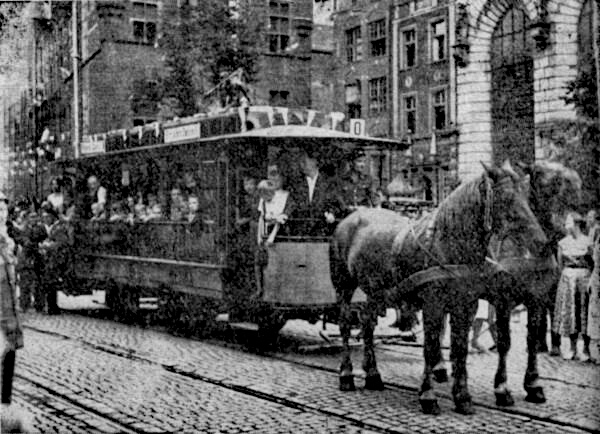|
Winter Service Vehicle
A winter service vehicle (WSV), or snow removal vehicle, is a vehicle specially designed or adapted to clear thoroughfares of ice and snow. Winter service vehicles are usually based on a dump truck chassis, with adaptations allowing them to carry specially designed snow removal equipment. Many authorities also use smaller vehicles on sidewalks, footpaths, and cycleways. Road maintenance agencies and contractors in temperate or polar areas often own several winter service vehicles, using them to keep the roads clear of snow and ice and safe for driving during winter. Airports use winter service vehicles to keep both aircraft surfaces, and runways and taxiways free of snow and ice, which, besides endangering aircraft takeoff and landing, can interfere with the aerodynamics of the craft. The earliest winter service vehicles were snow rollers, designed to maintain a smooth, even road surface for sleds, although horse-drawn snowplows and gritting vehicles are recorded in use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landing
Landing is the last part of a flight, where a flying animal, aircraft, or spacecraft returns to the ground. When the flying object returns to water, the process is called alighting, although it is commonly called "landing", "touchdown" or "splashdown" as well. A normal aircraft flight would include several parts of flight including taxi, takeoff, climb, cruise, descent and landing. Aircraft Aircraft usually land at an airport on a firm runway or helicopter landing pad, generally constructed of asphalt concrete, concrete, gravel or grass. Aircraft equipped with pontoons (floatplane) or with a boat hull-shaped fuselage (a flying boat) are able to land on water. Aircraft also sometimes use skis to land on snow or ice. To land, the airspeed and the rate of descent are reduced such that the object descends at a low enough rate to allow for a gentle touch down. Landing is accomplished by slowing down and descending to the runway. This speed reduction is accomplished by re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County, Wisconsin, Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, Milwaukee is the List of United States cities by population, 31st largest city in the United States, the fifth-largest city in the Midwestern United States, and the second largest city on Lake Michigan's shore behind Chicago. It is the main cultural and economic center of the Milwaukee metropolitan area, the fourth-most densely populated metropolitan area in the Midwestern United States, Midwest. Milwaukee is considered a global city, categorized as "Gamma minus" by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network, with a regional List of U.S. metropolitan areas by GDP, GDP of over $102 billion in 2020. Today, Milwaukee is one of the most ethnicity, ethnically and Cultural diversity, cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavement (material)
A road surface (British English), or pavement (American English), is the durable surface material laid down on an area intended to sustain vehicular or foot traffic, such as a road A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation. There are many types of ... or walkway. In the past, gravel road surfaces, hoggin, cobblestone and sett (paving), granite setts were extensively used, but these have mostly been replaced by asphalt or concrete laid on a compacted base course. Asphalt mixtures have been used in pavement construction since the beginning of the 20th century and are of two types: metalled (hard-surfaced) and unmetalled roads. Metalled roadways are made to sustain vehicular load and so are usually made on frequently used roads. Unmetalled roads, also known as gravel roads, are rough and can sustai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal-powered Transport
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to animal-powered transport: Animal-powered transport – broad category of the human use of non-human working animals (also known as "beasts of burden") for the movement of people and goods. Humans may ride some of the larger of these animals directly on their backs, use them as pack animals for carrying goods, or harness them, singly or in teams, to pull (or haul) sleds or wheeled vehicles. Animals domesticated for transport Terrestrial * camel, Arabian, and Bactrian * carabao * deer * dog ** sled dog ** Dogcart (dog-drawn) * elephant * equine ** donkey ** mule ** hinny ** horse *** pack horse *** draught horse *** riding horse *** coach horse * llama * moose * ostrich * ox * reindeer * sheep * yak Amphibious * Turtles were used for riding as a sport in early 20th-century Australia Marine * Dolphins (to carry markers to attach to detected mines) Aerial * Pigeon (for carryin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
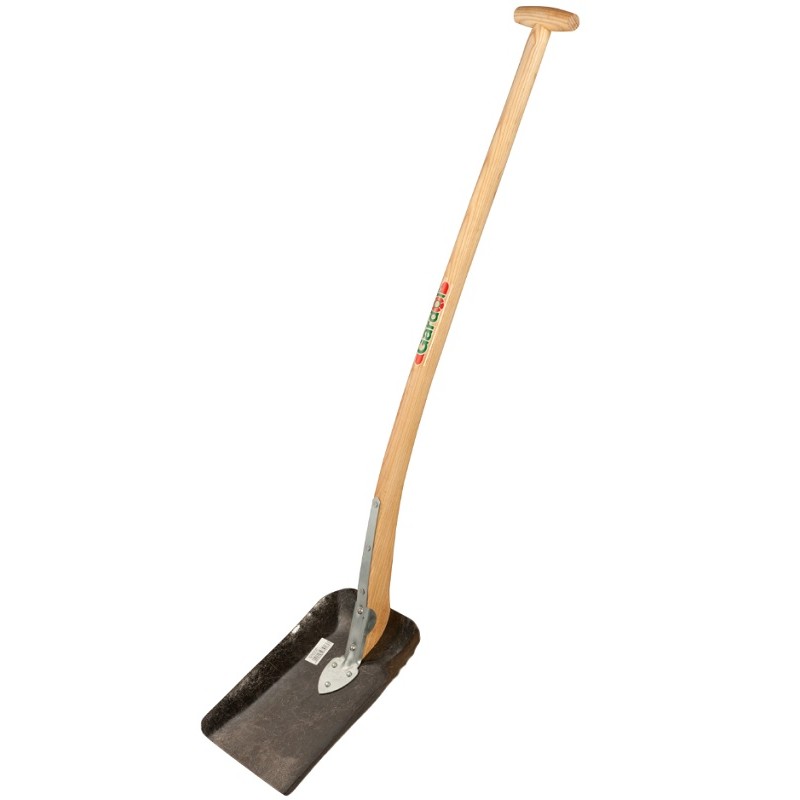
Shovel
