|
Winchcombe Carson Woolstores
Winchcombe Carson Woolstores is a heritage-listed warehouse at 54 Vernon Terrace, Teneriffe, City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by architect Claude William Chambers and built in 1910-11 by Stuart Brothers of Sydney who extended it in 1934. The woolstore was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 21 October 1992. History The first Winchcombe Carson building is the oldest extant woolstore in the Teneriffe precinct. Frederick Earle Winchcombe purchased some of the land himself in February 1910, while the remaining homes along the Vernon Terrace frontage were obtained by the company. The building was designed by noted Brisbane architect Claude Chambers. The Stuart Bros of Sydney built No 1 during 1910-11 and in 1934 were responsible for the rear addition. As the company continued to expand with the wool industry, the adjacent land was acquired by 1955, so that a third store was built and allowance made for yet another. In 1979 Winchcombe Carson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teneriffe, Queensland
Teneriffe is an inner suburb of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, north-east of the CBD. In the , Teneriffe had a population of 5,335 people. Teneriffe was once an important wool trading hub and was the location of Australia's largest submarine base in World War II. The suburb was absorbed into Newstead in 1975, but re-established as a separate suburb in 2010. Teneriffe has a generally young and high income demographic, and is one of Brisbane's most expensive suburbs with a median house price in 2017 of over A$2 million. Residents have access to a riverside lifestyle, restaurants and extensive amenities. Toponymy One of the first European landowners in the area was James Gibbon. He purchased 48 hectares of land between Newstead and New Farm and named the property Teneriffe because it reminded him of Mount Teide in Tenerife, Canary Islands. Gibbon built Teneriffe House in 1865. The single storey building still stands today on what is known as Teneriffe Hill. Geography The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
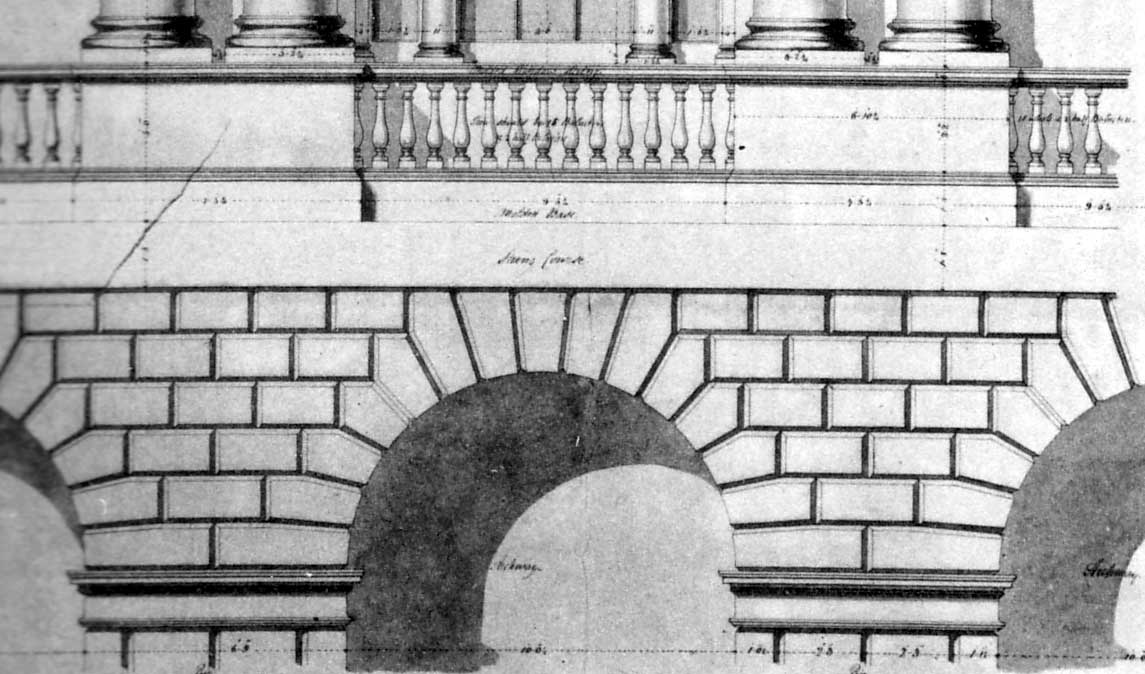
Voussoir
A voussoir () is a wedge-shaped element, typically a stone, which is used in building an arch or vault. Although each unit in an arch or vault is a voussoir, two units are of distinct functional importance: the keystone and the springer. The keystone is the centre stone or masonry unit at the apex of an arch. The springer is the lowest voussoir on each side, located where the curve of the arch springs from the vertical support or abutment of the wall or pier. The keystone is often decorated or enlarged. An enlarged and sometimes slightly dropped keystone is often found in Mannerist arches of the 16th century, beginning with the works of Giulio Romano, who also began the fashion for using voussoirs above rectangular openings, rather than a lintel (Palazzo Stati Maccarani, Rome, circa 1522). The word is a stonemason's term borrowed in Middle English from French verbs connoting a "turn" (''OED''). Each wedge-shaped voussoir ''turns aside'' the thrust of the mass above, transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RS Exton And Co Building
RS Exton and Co Building is a heritage-listed warehouse facade at 333 Ann Street, Brisbane City, City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by Claude William Chambers and built in 1907. It is also known as Ace House. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 17 December 1999. History The former RS Exton and Co Building was constructed in 1907 as the premises of the renowned painters and decorators, RS Exton and Co. The warehouse was designed by Brisbane architect, Claude W Chambers. Recently, the building was partially demolished and the facade only survives. Robert Skerrett Exton was a prolific painter, decorator and glazier who practiced in Brisbane from 1882 until 1921. In 1882 Robert Skerrit Exton established a painting and decorating partnership with George Gough. Both men were from Lincolnshire, England. Exton arrived in Brisbane and in the 1870s established himself as a glazier in Harcourt Street, Fortitude Valley. By 1880 Exton had moved to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland Institute Of Architects
The Queensland Institute of Architects was a professional society for architects in Queensland, Australia. It operated from 1888 until 1930, when it became a chapter of the Australian Institute of Architects. History The Queensland Institute of Architects was established in September 1888 in Brisbane with 16 members and Francis Drummond Greville Stanley as its president. Apart from Stanley, its founding members included: * Richard Gailey (vice president) * George Henry Male Addison * Claude William Chambers * John James Clark * John Jacob Cohen * Francis Richard Hall * Henry Hunter Presidents * 1888: Francis Drummond Greville Stanley * 1918–19: George Brockwell Gill * 1923–24: Thomas Blair Moncrieff Wightman * 1927–1931: Lange Powell Other notable members * Leslie Corrie See also *Architecture of Australia Architecture of Australia has generally been consistent with architectural trends in the wider Western world, with some special adaptations to compensate for d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Changing Room,
Change or Changing may refer to: Alteration * Impermanence, a difference in a state of affairs at different points in time * Menopause, also referred to as "the change", the permanent cessation of the menstrual period * Metamorphosis, or change, a biological process by which an animal physically develops after birth or hatching * Personal development, or personal change, activities that improve awareness and identity * Social change, an alteration in the social order of a society * Technological change, invention, innovation, and diffusion of technology Organizations and politics * Change 2011, a Finnish political party * Change We Need, a slogan for Barack Obama's 2008 presidential campaign * Change.gov, the transition website for the incoming Obama administration in 2008–2009 * Change.org, a petition website operated by Change.org, Inc. * Communities Helping All Neighbors Gain Empowerment (CHANGE), a civic organization based in Winston-Salem, North Carolina * Movement f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dining Room
A dining room is a room (architecture), room for eating, consuming food. In modern times it is usually adjacent to the kitchen for convenience in serving, although in medieval times it was often on an entirely different floor level. Historically the dining room is furnished with a rather large dining table and several dining chairs; the most common shape is generally rectangular with two armed end chairs and an even number of un-armed side chairs along the long sides. History In the Middle Ages, upper class, upper-class British people, Britons and other European nobility in castles or large manor houses dined in the great hall. This was a large multi-function room capable of seating the bulk of the population of the house. The family would sit at the head table on a raised dais, with the rest of the population arrayed in order of diminishing rank away from them. Tables in the great hall would tend to be long trestle tables with benches. The sheer number of people in a Grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bracket (architecture)
A bracket is an architectural element: a structural or decorative member. It can be made of wood, stone, plaster, metal, or other media. It projects from a wall, usually to carry weight and sometimes to "...strengthen an angle". A corbel or console are types of brackets. In mechanical engineering a bracket is any intermediate component for fixing one part to another, usually larger, part. What makes a bracket a bracket is that it is intermediate between the two and fixes the one to the other. Brackets vary widely in shape, but a prototypical bracket is the L-shaped metal piece that attaches a shelf (the smaller component) to a wall (the larger component): its vertical arm is fixed to one (usually large) element, and its horizontal arm protrudes outwards and holds another (usually small) element. This shelf bracket is effectively the same as the architectural bracket: a vertical arm mounted on the wall, and a horizontal arm projecting outwards for another element to be attached o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lighting
