. Continued traffic action ejects both asphalt and the underlying soil material to create a hole in the pavement. Formation According to the US Army Corps of Engineers's Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, pothole formation requires two factors to be present at the same time: water and traffic. Water weakens the soil beneath the pavement while traffic applies the loads that stress the pavement past the breaking point. Potholes form progressively from fatigue of the road surface which can lead to a precursor failure pattern known as crocodile (or alligator) cracking. Eventually, chunks of pavement b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Smolyan Province
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Formations Of Bulgaria
Bulgaria is a country in south-eastern Europe situated in the north-eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula. The country has a great variety of topographical features and diverse landscape ranging from the Alpine snow-capped peaks in Rila, Pirin and the Balkan Mountains to the mild and sunny Black Sea coast; from the typically continental Danubian Plain in the north to the strong Mediterranean climatic influence in the valleys of Macedonia and the lowlands in the southernmost parts of Thrace. The diverse morphological, climatic and hydrological conditions of Bulgaria favour the formation of a large number of geological features. Partial list of rock formations in Bulgaria See also * Geography of Bulgaria *List of protected areas of Bulgaria * List of mountains in Bulgaria *List of caves in Bulgaria *List of islands of Bulgaria * List of lakes of Bulgaria Citations Sources References * External links * * {{Europe topic, List of rock formations in, UK_only=ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
100 Tourist Sites Of Bulgaria
100 Tourist Sites of Bulgaria is a Bulgarian national movement established in 1966 to promote tourism among Bulgaria's most significant cultural, historic, and natural landmarks. As part of this program, sites of cultural and historical significance have been selected, ranging from historic places and monuments to archaeological and architectural sanctuaries, museums, monasteries, as well as national parks, mountain peaks and other geological phenomena. Each of the chosen landmarks has its own individual seal, which is stamped onto pages of an official passport-like booklet issued by the Bulgarian Tourist Union (BTU). A booklet can be purchased at any tourist union center or on location at any of the sites and it costs a symbolic 1 lev. The booklet comes with a separate map which includes a list of the sites, their addresses and working hours. The maximum number of collectible stamps per booklet is 100 and, contrary to the movement's title, the exact number of official sites exce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chepelare
Chepelare ( bg, Чепеларе ) is the principal town in Chepelare Municipality, part of Smolyan Province in Southern Bulgaria. It is situated in the central part of the Rhodopes, on the banks of Chepelare River. Chepelare is a popular winter resort with one of the longest ski runs in Southeastern Europe. It is located near Pamporovo, one of the biggest Bulgarian ski resorts. As of December 2009, the town has a population of 5,412 inhabitants.Bulgarian National Statistical Institute - towns in 2009 The town is known for the only ski and snowboard factory in the . The factory cooperates with the ski brand '' |
Spruces
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Piceoideae. Spruces are large trees, from about 20 to 60 m (about 60–200 ft) tall when mature, and have whorled branches and conical form. They can be distinguished from other members of the pine family by their needles (leaves), which are four-sided and attached singly to small persistent peg-like structures (pulvini or sterigmata) on the branches, and by their cones (without any protruding bracts), which hang downwards after they are pollinated. The needles are shed when 4–10 years old, leaving the branches rough with the retained pegs. In other similar genera, the branches are fairly smooth. Spruce are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera (moth and butterfly) species, such as the eastern spruce b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conifers
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extant conifers are perennial woody plants with secondary growth. The great majority are trees, though a few are shrubs. Examples include cedars, Douglas-firs, cypresses, firs, junipers, kauri, larches, pines, hemlocks, redwoods, spruces, and yews.Campbell, Reece, "Phylum Coniferophyta". Biology. 7th. 2005. Print. P. 595 As of 1998, the division Pinophyta was estimated to contain eight families, 68 genera, and 629 living species. Although the total number of species is relatively small, conifers are ecologically important. They are the dominant plants over large areas of land, most notably the taiga of the Northern Hemisphere, but also in similar cool climates in mountains further south. Boreal conifers have many wintertime adaptations. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sump (cave)
A sump, or siphon, is a passage in a cave that is submerged under water. A sump may be static, with no inward or outward flow, or active, with continuous through-flow. Static sumps may also be connected underwater to active stream passage. When short in length, a sump may be called a duck, however this can also refer to a section or passage with some (minimal) airspace above the water. Depending on hydrological factors specific to a cave – such as the sea tide, changes in river flow, or the relationship with the local water table – sumps and ducks may fluctuate in water level and depth (and sometimes in length, due to the shape of adjacent passage). Exploration past a sump Diving Short sumps may be passed simply by holding one's breath while ducking through the submerged section (for example, Sump 1 in Swildon's Hole). This is known as "free diving" and can only be attempted if the sump is known to be short and not technically difficult (e.g. constricted or requiring nav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologists
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, although backgrounds in physics, chemistry, biology, and other sciences are also useful. Field research (field work) is an important component of geology, although many subdisciplines incorporate laboratory and digitalized work. Geologists can be classified in a larger group of scientists, called geoscientists. Geologists work in the energy and mining sectors searching for natural resources such as petroleum, natural gas, precious and base metals. They are also in the forefront of preventing and mitigating damage from natural hazards and disasters such as earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis and landslides. Their studies are used to warn the general public of the occurrence of these events. Geologists are also important contributors to climate chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
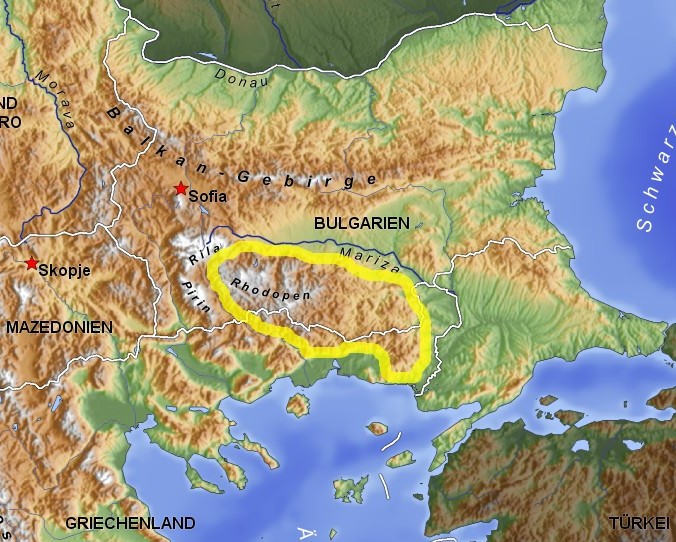
Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes (; bg, Родопи, ; el, Ροδόπη, ''Rodopi''; tr, Rodoplar) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at . The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge. A significant part of Bulgaria's hydropower resources are located in the western areas of the range. There are a number of hydro-cascades and dams used for electricity production, irrigation, and as tourist destinations. In Greece, there are also the hydroelectric power plants of Thisavros and Platanovrysi. The Rhodopes have a rich cultural heritage including a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called ''exogene'' caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called ''endogene'' caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as ''speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorgani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)