A shovel is a tool used for digging, lifting, and moving bulk materials, such as soil, coal, gravel, snow, sand, or ore. Most shovels are hand tools consisting of a broad blade fixed to a medium-length handle. Shovel blades are usually made of sheet steel or hard plastics and are very strong. Shovel handles are usually made of wood (especially specific varieties such as ash or maple) or glass-reinforced plastic (fiberglass). Hand shovel blades made of sheet steel usually have a folded seam or hem at the back to make a socket for the handle. This fold also commonly provides extra rigidity to the blade. The handles are usually riveted in place. A T-piece is commonly fitted to the end of the handle to aid grip and control where the shovel is designed for moving soil and heavy materials. These designs can all be easily mass-produced. The term ''shovel'' also applies to larger excavating machines called power shovels, which serve the same purpose—digging, lifting, and moving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Early may refer to: History * The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.: ** Early Christianity ** Early modern Europe Places in the United States * Early, Iowa * Early, Texas * Early ..., High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Snow And Ice Data Center
The National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) is a United States information and referral center in support of polar and cryospheric research. NSIDC archives and distributes digital and analog snow and ice data and also maintains information about snow cover, avalanches, glaciers, ice sheets, freshwater ice, sea ice, ground ice, permafrost, atmospheric ice, paleo glaciology, and ice cores. NSIDC is part of the University of Colorado Boulder Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES), and is affiliated with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) National Centers for Environmental Information through a cooperative agreement. NSIDC serves as one of twelve Distributed Active Archive Centers funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration to archive and distribute data from NASA's past and current satellites and field measurement programs. NSIDC also supports the National Science Foundation through the Exchange For L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowplow
A snowplow (also snow plow, snowplough or snow plough) is a device intended for mounting on a vehicle, used for removing snow and ice from outdoor surfaces, typically those serving transportation purposes. Although this term is often used to refer to vehicles mounting such devices, more accurately they are known as winter service vehicles, especially in areas that regularly receive large amounts of snow every year, or in specific environments such as airfields. In other cases, pickup trucks and front end loaders are outfitted with attachments to fulfill this purpose. Some regions that do not frequently see snow may use graders to remove compacted snow and ice off the streets. Snowplows can also be mounted on rail cars or locomotives to clear railway tracks. Usage A snowplow works by using a blade to push snow to the side to clear it from a surface. Modern plows may include technology to make it easier to perform the work and stay on the road. These include Global Positioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse-drawn Vehicle
A horse-drawn vehicle is a mechanized piece of equipment pulled by one horse or by a team of horses. These vehicles typically had two or four wheels and were used to carry passengers and/or a load. They were once common worldwide, but they have mostly been replaced by automobiles and other forms of self-propelled transport. General Horses were domesticated circa 3500 BCE. Prior to that oxen were used. Historically a wide variety of arrangements of horses and vehicles have been used, from chariot racing, which involved a small vehicle and four horses abreast, to horsecars or trollies, which used two horses to pull a car that was used in cities before electric trams were developed. A two-wheeled horse-drawn vehicle is a cart (see various types below, both for carrying people and for goods). Four-wheeled vehicles have many names – one for heavy loads is most commonly called a wagon. Very light carts and wagons can also be pulled by donkeys (much smaller than horses), p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sled
A sled, skid, sledge, or sleigh is a land vehicle that slides across a surface, usually of ice or snow. It is built with either a smooth underside or a separate body supported by two or more smooth, relatively narrow, longitudinal runners similar in principle to skis. This reduces the amount of friction, which helps to carry heavy loads. Some designs are used to transport passengers or cargo across relatively level ground. Others are designed to go downhill for recreation, particularly by children, or competition. (Compare cross-country skiing with its downhill cousin.) Shades of meaning differentiating the three terms often reflect regional variations depending on historical uses and prevailing climate. In British English, ''sledge'' is the general term, and more common than ''sled''. '' Toboggan'' is sometimes used synonymously with ''sledge'' but more often to refer to a particular type of sledge without runners. ''Sleigh'' refers to a moderate to large-sized, usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |