|
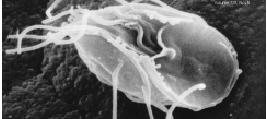
Willkommlangea Reticulata
''Willkommlangea reticulata'' is a slime mold species from the order Physarales and the only species of the genus ''Willkommlangea''. It is common worldwide, but rare in Europe. The tropics are possibly the main area of habitat. Characteristics The plasmodium is orange to scarlet. The fruit bodies are mainly plasmodiocarps, which are worm to net-shaped, beige, ochre or yellow to red-brown coloured and red spotted. The strands are occasionally so closely bound together that they produce pseudo-aethaliae, rarely cushion-form fruit bodies, which have a diameter from and expand over several centimetres wide. The hypothallus is inconspicuous or is missing. The sturdy, crossways puckered peridium is macroscopic light ochre to dark red-brown, in transmitted light yellowish to red-brown and covered with whitish or yellow to red-brown chalk, which occasionally produce a consistent crust. It opens irregularly lengthways, the edge, however, continues to permanently stick with the substrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Kuntze
Carl Ernst Otto Kuntze (23 June 1843 – 27 January 1907) was a German botanist. Biography Otto Kuntze was born in Leipzig. An apothecary in his early career, he published an essay entitled ''Pocket Fauna of Leipzig''. Between 1863 and 1866 he worked as tradesman in Berlin and traveled through central Europe and Italy. From 1868 to 1873 he had his own factory for essential oils and attained a comfortable standard of living. Between 1874 and 1876, he traveled around the world: the Caribbean, United States, Japan, China, South East Asia, Arabian peninsula and Egypt. The journal of these travels was published as "Around the World" (1881). From 1876 to 1878 he studied Natural Science in Berlin and Leipzig and gained his doctorate in Freiburg with a monography of the genus '' Cinchona''. He edited the botanical collection from his world voyage encompassing 7,700 specimens in Berlin and Kew Gardens. The publication came as a shock to botany, since Kuntze had entirely revised taxonom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Baptista Von Albertini
Johannes Baptista von Albertini (17 February 1769 – 6 December 1831) was a German botanist, mycologist and clergyman of the Moravian Church. He was born in the town of Neuwied. He studied theology in Niesky and at the seminary in Barby. During this period he became a friend of Friedrich Schleiermacher (1768–1834), who later became a renowned theologian. In 1796 Albertini became a lecturer at the seminary in Niesky, and in 1804 was a minister in Niesky. In 1814 he was elected bishop, and in 1824 was chairman of the ''Unitätsältestenkonferenz'', the denomination's executive board, in Berthelsdorf. He was a gifted speaker and a highly influential minister, and in 1805 a compilation of his sermons was published as ''30 Predigten für Freunde und Mitglieder der Brüdergemeine'' (Thirty Sermons for Friends and Members of the Moravian Brethren's Church). In the field of mycology he was co-author with Lewis David de Schweinitz (1780–1834) of a work on Upper Lusatian fungi titled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Otto Kuntze
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Eukaryote Genera
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda.' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa Genera
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional and currently no longer supported classification schemes, Amoebozoa is ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked "supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, variously named Unikonta, Amorphea or Opimoda. Amoebozoa includes many of the best-known amoeboid organis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxogastria
Myxogastria/Myxogastrea (myxogastrids, International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, ICZN) or Myxomycetes (International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, ICN), is a Class (biology), class of slime molds that contains 5 order (biology), orders, 14 family (biology), families, 62 genera, and 888 species. They are colloquially known as the ''plasmodial'' or ''acellular'' slime moulds. All species pass through several, very different morphology (biology), morphologic phases, such as microscopic individual cells, slimy amorphous organisms visible with the naked eye and conspicuously shaped fruit body, fruit bodies. Although they are monocellular, they can reach immense widths and weights: in extreme cases they can be up to across and weigh up to . The class Myxogastria is distributed worldwide, but it is more common in temperate regions where it has a higher biodiversity than in polar regions, the subtropics or tropics. They are mainly found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denmark
) , song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast") , song_type = National and royal anthem , image_map = EU-Denmark.svg , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark , established_title = History of Denmark#Middle ages, Consolidation , established_date = 8th century , established_title2 = Christianization , established_date2 = 965 , established_title3 = , established_date3 = 5 June 1849 , established_title4 = Faroese home rule , established_date4 = 24 March 1948 , established_title5 = European Economic Community, EEC 1973 enlargement of the European Communities, accession , established_date5 = 1 January 1973 , established_title6 = Greenlandic home rule , established_date6 = 1 May 1979 , official_languages = Danish language, Danish , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = German language, GermanGerman is recognised as a protected minority language in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johan Lange
Johan Martin Christian Lange (20 March 1818 – 3 April 1898) was a prominent Danish botanist. He held the post of Librarian at the Botanical library of the University of Copenhagen from 1851 to 1858. He was Director of the Botanical Garden there from 1856 to 1876, the Reader of botany at the Danish Technical University from 1857 to 1862, and Reader of Botany at the Royal Veterinary and Agricultural University from 1858 to 1893, achieving full professor standing in 1892. He began editing the Flora Danica in 1858, and was its last editor. Together with Japetus Steenstrup, Johan Lange was the publisher of Flora Danica fasc. 44 (1858). Thereafter, he edited alone fasc. 45-51 (1861–83) and Supplement vols 2-3 (1865–74), in total 600 plates. After having finished the publication of Flora Danica, he issued ''Nomenclator Floræ Danicæ'' in 1887 - a volume indexing all planches in Flora Danica alphabetically, systematically and chronologically. He travelled throughout Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanist
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek word (''botanē'') meaning "pasture", " herbs" "grass", or " fodder"; is in turn derived from (), "to feed" or "to graze". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of land plants of which some 391,000 species are vascular plants (including approximately 369,000 species of flowering plants), and approximately 20,000 are bryophytes. Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Moritz Willkomm
Heinrich Moritz Willkomm (29 June 1821, Herwigsdorf – 26 August 1895, Schloss Wartenberg in Wartenberg am Rollberg, Bohemia) was a German academic and botanist. He studied medicine at the University of Leipzig, later being named a professor of natural history in Tharandt (1855). In 1868 he was appointed professor of botany and director of the botanical garden at the University of Dorpat, and from 1874 to 1892, maintained similar roles at the University of Prague.JSTOR Global Plants biography of Willkomm, Heinrich Moritz (1821-1895) In 1844–45 and 1850–51, he collected plants in and . His main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Ernst Otto Kuntze
Carl Ernst Otto Kuntze (23 June 1843 – 27 January 1907) was a German botanist. Biography Otto Kuntze was born in Leipzig. An apothecary in his early career, he published an essay entitled ''Pocket Fauna of Leipzig''. Between 1863 and 1866 he worked as tradesman in Berlin and traveled through central Europe and Italy. From 1868 to 1873 he had his own factory for essential oils and attained a comfortable standard of living. Between 1874 and 1876, he traveled around the world: the Caribbean, United States, Japan, China, South East Asia, Arabian peninsula and Egypt. The journal of these travels was published as "Around the World" (1881). From 1876 to 1878 he studied Natural Science in Berlin and Leipzig and gained his doctorate in Freiburg with a monography of the genus ''Cinchona''. He edited the botanical collection from his world voyage encompassing 7,700 specimens in Berlin and Kew Gardens. The publication came as a shock to botany, since Kuntze had entirely revised taxonomy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis David Von Schweinitz
Lewis David de Schweinitz (13 February 1780 – 8 February 1834) was a German-American botanist and mycologist. He is considered by some the "Father of North American Mycology", but also made significant contributions to botany. Education Born in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, a great-grandson of Count Nikolaus Ludwig von Zinzendorf und Pottendorf, founder and patron of the Moravian Church, in 1787 Schweinitz was placed in the institution of the Moravian community at Nazareth, Pennsylvania, where he remained for 11 years and was a successful and industrious student. Schweinitz later entered the Theological seminary at Niesky (Saxony) in 1798. In 1805, he published the ''Conspectus Fungorum in Lusatiae'' in collaboration with his teacher, Professor J.B. Albertini. Early career In 1807 he went to Gnadenberg (in Silesia), then subsequently to Gnadau to work as a preacher in the Moravian church. A work appointment in the United States led him on a route through Denmark and Sweden, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |