|
Wimmeria Mexicana
''Wimmeria mexicana'' is a large shrub or small tree, often reaching in height, that is common in the Southeastern United States and in regions of Mexico, including the states of Oaxaca, Chihuahua, and central to eastern Sonora. It is commonly called papelío and algodoncillo.Felger, Johnson, & Wilson, p. 133 Description The branches and trunk, in diameter, are erect to ascending, making it more tall than wide. Large, flaky, papery, gray plates cover its smooth, white bark. Young twigs, petioles, and flower axils sometimes have short, tiny hairs, but are mostly glabrous. The crown is spread out and sparse. The leaves, exstipulate and 2–6 cm in length, alternate and vary in shape between lanceolate, elliptic, and obovate. Flowers tend to be 7.5–8 mm wide, white to cream colored, bisexual, with 5 petals on 5 sepals, and arranged in axillary cyme. The fruits, 1–1.4 cm across, are papery, one-seeded, three-lobed samaras, similar to species of ''Dodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Mariano Mociño
José Mariano Mociño Suárez Lozano (24 September 1757 – 12 June 1820), or simply José Mariano Mociño, was a naturalist from New Spain. After having studied philosophy and medicine, he conducted early research on the botany, geology, and anthropology of his country and other parts of North America. Biography He was born in Temascaltepec (modern-day Mexico State) in 1757. Being poor, he worked in many different jobs to study in the ''Seminario Tridentino de México'', where he devoted himself especially to physics, mathematics, botany, and chemistry. In 1778 he graduated in philosophy. In 1791 he was called to join the scientific expedition of Martín de Sessé, the Royal Botanical Expedition, which had started in 1787. They traveled across New Spain, reaching the most inhospitable places of the Empire, being especially notable his trips to the Pacific Northwest. Although the pay for his job was minimal, he created one of the most important natural history collections of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepal
A sepal () is a part of the flower of angiosperms (flowering plants). Usually green, sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom., p. 106 The term ''sepalum'' was coined by Noël Martin Joseph de Necker in 1790, and derived . Collectively the sepals are called the calyx (plural calyces), the outermost whorl of parts that form a flower. The word ''calyx'' was adopted from the Latin ,Jackson, Benjamin, Daydon; A Glossary of Botanic Terms with their Derivation and Accent; Published by Gerald Duckworth & Co. London, 4th ed 1928 not to be confused with 'cup, goblet'. ''Calyx'' is derived from Greek 'bud, calyx, husk, wrapping' ( Sanskrit 'bud'), while is derived from Greek 'cup, goblet', and the words have been used interchangeably in botanical Latin. After flowering, most plants have no more use for the calyx which withers or becomes vestigial. Some plants retain a thorny calyx, either dried or live, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Adolph Timotheus Radlkofer
Ludwig Adolph Timotheus Radlkofer (19 December 1829, in Munich – 16 February 1927, in Munich), was a Bavarian taxonomist and botanist. Radlkofer became a physician in 1854 and earned a PhD in botany at Jena the following year. He became an associate professor of botany at the University of Munich in 1859 as well as deputy director of the botanical garden and herbarium. In 1892 he was named director of the Botanical Museum. He was made emeritus professor in 1913 and died in 1927 in the same room in which he was born. Radlkofer's main work was on the family Sapindaceae. His collections, sent by botanists from all over the world, are housed in Munich. The South African flower ''Greyia radlkoferi'' is named for him, as are the South American based genera of '' Radlkoferotoma'', and '' Radlkofera'', a monotypic genus of flowering plants from Africa belonging to the family Sapindaceae. The former genus ''Radlkoferella'' (a wastebasket genus) is now called ''Pouteria'',. Publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Theodor Hartweg
