|
Windows NT 6.1
Windows NT is a proprietary graphical operating system produced by Microsoft, the first version of which was released on July 27, 1993. It is a processor-independent, multiprocessing and multi-user operating system. The first version of Windows NT was Windows NT 3.1 and was produced for workstations and server computers. It was a commercially focused operating system intended to complement consumer versions of Windows that were based on MS-DOS (including Windows 1.0 through Windows 3.1x). Gradually, the Windows NT family was expanded into Microsoft's general-purpose operating system product line for all personal computers, deprecating the Windows 9x family. "NT" was formerly expanded to "New Technology" but no longer carries any specific meaning. Starting with Windows 2000, "NT" was removed from the product name and is only included in the product version string along with several low-level places within the system. In fact, NT was a trademark of Northern Telecom (later Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washington, United States. Its best-known software products are the Windows line of operating systems, the Microsoft Office suite, and the Internet Explorer and Edge web browsers. Its flagship hardware products are the Xbox video game consoles and the Microsoft Surface lineup of touchscreen personal computers. Microsoft ranked No. 21 in the 2020 Fortune 500 rankings of the largest United States corporations by total revenue; it was the world's largest software maker by revenue as of 2019. It is one of the Big Five American information technology companies, alongside Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, and Meta. Microsoft was founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen on April 4, 1975, to develop and sell BASIC interpreters for the Altair 8800. It rose to do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
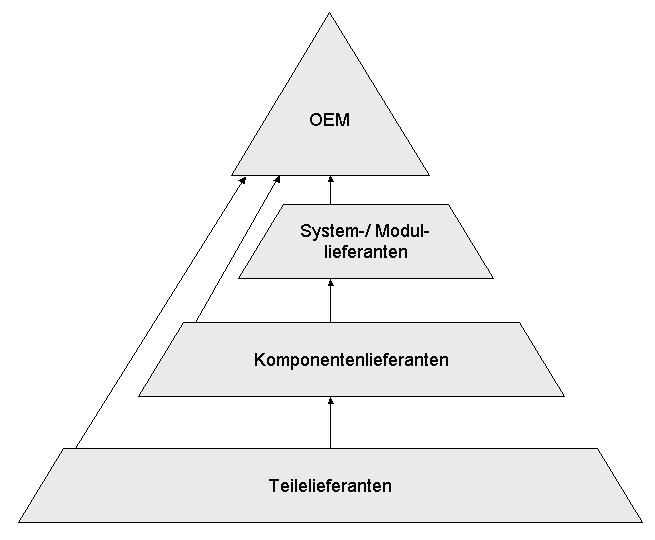
Original Equipment Manufacturer
An original equipment manufacturer (OEM) is generally perceived as a company that produces non-aftermarket parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. It is a common industry term recognized and used by many professional organizations such as SAE International, ISO, and others. However, the term is also used in several other ways, which causes ambiguity. It sometimes means the maker of a system that includes other companies' subsystems, an end-product producer, an automotive part that is manufactured by the same company that produced the original part used in the automobile's assembly, or a value-added reseller.Ken Olsen: PDP-1 and PDP-8 (page 3) , economicadventure.com Automotive parts When referring to auto parts, OEM refers to the manufactur ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C Sharp (programming Language)
C# (pronounced ) is a general-purpose, high-level multi-paradigm programming language. C# encompasses static typing, strong typing, lexically scoped, imperative, declarative, functional, generic, object-oriented (class-based), and component-oriented programming disciplines. The C# programming language was designed by Anders Hejlsberg from Microsoft in 2000 and was later approved as an international standard by Ecma (ECMA-334) in 2002 and ISO/IEC (ISO/IEC 23270) in 2003. Microsoft introduced C# along with .NET Framework and Visual Studio, both of which were closed-source. At the time, Microsoft had no open-source products. Four years later, in 2004, a free and open-source project called Mono began, providing a cross-platform compiler and runtime environment for the C# programming language. A decade later, Microsoft released Visual Studio Code (code editor), Roslyn (compiler), and the unified .NET platform (software framework), all of which support C# and are free, open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assembly Language
In computer programming, assembly language (or assembler language, or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as Assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language usually has one statement per machine instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported. The first assembly code in which a language is used to represent machine code instructions is found in Kathleen and Andrew Donald Booth's 1947 work, ''Coding for A.R.C.''. Assembly code is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an ''assembler''. The term "assembler" is generally attributed to Wilkes, Wheeler and Gill in their 1951 book ''The Preparation of Programs for an Electronic Digital Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced like the letter c'') is a General-purpose language, general-purpose computer programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie, and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems, device drivers, protocol stacks, though decreasingly for application software. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the measuring programming language popularity, most widely used programming languages, with C compilers avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shared Source Initiative
The Shared Source Initiative (SSI) is a source-available software licensing scheme launched by Microsoft in May 2001. The program includes a spectrum of technologies and licenses, and most of its source code offerings are available for download after eligibility criteria are met. Overview Microsoft's Shared Source Initiative allows individuals and organizations to access Microsoft's source code for reference (e.g. when developing complementary systems), for review and auditing from a security perspective (mostly wanted by some large corporations and governments), and for development (academic institutions, OEMs, individual developers). As part of the framework, Microsoft released 5 licenses for general use. Two of them, Microsoft Public License and Microsoft Reciprocal License, have been approved by the Open Source Initiative as open source licenses and are regarded by the Free Software Foundation as free software licenses. Other shared source licenses are proprietary, and thus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Source-available Software
Source-available software is software released through a source code distribution model that includes arrangements where the source can be viewed, and in some cases modified, but without necessarily meeting the criteria to be called open-source. The licenses associated with the offerings range from allowing code to be viewed for reference to allowing code to be modified and redistributed for both commercial and non-commercial purposes. Distinction from free and open-source software Any software is source-available software as long its source code is distributed along with it, even if the user has no legal rights to use, share, modify or even compile it. It is possible for a software to be both source-available software and proprietary software (For example: Id Software Doom). In contrast, the definitions of free software and open-source software are much narrower. Free software and/or open-source software is also always ''source-available software'', but not all source-avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proprietary Software
Proprietary software is software that is deemed within the free and open-source software to be non-free because its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner exercises a legal monopoly afforded by modern copyright and intellectual property law to exclude the recipient from freely sharing the software or modifying it, and—in some cases, as is the case with some patent-encumbered and EULA-bound software—from making use of the software on their own, thereby restricting his or her freedoms. It is often contrasted with open-source or free software. For this reason, it is also known as non-free software or closed-source software. Types Origin Until the late 1960s computers—large and expensive mainframe computers, machines in specially air-conditioned computer rooms—were usually leased to customers rather than sold. Service and all software available were usually supplied by manufacturers without separate charge until 1969. Computer vendors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Client Access License
A client access license (CAL) is a commercial software license that allows client computers to use server software services. Most commercial desktop apps are licensed so that payment is required for each installation, but some server products can be licensed so that payment is required for each device or user that accesses the service provided by the software. For example, an instance of Windows Server 2016 for which ten User CALs are purchased allows 10 distinct users to access the server. Licensing Commercial apps are licensed to end users or businesses: in a legally binding agreement between the proprietor of the software (the "licensor") and the end user or business (the "licensee"), the licensor gives permission to the licensee to use the app under certain limitations, which are set forth in the license agreement. In case of Microsoft, the consumer retail or "off-the-shelf" products generally use very similar licence agreements, allowing the licensee to use the software on on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BizSpark
Microsoft for Startups, formerly known as Microsoft BizSpark, is a Microsoft program that provides support, Azure credits and free licenses to selected Microsoft products to software Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work. At the lowest programming level, executable code consists ... entrepreneurs and start ups. providing the benefits and the perks to the selected members of this program for a term of 3 years. Microsoft launched ''BizSpark One'' in 2009 as an enhanced service for selected startups. The BizSpark program was discontinued on February 14, 2018. and replaced by the Microsoft for Startups program. In October 2021 a new hub for Founders was added providing improved oversight of benefits and the startup company profile. References External linksMicrosoft for Startups site [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DreamSpark Premium
Microsoft Azure Dev Tools for Teaching or simply Azure Dev Tools for Teaching is a Microsoft program to provide students with Microsoft software design, Microsoft developer tools, Cloud Computing Access and learning resources. The program is available for university/college and K-12 students Azure for Student and Azure Dev Tools for teaching are available in more than 140 countries. It has formerly been known as Microsoft Imagine, DreamSpark and MSDN-AA. Azure Dev Tools for Teaching (previously known as Microsoft Imagine Standard and Premium) is a subscription-based offering for accredited schools and departments providing access to tools commonly used in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) programs. It provides professional developer and designer tools, software, and services from Microsoft to faculty and students. Many academic institutions provide information and resources for Azure Dev Tools for teaching and Azure for student under their academic IT Service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DreamSpark
Microsoft Azure Dev Tools for Teaching or simply Azure Dev Tools for Teaching is a Microsoft program to provide students with Microsoft software design, Microsoft developer tools, Cloud Computing Access and learning resources. The program is available for university/college and K-12 students Azure for Student and Azure Dev Tools for teaching are available in more than 140 countries. It has formerly been known as Microsoft Imagine, DreamSpark and MSDN-AA. Azure Dev Tools for Teaching (previously known as Microsoft Imagine Standard and Premium) is a subscription-based offering for accredited schools and departments providing access to tools commonly used in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) programs. It provides professional developer and designer tools, software, and services from Microsoft to faculty and students. Many academic institutions provide information and resources for Azure Dev Tools for teaching and Azure for student under their academic IT Service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |