|
Wishbone Scarp
The Wishbone scarp is a Pacific Ocean floor feature in the oceanic crust, that if it were on land would be similar to a mountain range fault system over long. It commences in the north near the Osbourn Trough although it is likely to be related tectonically to the Manihiki scarp somewhat to its north. To the south it splits into west and east scarps that have been intercepted by the Louisville hotspot with the West Wishbone scarp continuing until it intercepts the Chatham Rise. There is now evidence that the entire scarp has a fracture zone origin resolving previous uncertainty on this issue. To the east of the eastern scarp are the very deep Pacific mid ocean basins, while to the west of the western scarp we have the shallower but currently very tectonically active Hikurangi Margin. Geology To its north it can be related to the Manihiki Plateau which has a water depth between to , with the East Manihiki scarp which is a ridge that is up to above the Manihiki Platea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At , it is the largest tectonic plate. The plate first came into existence 190 million years ago, at the triple junction between the Farallon, Phoenix, and Izanagi Plates. The Pacific Plate subsequently grew to where it underlies most of the Pacific Ocean basin. This reduced the Farallon Plate to a few remnants along the west coast of North America and the Phoenix Plate to a small remnant near the Drake Passage, and destroyed the Izanagi Plate by subduction under Asia. The Pacific Plate contains an interior hot spot forming the Hawaiian Islands. Boundaries The north-eastern side is a divergent boundary with the Explorer Plate, the Juan de Fuca Plate and the Gorda Plate forming respectively the Explorer Ridge, the Juan de Fuca Ridge and the Gorda Ridge. In the middle of the eastern side is a transform boundary with the North American Plate along the San Andreas Fault, and a boundary with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages of break-up, involving the separation of Antarctica from South America (forming the Drake Passage) and Australia, occurred during the Paleogene. Gondwana was not considered a supercontinent by the earliest definition, since the landmasses of Baltica, Laurentia, and Siberia were separated from it. To differentiate it from the Indian region of the same name (see ), it is also commonly called Gondwanaland. Gondwana was formed by the accretion of several cratons. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Palaeozoic Era, covering an area of about , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. During the Carboniferous Period, it merged with Laurasia to form a larger supercontinent called Pangaea. Gondwana (and Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
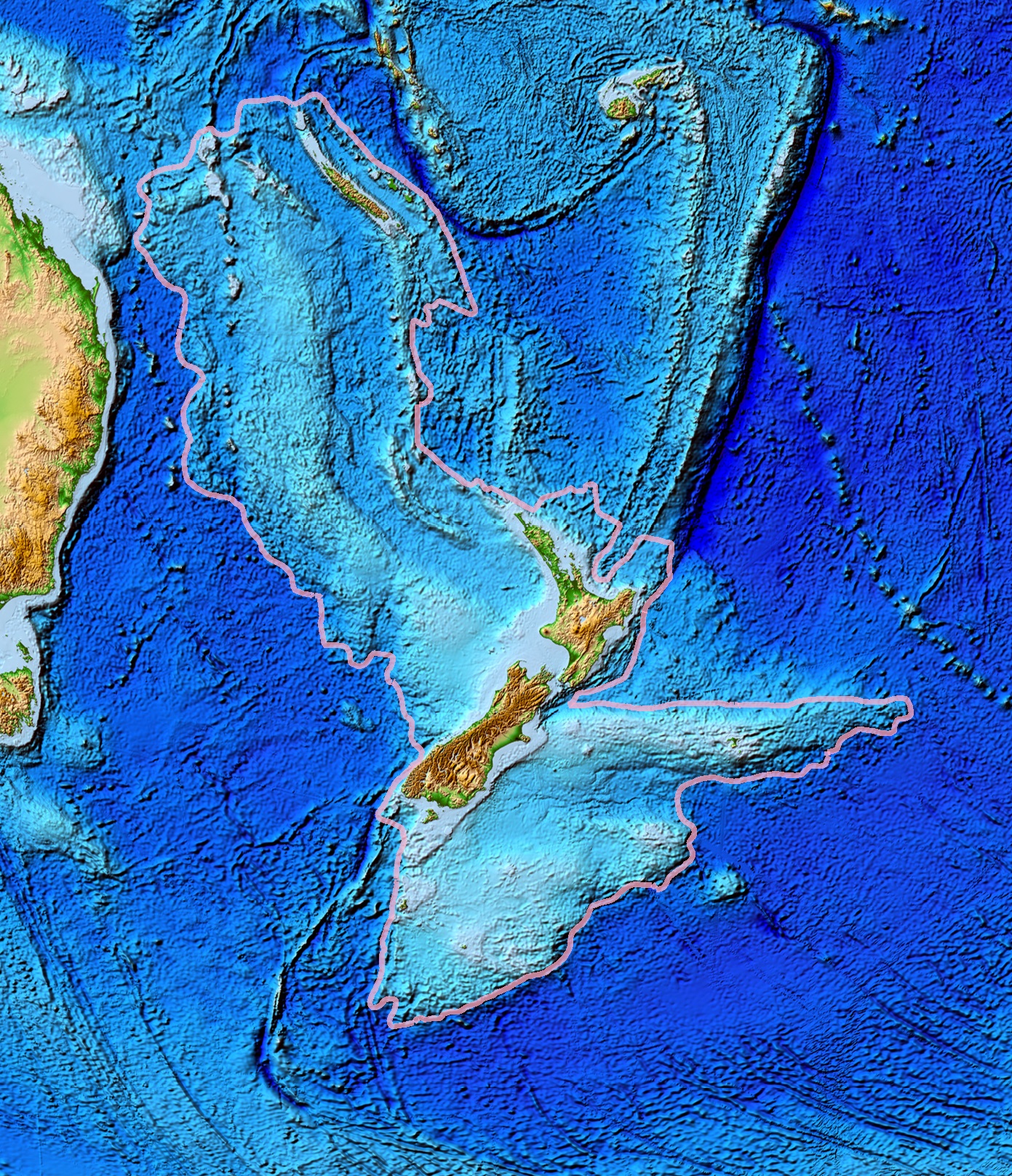
Geology Of Zealandia
Zealandia is an area of mostly submerged continental crust that contains New Zealand and New Caledonia. Geology The Zealandia continent is largely made up of two nearly parallel ridges, separated by a failed rift, where the rift breakup of the continent stops and becomes a filled graben. The ridges rise above the sea floor to heights of , with a few rocky islands rising above sea level. The ridges are continental rock, but are lower in elevation than normal continents because their crust is thinner than usual, approximately thick, and consequently, they do not float so high above Earth's mantle as that of most landmasses. About 25 million years ago, the southern part of Zealandia (on the Pacific Plate) began to shift relative to the northern part (on the Indo-Australian Plate). The resulting displacement by approximately along the Alpine Fault is evident in geological maps. Movement along this plate boundary also has offset the New Caledonia Basin from its previous con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
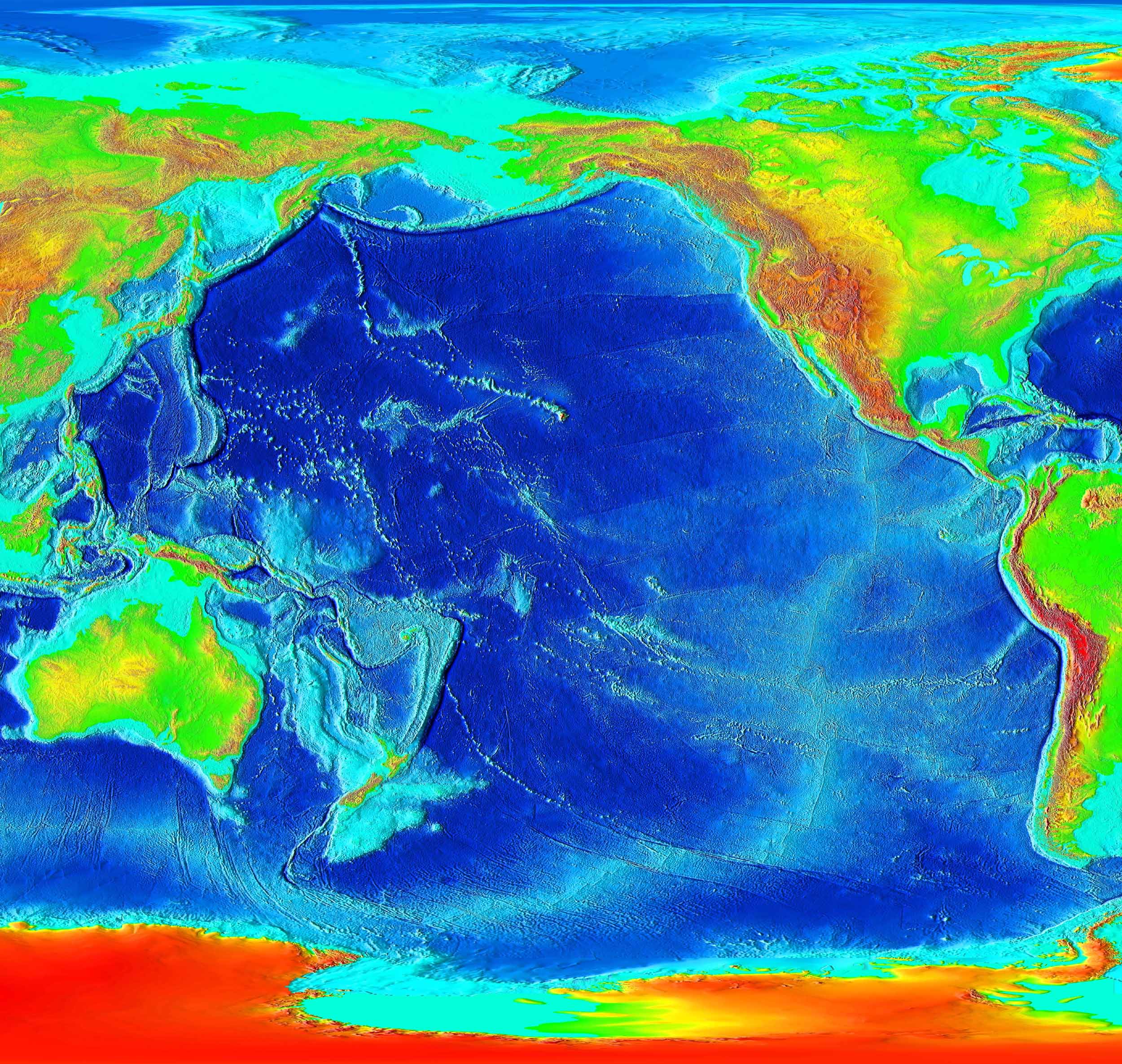
Geology Of The Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean evolved in the Mesozoic from the Panthalassic Ocean, which had formed when Rodinia rifted apart around 750 Ma. The first ocean floor which is part of the current Pacific Plate began 160 Ma to the west of the central Pacific and subsequently developed into the largest oceanic plate on Earth. The East Pacific Rise near Easter Island is the fastest spreading mid-ocean ridge, with a spreading rate of over 15 cm/yr. The Pacific Plate moves generally towards the northwest at between 7 and 11 cm/yr while the Juan De Fuca Plate has an east-northeasterly movement of some 4 cm/yr. Most subduction zones around the rim of the Pacific are directed away from a large area in the southern Pacific. At the core–mantle boundary below this area there is a large low-shear velocity province (LLSVP). Most of Pacific hotspots are located above the LLSVP while the longest Pacific hotspot tracks are located at or near its boundaries pointing at the positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kermadec Trench
The Kermadec Trench is a linear ocean trench in the south Pacific Ocean. It stretches about from the Louisville Seamount Chain in the north (26°S) to the Hikurangi Plateau in the south (37°S), north-east of New Zealand's North Island. Together with the Tonga Trench to the north, it forms the -long, near-linear Kermadec-Tonga subduction system, which began to evolve in the Eocene when the Pacific Plate started to subduct beneath the Australian Plate. Convergence rates along this subduction system are among the fastest on Earth, /yr in the north and /yr in the south. Geology The Kermadec Trench is one of Earth's deepest oceanic trenches, reaching a depth of . Formed by the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Indo-Australian Plate, it runs parallel with and to the east of the Kermadec Ridge and island arc. The Tonga Trench marks the continuation of subduction to the north. The Kermadec Trench has a southern continuation in the turbidite-filled Hikurangi Trough, but a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hikurangi Plateau
The Hikurangi Plateau is an oceanic plateau in the South Pacific Ocean east of the North Island of New Zealand. It is part of a large igneous province (LIP) together with Manihiki and Ontong Java, now located and north of Hikurangi respectively. Mount Hikurangi, in Māori mythology the first part of the North Island to emerge from the ocean, gave its name to the plateau. Geological setting The Hikurangi Plateau covers approximately and reaches below sea level. Hikurangi Plateau is cut by the Hikurangi Channel, a 2000 km abyssal channel that starts at Kaikoura and runs along the Hikurangi Trench as far as the Māhia Peninsula before crossing the plateau and ending in the South-west Pacific abyssal plain. Tectonic evolution Two models have been proposed for the formation of Hikurangi. It can be derived from the mantle plume that caused the break-up of Gondwana and the separation of Zealandia from Antarctica 107 Ma. Alternatively, it could have formed togeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontong Java Plateau
The Ontong Java Plateau (OJP) is a massive oceanic plateau located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, north of the Solomon Islands. The OJP was formed around (Ma) with a much smaller volcanic event around 90 Ma. Two other southwestern Pacific plateaus, Manihiki and Hikurangi, now separated from the OJP by Cretaceous oceanic basins, are of similar age and composition and probably formed as a single plateau and a contiguous large igneous province together with the OJP. When eruption of lava had finished, the Ontong Java–Manihiki–Hikurangi plateau covered 1% of Earth's surface and represented a volume of of basaltic magma. This "Ontong Java event", first proposed in 1991, represents the largest volcanic event of the past 200 million years, with a magma eruption rate estimated at up to per year over 3 million years, several times larger than the Deccan Traps. The smooth surface of the OJP is punctuated by seamounts such as the Ontong Java Atoll, one of the largest atolls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
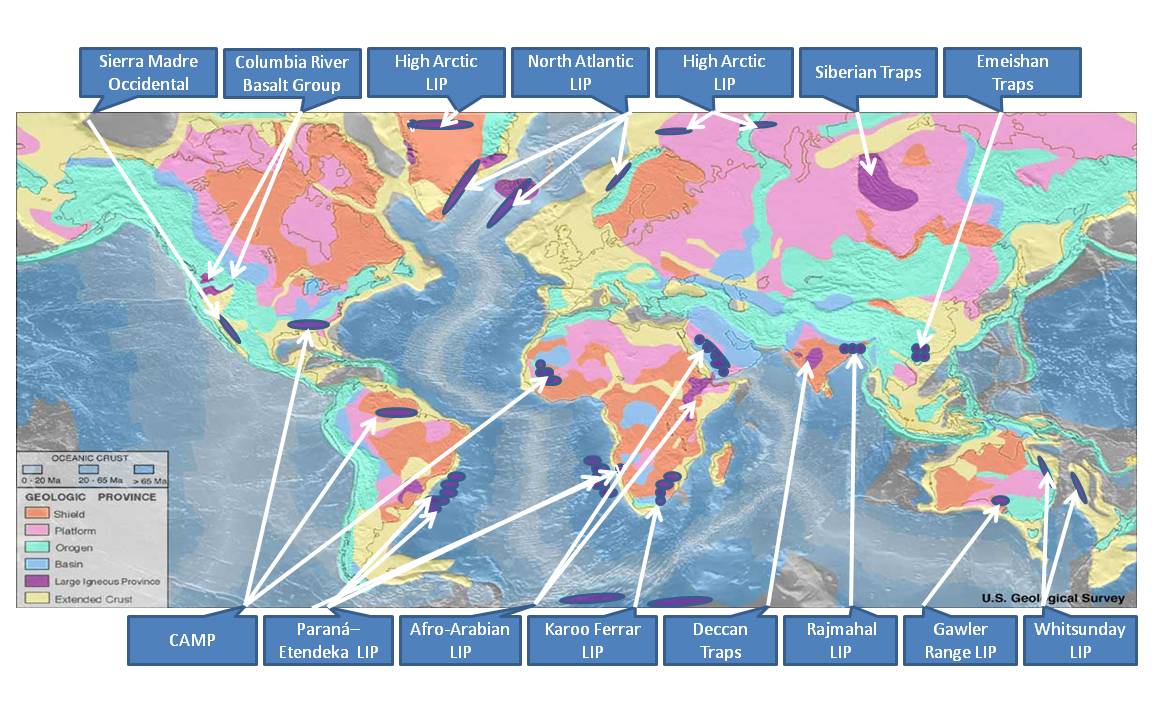
Large Igneous Province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with mass extinctions and rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems. Definition In 1992 researchers first used the term ''large igneous province'' to describe very large accumulations—areas greater than 100,000 square kilometers (approximately the area of Iceland)—of mafic igneous rocks that were erupted or emplaced at depth within an extremely short geological time interval: a few million years or less. Maf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenix Plate
The Phoenix Plate (also known as the Aluk Plate or Drake Plate) was a tectonic plate that existed during the early Paleozoic through late Cenozoic time. It formed a triple junction with the Izanagi and Farallon plates in the Panthalassa Ocean as early as 410 million years ago, during which time the Phoenix Plate was subducting under eastern Gondwana. By the Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous 150–130 million years ago, the Pacific Plate arose from the Izanagi-Farallon-Phoenix triple junction, resulting in the creation of the Izanagi-Pacific-Phoenix and Farallon-Pacific-Phoenix triple junctions. Subduction ceased east of Australia about 120 million years ago, during which time a transform/transpressional boundary formed. This transform/transpressional boundary with the Phoenix Plate lasted until about 80 million years ago as the plate continued to descend southwards as a result of Late Cretaceous subduction under the Antarctic Peninsula. During the Late Cretaceous o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean 180Ma
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Zealandia
Zealandia (pronounced ), also known as (Māori) or Tasmantis, is an almost entirely submerged mass of continental crust that subsided after breaking away from Gondwanaland 83–79 million years ago.Gurnis, M., Hall, C.E., and Lavier, L.L., 2004, Evolving force balance during incipient subduction: Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, v. 5, Q07001, https://doi.org/10.01029/02003GC000681 It has been described variously as a submerged continent, a continental fragment (or microcontinent), and a continent. The name and concept for Zealandia was proposed by Bruce Luyendyk in 1995, and satellite imagery shows it to be almost the size of Australia. A 2021 study suggests Zealandia is 1 billion years old, about twice as old as geologists previously thought. By approximately 23 million years ago the landmass may have been completely submerged. Today, most of the landmass (94%) remains submerged beneath the Pacific Ocean. New Zealand is the largest part of Zealandia that is above sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)