Lighting or illumination is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetic effects. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight. Daylighting (using windows, skylights, or light shelves) is sometimes used as the main source of light during daytime in buildings. This can save energy in place of using artificial lighting, which represents a major component of energy consumption in buildings. Proper lighting can enhance task performance, improve the appearance of an area, or have positive psychological effects on occupants. Indoor lighting is usually accomplished using light fixtures, and is a key part of interior design. Lighting can also be an intrinsic component of landscape projects. History With the discovery of fire, the earliest form of artificial lighting used to illuminate an area were campfires or torches. As early as 400,000 years ago, fire was kindl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awning
An awning or overhang is a secondary covering attached to the exterior wall of a building. It is typically composed of canvas woven of acrylic, cotton or polyester yarn, or vinyl laminated to polyester fabric that is stretched tightly over a light structure of aluminium, iron or steel, possibly wood or transparent material (used to cover solar thermal panels in the summer, but that must allow as much light as possible in the winter). The configuration of this structure is something of a truss, space frame or planar frame. Awnings are also often constructed of aluminium understructure with aluminium sheeting. These aluminium awnings are often used when a fabric awning is not a practical application where snow load as well as wind loads may be a factor. The location of an awning on a building may be above a window, a door, or above the area along a sidewalk. With the addition of columns an awning becomes a canopy, which is able to extend further from a building, as in the case of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entablature
An entablature (; nativization of Italian , from "in" and "table") is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and are commonly divided into the architrave (the supporting member immediately above; equivalent to the lintel in post and lintel construction), the frieze (an unmolded strip that may or may not be ornamented), and the cornice (the projecting member below the pediment). The Greek and Roman temples are believed to be based on wooden structures, the design transition from wooden to stone structures being called petrification. Overview The structure of an entablature varies with the orders of architecture. In each order, the proportions of the subdivisions (architrave, frieze, cornice) are defined by the proportions of the column. In Roman and Renaissance interpretations, it is usually approximately a quarter of the height of the column. Varian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, around the top edge of a pedestal, or along the top of an interior wall. A simple cornice may be formed just with a crown, as in crown moulding atop an interior wall or above kitchen cabinets or a bookcase. A projecting cornice on a building has the function of throwing rainwater free of its walls. In residential building practice, this function is handled by projecting gable ends, roof eaves and gutters. However, house eaves may also be called "cornices" if they are finished with decorative moulding. In this sense, while most cornices are also eaves (overhanging the sides of the building), not all eaves are usually considered cornices. Eaves are primarily functional and not necessarily decorative, while cornices have a decorative aspect. A building's projecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |