|
Winyaw People
The Winyaw were a Native American tribe living near Winyah Bay, Black River, and the lower course of the Pee Dee River in South Carolina. The Winyaw people disappeared as a distinct entity after 1720 and are thought to have merged with the Waccamaw. Name The meaning of the name ''Winyaw'' is unknown. Winyaw has also been written as Winyah, Weenee, and Wineaw. History The Winyaw might have been the Yenyohol mentioned in 1521 by Francisco de Chicora, a Native American captive held by the Spanish. If so, they may have been carried away during Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón's expedition during that same year. The Winyaw were first mentioned by colonists of South Carolina after 1670. The tribe at first allied with the English colonists who settled in Charles Town, but this friendship soon was shattered when European slave dealers instigated a war against them in 1683 as an excuse to capture slaves. During the Tuscarora War of 1711, John Barnwell brought 24 "Wineaws" on his expeditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winyah Bay
The Winyaw were a Native American tribe living near Winyah Bay, Black River, and the lower course of the Pee Dee River in South Carolina. The Winyaw people disappeared as a distinct entity after 1720 and are thought to have merged with the Waccamaw. Name The meaning of the name ''Winyaw'' is unknown. Winyaw has also been written as Winyah, Weenee, and Wineaw. History The Winyaw might have been the Yenyohol mentioned in 1521 by Francisco de Chicora, a Native American captive held by the Spanish. If so, they may have been carried away during Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón's expedition during that same year. The Winyaw were first mentioned by colonists of South Carolina after 1670. The tribe at first allied with the English colonists who settled in Charles Town, but this friendship soon was shattered when European slave dealers instigated a war against them in 1683 as an excuse to capture slaves. During the Tuscarora War of 1711, John Barnwell brought 24 "Wineaws" on his expedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucas Vázquez De Ayllón
Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón (c. 1480 – 18 October 1526) was a Spanish magistrate and explorer who in 1526 established the short-lived San Miguel de Gualdape colony, one of the first European attempts at a settlement in what is now the United States. Ayllón's account of the region inspired a number of later attempts by the Spanish and French governments to colonize the southeastern United States. Early life and education Ayllón was born in Toledo around 1480, the younger son of a prominent family whose roots traced back to a high-ranking ''mozarab'' judge in Islamic Spain. His parents were city councilman Juan Vázquez de Ayllón and Inés de Villalobos. Ayllón received a good education in law and his father's position gave him valuable insights into the practice of politics. In Hispaniola In 1502, the Spanish Monarchs sent Nicolás de Ovando to serve as governor of Hispaniola in the Indies. Ayllón accompanied Ovando's flotilla and arrived at the capital, Santo Domingo, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Native American Tribes
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no) , anthem = "Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind" , Former = Province of South Carolina , seat = Columbia , LargestCity = Charleston , LargestMetro = Greenville (combined and metro)Columbia (urban) , BorderingStates = Georgia, North Carolina , OfficialLang = English , population_demonym = List of U.S. state residents names, South Carolinian , Governor = , Lieutenant Governor = , Legislature = South Carolina General Assembly, General Assembly , Upperhouse = South Carolina Senate, Senate , Lowerhouse = South Carolina House of Representatives, House of Representatives , Judiciary = South Carolina Supreme Court , Senators = , Representative = 6 Republicans1 Democrat , postal_code = SC , TradAbbreviation = S.C. , area_rank = 40th , area_total_sq_mi = 32,020 , area_total_km2 = 82,932 , area_land_sq_mi = 30,109 , area_land_km2 = 77,982 , area_water_sq_mi = 1,911 , area_wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santee River
} The Santee River is a river in South Carolina in the United States, and is long. The Santee and its tributaries provide the principal drainage for the coastal areas of southeastern South Carolina and navigation for the central coastal plain of South Carolina, emptying into the Atlantic Ocean about halfway between Myrtle Beach and Charleston near the community of McClellanville. The farthest headwaters lie away on the Catawba River in North Carolina. Besides the Catawba, other principal rivers of the Santee watershed include the Congaree, Broad, Linville, Saluda and the Wateree. The watershed drains a large portion of the Piedmont regions of South and North Carolina. The Santee River is the second largest river on the eastern coast of the United States, second only to the Susquehanna River in drainage area and flow. Much of the upper river is impounded by the expansive, horn-shaped Lake Marion reservoir, formed by the -long Santee Dam. The dam was built during the Great D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
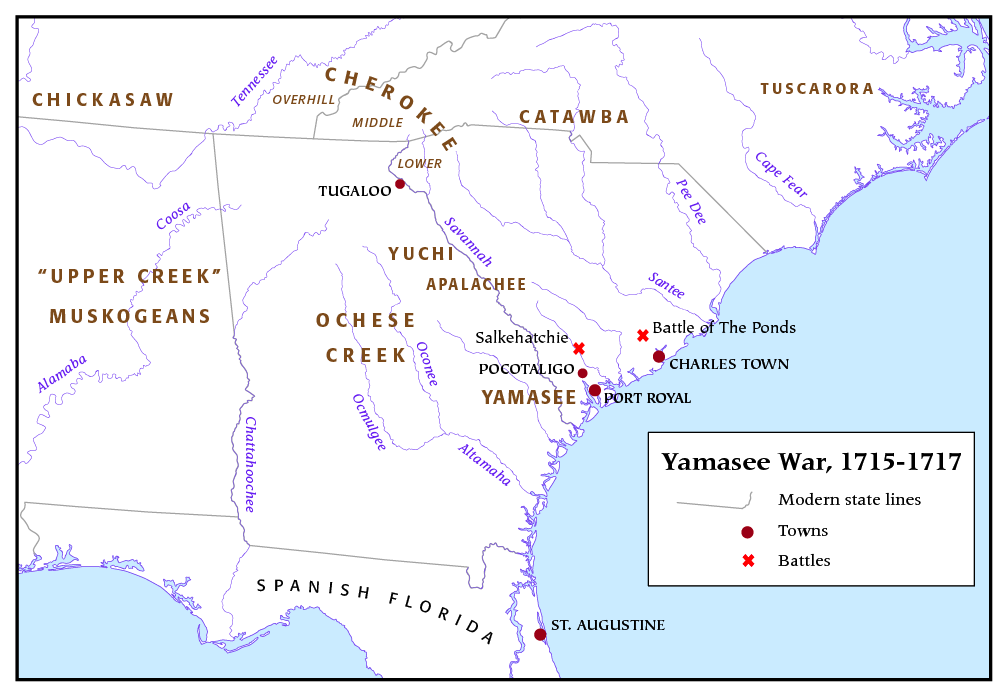
Yamasee War
The Yamasee War (also spelled Yamassee or Yemassee) was a conflict fought in South Carolina from 1715 to 1717 between British settlers from the Province of Carolina and the Yamasee and a number of other allied Native American peoples, including the Muscogee, Cherokee, Catawba, Apalachee, Apalachicola, Yuchi, Savannah River Shawnee, Congaree, Waxhaw, Pee Dee, Cape Fear, Cheraw, and others. Some of the Native American groups played a minor role, while others launched attacks throughout South Carolina in an attempt to destroy the colony. Native Americans killed hundreds of colonists and destroyed many settlements, and they killed traders throughout the southeastern region. Colonists abandoned the frontiers and fled to Charles Town, where starvation set in as supplies ran low. The survival of the South Carolina colony was in question during 1715. The tide turned in early 1716 when the Cherokee sided with the colonists against the Creek, their traditional enemy. The last Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheraw
The Cheraw people, also known as the Saraw or Saura, were a Siouan-speaking tribe of indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, in the Piedmont area of North Carolina near the Sauratown Mountains, east of Pilot Mountain and north of the Yadkin River. They lived in villages near the Catawba River.Rudes ''et al.'' 310 Their first European and African contact was with the Hernando De Soto Expedition in 1540. The early explorer John Lawson included them in the larger eastern-Siouan confederacy, which he called "the Esaw Nation."''Handbook of the American Indian North of Mexico'', 1906 After attacks in the late 17th century and early 18th century, they moved to the southeast around the Pee Dee River, where the Cheraw name became more widely used. They became extinct as a tribe, although some descendants survived as remnant peoples. Name Originally known as the Saraw, they became known by the name of one of their villages, Cheraw.Demallie 296 They are also known as the Chará ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuscarora War
The Tuscarora War was fought in North Carolina from September 10, 1711 until February 11, 1715 between the Tuscarora people and their allies on one side and European American settlers, the Yamassee, and other allies on the other. This was considered the bloodiest colonial war in North Carolina. The Tuscarora signed a treaty with colonial officials in 1718 and settled on a reserved tract of land in Bertie County, North Carolina. The war incited further conflict on the part of the Tuscarora and led to changes in the slave trade of North and South Carolina. The first successful settlement of North Carolina began in 1653. The Tuscarora lived in peace with the settlers for more than 50 years, while nearly every other colony in America was involved in some conflict with Native Americans. Most of the Tuscarora migrated north to New York after the war, where they joined the Five Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy as the sixth nation. History The Tuscarora were an Iroquoian-speaking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francisco De Chicora
Francisco de Chicora was the baptismal name given to a Native American kidnapped in 1521, along with 70 others, from near Winyah Bay by Spanish explorer Francisco Gordillo and slave trader Pedro de Quexos, based in Santo Domingo and the first Europeans to reach the area. From analysis of the account by Peter Martyr, court chronicler, the ethnographer John R. Swanton believed that Chicora was from a Catawban group. In Hispaniola, where he and the other captives were taken, Chicora learned Spanish, was baptized a Catholic, and worked for Lucas Vasquez de Ayllón, a colonial official. Most of the natives died within two years. Accompanying Ayllón to Spain, de Chicora met with the chronicler Peter Martyr and told him much about his people. Martyr combined this information with accounts by explorers and recorded it as the "Testimony of Francisco de Chicora," published with his seventh ''Decade'' in 1525. In 1526 Chicora accompanied Ayllón on a major expedition to North America w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black River (South Carolina)
The Black River is a blackwater river in South Carolina in the United States. It courses through Sumter, Clarendon, and Williamsburg counties before merging with the Great Pee Dee River in Georgetown County Georgetown County is a county located in the U.S. state of South Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 63,404. Its county seat is Georgetown. The county was founded in 1769. It is named for George III of the United Kingdom. Georg .... The river was called the Wee Nee by the Native Americans who once inhabited the area. In June 2001, a 75-mile segment of the river was designated a State Scenic River. See also * List of South Carolina rivers * Mansfield Plantation References Rivers of South Carolina Tributaries of the Pee Dee River Rivers of Williamsburg County, South Carolina Rivers of Georgetown County, South Carolina Rivers of Clarendon County, South Carolina Rivers of Sumter County, South Carolina Rivers of Lee County, South Carolina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans In The United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States (Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United States are generally known by other terms). There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. As defined by the United States Census, "Native Americans" are Indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives. Indigenous peoples of the United States who are not listed as American Indian or Alaska Native include Native Hawaiians, Samoan Americans, and the Chamorro people. The US Census groups these peoples as " Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islanders". European colonization of the Americas, which began in 1492, resulted in a precipitous decline in Native American population because of new diseases, wars, ethnic cleansin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waccamaw
The Waccamaw people were an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, who lived in villages along the Waccamaw and Pee Dee rivers in North and South Carolina in the 18th century.Lerch 328 Language Very little remains of the Waccamaw's ancestral Woccon language today, it was one of the two Catawban branches of the Siouan language family. The language was lost due to devastating population losses and social disruptions during the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. It is attested today in a vocabulary of 143 words, printed in 1709. History While the Waccamaw were never populous, the arrival of settlers and their diseases in the 16th century resulted in devastating population loss and dispersal. In 1600, anthropologist James Mooney estimated the population of the "Waccamaw, Winyaw, Hook, &c" at 900 people, while the 1715 census registers only one remaining Waccamaw village with a total population of 106 people, 36 of them men. According to the early 20th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)