Karl Theodor Hartweg (18 June 1812 – 3 February 1871) was a German botanist. He collected numerous new species of plants in Colombia, Ecuador, Guatemala, Mexico and California in the United States, collecting for the London Horticultural Society. Many of the species he discovered were formally published, with attribution, by George Gordon, the Foreman of the London Horticultural Society Gardens and a specialist in the conifers which were well represented in Hartweg's collections. Many plants collected in Mexico by Hartweg from 1836 onward were identified and catalogued by George Bentham George Bentham (22 September 1800 – 10 September 1884) was an English botanist, described by the weed botanist Duane Isely as "the premier systematic botanist of the nineteenth century". Born into a distinguished family, he initially studi ... in ''Plantas Hartwegianas''. References * * * External linksPlantas Hartwegianas 1812 births 1871 deaths Botanists active in North Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Botting Hemsley
William Botting Hemsley (29 December 1843, in East Hoathly – 7 October 1924, in Kent) was an English botanist and 1909 Victoria Medal of Honour recipient. He was born in East Hoathly, Sussex and in 1860 started work at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew as an Improver, then Assistant for India in the Herbarium, finally Keeper of Herbarium and Library. He wrote a number of botanical works. In 1888, a genus of flowering plants from south-east Asia, belonging to the family Cucurbitaceae was named ''Hemsleya'' in his honour. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural science, natural knowledge, incl ... in June 1889. Publications * * ''Biologica Centrali-Americana Botany. Vol. I '', 1879–1888 * Biologica Centrali-Americana Botany. Vol. III', 1882–1886 * ''Botany o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Jackson Hooker
Sir William Jackson Hooker (6 July 178512 August 1865) was an English botanist and botanical illustrator, who became the first director of Kew when in 1841 it was recommended to be placed under state ownership as a botanic garden. At Kew he founded the Herbarium and enlarged the gardens and arboretum. Hooker was born and educated in Norwich. An inheritance gave him the means to travel and to devote himself to the study of natural history, particularly botany. He published his account of an expedition to Iceland in 1809, even though his notes and specimens were destroyed during his voyage home. He married Maria, the eldest daughter of the Norfolk banker Dawson Turner, in 1815, afterwards living in Halesworth for 11 years, where he established a herbarium that became renowned by botanists at the time. He held the post of Regius Professor of Botany at Glasgow University, where he worked with the botanist and lithographer Thomas Hopkirk and enjoyed the supportive friendshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wimmeria Concolor
''Wimmeria'' is a genus of shrubs to small trees in the family Celastraceae. It is named after German botanist Christian Friedrich Heinrich Wimmer (1803–1868). Species :''This list may be incomplete.'' * '' Wimmeria acapulcensis'' Lundell * '' Wimmeria acuminata'' L. O. Williams * '' Wimmeria bartlettii'' Lundell * '' Wimmeria caudata'' Lundell * '' Wimmeria chiapensis'' Lundell * '' Wimmeria concolor'' Cham. & Schltdl. * '' Wimmeria crenata'' Liebm. ex Lundell * '' Wimmeria cyclocarpa'' Radlk. ex Donn. Sm. * '' Wimmeria discolor'' Cham. & Schltdl. * '' Wimmeria guatemalensis'' Rose * '' Wimmeria integerrima'' Turcz. * '' Wimmeria lambii'' (Standl. & L. O. Williams) Lundell (synonym '' Maytenus lambii'')''Elsevier's Dictionary of Trees'', p. 965 * '' Wimmeria lanceolata'' Rose * ''Wimmeria mexicana'' ( Moc. & Sessé ex DC.) Lundell (synonym ''Celastrus mexicanus'') * '' Wimmeria microphylla'' Radlk. * '' Wimmeria montana'' Lundell * '' Wimmeria obtusifolia'' Standl. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilantro
Coriander (;coriander in the Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary ''Coriandrum sativum'') is an in the family . It is also known as Chinese parsley, dhania, or cilantro (). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamomile
Chamomile (American English) or camomile (British English; see spelling differences) ( or ) is the common name for several plants of the family Asteraceae. Two of the species, ''Matricaria recutita'' and ''Anthemis nobilis'', are commonly used to make herbal infusions for beverages. There is insufficient scientific evidence that consuming chamomile in foods or beverages has any beneficial effects on health. Etymology The word ''chamomile'' is derived via the French and Latin, from the Greek grc, χαμαίμηλον, khamaimēlon, earth apple, label=none, from grc, χαμαί, khamai, on the ground, label=none, and grc, μῆλον, mēlon, apple, label=none. First used in the 13th century, the spelling ''chamomile'' corresponds to the Latin and the Greek . The spelling ''camomile'' is a British derivation from the French. Species Some commonly used species include: * ''Matricaria chamomilla'' – often called "German chamomile" or "Water of Youth" * ''Chamaemelum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbal Tea
Herbal teas, also known as herbal infusions and less commonly called tisanes (UK and US , US also ), are beverages made from the infusion or decoction of herbs, spices, or other plant material in hot water. Oftentimes herb tea, or the plain term ''tea'', is used as a reference to all sorts of herbal teas. Many herbs are used in herbal medicine. Some herbal blends contain actual tea (e.g., the Indian classic masala chai). The term "herbal" tea is often used in contrast to the so-called ''true'' teas (e.g., black, green, white, yellow, oolong), which are prepared from the cured leaves of the tea plant, '' Camellia sinensis''. Unlike true teas (which are also available decaffeinated), most tisanes do not naturally contain caffeine. There are a number of plants, however, that ''do'' contain caffeine or another stimulant, like theobromine, cocaine or ephedrine. Some have the opposite effect, acting as a sedative. Some common infusions have specific names such as , ''mate'' (ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
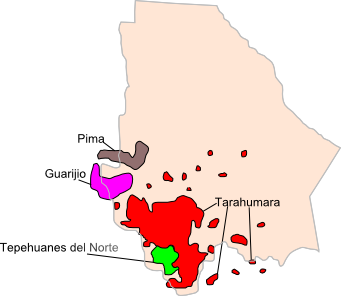
Guarijío People
The Guarijío are an indigenous people of Mexico. They primarily live in 17 villages near the West Sierra Madre Mountains in Chihuahua and the Sonoran border. Their homelands are remote and reached either on foot or horseback.Yetman 30 Their traditional Guarijio language has about 2100 speakers. Name The Guarijío people are also known as the Huarijío, Maculái, Macurái, Macurawe, Varihío, Varijío, Varohio, or Vorijío people. Language The Guarijío language is a Tarahumaran language of the Uto-Aztecan language family, written in the Latin script. A dictionary and grammar have been published for the language. Children primarily learn Spanish in school. History Guarijíos lived between the Tarahumara to the south and east and Mayo to the west. Spanish Jesuit missionaries arrived in their territory in the 1620s. The Jesuits established a mission in Chínipas, where some Guarijío and Guazapare people rebelled against them. After the Spanish military retaliated, the Guarijí ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodonaea
''Dodonaea'' is a genus of about 70 species of flowering plants, often known as hop-bushes, in the soapberry family, Sapindaceae. It has a cosmopolitan distribution in tropical, subtropical and warm temperate regions of Africa, the Americas, southern Asia and Australasia. By far the highest species diversity is in Australia. The genus is named after Rembert Dodoens, traditionally known as 'Dodonaeus'. They are shrubs and small trees growing to tall. The leaves are alternate, simple or pinnate. The flowers are produced in short racemes. The fruit is a capsule, often with two or three wings. ''Dodonaea'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including '' Aenetus eximia'' and '' Aenetus ligniveren''. Systematics ''Dodonaea'' is one of the largest genera in the Sapindaceae, and includes 70 species widely distributed in continental Australia. The only other species of the ''Dodonaea'' widely spread beyond mainland Australia, ''Dodonaea vis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |