|
Wivenhoe Town F
Wivenhoe ( ) is a town and civil parish in north-eastern Essex, England, approximately south-east of Colchester. Historically Wivenhoe village, on the banks of the River Colne, and Wivenhoe Cross, on the higher ground to the north, were two separate settlements; however, with considerable development in the 19th century, the two have since merged. At the 2011 census, the town had a population of 7,637, compared with 7,221 in 2001. The town's history centres on fishing, ship building and smuggling. Much of lower Wivenhoe is also a designated conservation area, with many streets being of particular architectural interest. Etymology The place-name ''Wivenhoe'' is Saxon in origin, deriving from the personal name ''Wifa's'' or ''Wife's'' spur or promontory (hoe). The place-name is now usually pronounced 'Wivvenho', but the Essex accent would traditionally have rendered it as 'Wivvenhoo'. According to folk etymology, the name derived from "Wyvernhoe", originating from the mythic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colchester (borough)
The City of Colchester is a local government district with city status, in Essex, England, named after its main settlement, Colchester. The city covers an area of and stretches from Dedham Vale on the Suffolk border in the north to Mersea Island on the Colne Estuary in the south. The borough was formed on 1 April 1974 by the merger of the former borough of Colchester, covering an area of around , with the urban districts of West Mersea and Wivenhoe, along with Lexden and Winstree Rural District. Demography The ''Essex County Standard'' of September 4, 2009 said that "Government estimates" made Colchester the most populous district in the county: its officially acknowledged population is second highest among non-London boroughs, behind Northampton. According to the Office for National Statistics as of 2008, Colchester had a population of approximately 181,000. Average life expectancy was 78.7 for males. and 83.3 for females. Based on ethnic groups, predominantly of 92% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Miners' Strike (1984-1985)
UK miners' strike may refer to: *UK miners' strike (1893) *South Wales miners' strike (1910) * National coal strike of 1912 *UK miners' strike (1921) *UK miners' strike (1953) *UK miners' strike (1969), a widespread unofficial strike *UK miners' strike (1972) *UK miners' strike (1974), called by Margaret Thatcher *UK miners' strike (1984–85) The miners' strike of 1984–1985 was a major industrial action within the British coal industry in an attempt to prevent colliery closures. It was led by Arthur Scargill of the National Union of Mineworkers (NUM) against the National Coal Boar ..., led by Arthur Scargill of the NUM See also * 1926 United Kingdom general strike {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abellio Greater Anglia
Greater Anglia (legal name Abellio East Anglia Limited) is a train operating company in Great Britain owned as a joint venture by Abellio (transport company), Abellio, the international arm of the state-owned Dutch national rail operator Nederlandse Spoorwegen, and the Japanese trading company Mitsui & Co. It operates the East Anglia franchise, providing the commuter and intercity services from its Central London terminus at Liverpool Street railway station, London Liverpool Street to Essex, Suffolk, Norfolk and parts of Hertfordshire and Cambridgeshire as well as many regional services throughout the East of England. Abellio began operating the franchise, then known as the Greater Anglia franchise, in February 2012. Initially, it traded under the same name until it rebranded as Abellio Greater Anglia in December 2013. Shortly after taking over operations, the company initiated a series of projects to improve service levels, including the procurement of new trains and the launc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walton-on-the-Naze Railway Station
Walton-on-the-Naze railway station is one of the two eastern termini of the Sunshine Coast Line, a branch of the Great Eastern Main Line, in the East of England. It serves the seaside town of Walton-on-the-Naze, Essex. It is down the line from London Liverpool Street. Its three-letter station code is WON. The preceding station on the line is . The station was opened by the Tendring Hundred Railway, a subsidiary of the Great Eastern Railway, in 1867. It is currently managed by Greater Anglia, which also operates all trains serving the station. History The station was opened as Walton-on-Naze on 17 May 1867 by the Tendring Hundred Railway, then worked by the Great Eastern Railway (GER). The GER acquired the Tendring Hundred Railway and the adjacent Clacton-on-Sea Railway on 1 July 1883. The Wivenhoe & Brightlingsea line was also absorbed by the GER on 9 June 1893. The line later became part of the London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) in 1923 and then part of the Eastern Reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clacton Railway Station
Clacton-on-Sea railway station is one of the two eastern termini of the Sunshine Coast Line, a branch of the Great Eastern Main Line, in the East of England, serving the town of Clacton-on-Sea, Essex. It is down the line from London Liverpool Street. Its three-letter station code is CLT. The preceding station on the line is . The station was opened in 1882 with the name Clacton. It is currently managed by Greater Anglia, which also operates all trains serving the station. The branch diverges from the Great Eastern Main Line at whence trains run to either , or Clacton-on-Sea. Clacton is on a spur from Thorpe-le-Soken which was built by the Clacton-on-Sea Railway and originally operated by the Great Eastern Railway. It opened some 15 years after the branch to Walton was opened. On 1 January 1923 the station passed to the London and North Eastern Railway following the 1921 Railways Act. After World War II and following nationalisation, it fell under the auspices of British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colchester Railway Station
Colchester railway station (also known as Colchester North) is on the Great Eastern Main Line (GEML) in the East of England, and is the primary station serving the city of Colchester, Essex. Its three-letter station code is COL. It is down the line from London Liverpool Street and on the GEML is situated between to the west and to the east. Colchester is also the location of a major junction where the GEML links to the Sunshine Coast Line, which runs south to and, via a short branch, to ; services to and from also join the GEML at the Colchester junction. The junction is grade-separated so trains branching to and from Colchester Town or the Sunshine Coast Line do not cross the main line. Colchester station was opened in 1843 by the Eastern Counties Railway. It is currently managed by Greater Anglia, which also operates all trains serving the station. History The station was opened on 29 March 1843 by the Eastern Counties Railway (ECR) and was named simply as Colchester. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Eastern Main Line
The Great Eastern Main Line (GEML, sometimes referred to as the East Anglia Main Line) is a major railway line on the British railway system which connects Liverpool Street station in central London with destinations in east London and the East of England, including , , , and . Its numerous branches also connect the main line to , , , Harwich and a number of coastal towns including Southend-on-Sea, , and .National Rail, ''Rail Services Around London & the South East'', (2006) Its main users are commuters travelling to and from London, particularly the City of London, which is served by Liverpool Street, and areas in east London, including the Docklands financial district via the London Underground and Docklands Light Railway connections at Stratford. The line is also heavily used by leisure travellers, as it and its branches serve a number of seaside resorts, shopping areas and countryside destinations. The route also provides the main artery for substantial freight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
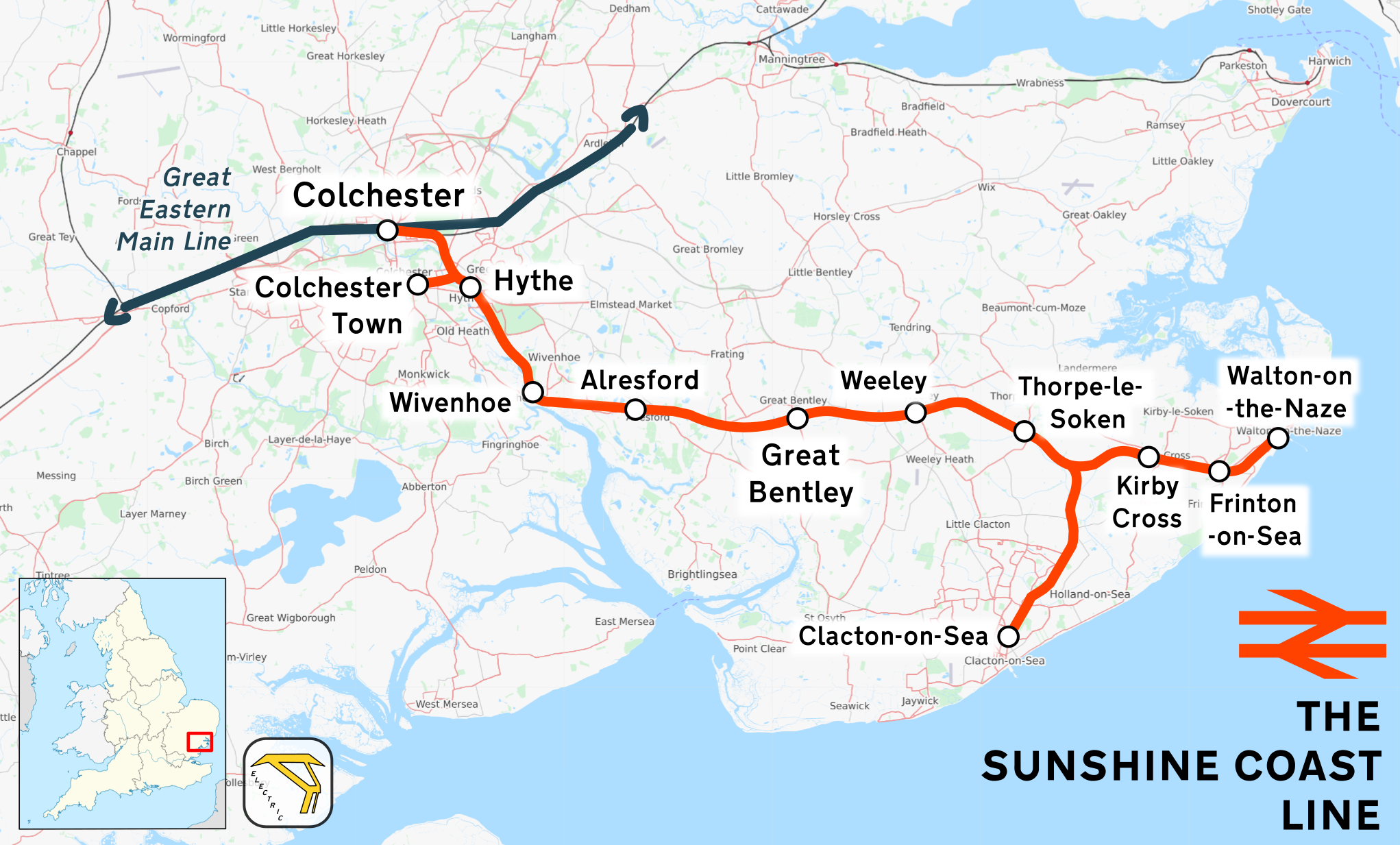
Sunshine Coast Line
The Sunshine Coast Line is the current marketing name of what originally was the Tendring Hundred Railway Line, a branch off the Great Eastern Main Line in the East of England. It links to the seaside resorts of and, via a branch, . The line is part of the Network Rail Strategic Route 7, SRS 07.08, and is classified as a London & South East commuter line. Passenger services on the line are currently operated by Greater Anglia. Trains for Clacton-on-Sea usually originate at London Liverpool Street, while those for Walton-on-the-Naze typically start at Colchester (or on Sundays). There are, however, limited morning and evening peak-time services in each direction between Walton-on-the-Naze and Liverpool Street. History Steam era The Great Eastern Main Line out of Shoreditch in London reached by 1843 and was extended to in 1846. The first short section of this branch line was built by the Colchester, Stour Valley, Sudbury & Halstead Railway to the port of , and ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wivenhoe Railway Station
Wivenhoe railway station is on the Sunshine Coast Line, a branch of the Great Eastern Main Line, in the East of England, serving the small town of Wivenhoe, Essex. It is down the line from London Liverpool Street and is situated between Hythe to the west and Alresford to the east. Its three-letter station code is WIV. The station was opened by the Tendring Hundred Railway, a subsidiary of the Great Eastern Railway, in 1863. It has two platforms, a staffed ticket office, and is currently operated by Abellio Greater Anglia, which also runs all trains serving the station. It is a short distance from the River Colne at Wivenhoe quay and its car park is the starting point of the Wivenhoe Trail, a cycle track that runs alongside the river to Colchester. History Wivenhoe station was opened on 8 May 1863 by the Tendring Hundred Railway, which was worked by the Great Eastern Railway. From July 1879 its name was spelt Wyvenhoe; in October 1911 it reverted to the original spelling, W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Constable
John Constable (; 11 June 1776 – 31 March 1837) was an English landscape painter in the Romanticism, Romantic tradition. Born in Suffolk, he is known principally for revolutionising the genre of landscape painting with his pictures of Dedham Vale, the area surrounding his home – now known as "Constable Country" – which he invested with an intensity of affection. "I should paint my own places best", he wrote to his friend John Fisher in 1821, "painting is but another word for feeling". Constable's most famous paintings include ''Wivenhoe Park (painting), Wivenhoe Park'' (1816), ''The Vale of Dedham (painting), Dedham Vale'' (1821) and ''The Hay Wain'' (1821). Although his paintings are now among the most popular and valuable in Art of the United Kingdom, British art, he was never financially successful. He became a member of the establishment after he was elected to the Royal Academy of Arts at the age of 52. His work was embraced in France, where he sold more than in his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Martin Rebow
Isaac Martin Rebow (28 November 1731 – 3 October 1781) was a British landowner and politician who sat in the House of Commons between 1755 and 1781. Early life Rebow was born on 28 November 1731, the son of Isaac Lemyng Rebow, MP and his wife Mary Martin, daughter of Captain Matthew Martin, MP. He was educated at Eton College from 1745 to 1748 and was admitted at Trinity College, Cambridge on 8 December 1748. He was awarded BA in 1753. He succeeded his father in 1735, inheriting Wivenhoe Park near Colchester, and in 1759 commissioned Thomas Reynolds to build a house there. Career In the 1754 general election Rebow stood for Parliament at Colchester and was defeated by a narrow margin. However the poll was conducted in a scandalous manner and Rebow was seated as Member of Parliament on petition in 1755. The main local issue was the loss of the Borough's charter and the campaign to regain it. The displaced member Charles Gray was chastened by the experience but in the 1761 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wivenhoe House
Wivenhoe House is a grade II-listed house located in Colchester, Essex. It is in use as a 4-star hotel. History Wivenhoe House's history began in 1759 when Isaac Rebow asked Thomas Reynolds to build the house. In 1816, owner Major-General Francis Slater Rebow commissioned John Constable to commit the house to canvas for the fee of 100 guineas. The painting, ''Wivenhoe Park'', is now displayed at the National Gallery of Art in Washington, D.C. This was the same General Rebow who returned from the Peninsular Wars with two cork oak cuttings in his boots. Today, those two oak trees stand proudly within the grounds. When General Rebow died in 1845 the estate passed to his son-in-law, future English Liberal Party MP John Gurdon Rebow. He commissioned the architect Thomas Hopper to remodel the House in 1846, and William Andrews Nesfield to advise on the relocation of the coach roads and entrances and to advise on the planting of the park and the flower garden. John Gurdon Rebo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_p62b_-_Colchester_railway_station_and_Essex_Hall_asylum.jpg)