|
William Wilberforce (MP)
William Wilberforce (24 August 1759 – 29 July 1833) was a British politician, a philanthropist, and a leader of the movement to abolish the slave trade. A native of Kingston upon Hull, Yorkshire, he began his political career in 1780, and became an independent Member of Parliament (MP) for Yorkshire (1784–1812). In 1785, he underwent a conversion experience and became an Evangelical Anglican, which resulted in major changes to his lifestyle and a lifelong concern for reform. In 1787, Wilberforce came into contact with Thomas Clarkson and a group of activists against the slave trade, including Granville Sharp, Hannah More and Charles Middleton. They persuaded Wilberforce to take on the cause of abolition, and he became a leading English abolitionist. He headed the parliamentary campaign against the British slave trade for 20 years until the passage of the Slave Trade Act of 1807. Wilberforce was convinced of the importance of religion, morality and education. He champione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Anton Hickel
Karl Anton Hickel (1745 – 30 October 1798) was an 18th-century Austrian painter. Life Hickel was born in Česká Lípa, Bohemia, and enrolled in the Academy of Fine Arts Vienna in Vienna, Austria in 1758. After graduation, he worked as a painter under his brother, Joseph Hickel, who was also a painter. Beginning in 1779, he served as a traveling portrait painter. He spent considerable time in Munich where he painted Charles Theodore, Elector of Bavaria, among others. He then traveled in southern Germany, Switzerland, then to Mannheim and Mainz. He moved to Switzerland in 1785, and then became the official court painter of Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor. In 1786, he travelled to France where he painted under the patronage of Marie Antoinette and Marie-Louise, princesse de Lamballe. He died in Hamburg. Gallery Image:Anton Hickel 001.JPG, Roxelana and Suleiman the Magnificent Image:Anton Hickel 002.jpg, Charles Theodore, Elector of Bavaria Image:William wilberforce.jpg, Willia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
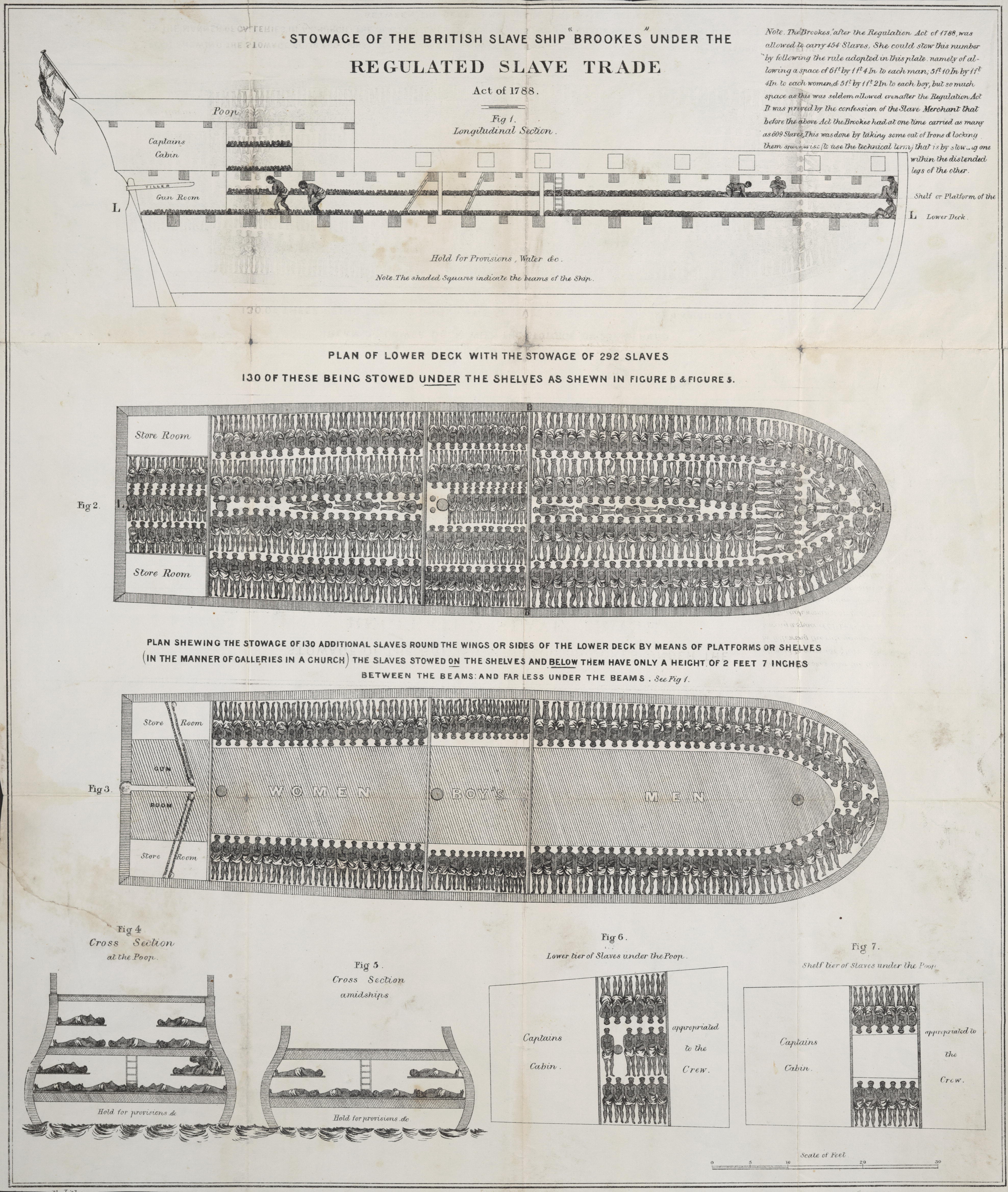
Atlantic Slave Trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Passage, and existed from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The vast majority of those who were transported in the transatlantic slave trade were people from Central and West Africa that had been sold by other West Africans to Western European slave traders,Thornton, p. 112. while others had been captured directly by the slave traders in coastal raids; Europeans gathered and imprisoned the enslaved at forts on the African coast and then brought them to the Americas. Except for the Portuguese, European slave traders generally did not participate in the raids because life expectancy for Europeans in sub-Saharan Africa was less than one year during the period of the slave trade (which was prior to the widespread availability of quini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society For The Prevention Of Cruelty To Animals
The Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (RSPCA) is a charity operating in England and Wales that promotes animal welfare. The RSPCA is funded primarily by voluntary donations. Founded in 1824, it is the oldest and largest animal welfare organisation in the world and is one of the largest charities in the UK. The organisation also does international outreach work across Europe, Africa and Asia. The charity's work has inspired the creation of similar groups in other jurisdictions, starting with the Ulster Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (founded in 1836), and including the Scottish Society for Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (1839), the Dublin Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (1840), the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (1866), the Royal New Zealand Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (1882), the Singapore Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (1959) and various groups which eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Mission Society
The Church Mission Society (CMS), formerly known as the Church Missionary Society, is a British mission society working with the Christians around the world. Founded in 1799, CMS has attracted over nine thousand men and women to serve as mission partners during its 200-year history. The society has also given its name "CMS" to a number of daughter organisations around the world, including Australia and New Zealand, which have now become independent. History Foundation The original proposal for the mission came from Charles Grant and George Uday of the East India Company and David Brown, of Calcutta, who sent a proposal in 1787 to William Wilberforce, then a young member of parliament, and Charles Simeon, a young clergyman at Cambridge University. The ''Society for Missions to Africa and the East'' (as the society was first called) was founded on 12 April 1799 at a meeting of the Eclectic Society, supported by members of the Clapham Sect, a group of activist Anglicans who met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierra Leone has a tropical climate, with diverse environments ranging from savanna to rainforests. The country has a population of 7,092,113 as of the 2015 census. The capital and largest city is Freetown. The country is divided into five administrative regions, which are subdivided into Districts of Sierra Leone, 16 districts. Sierra Leone is a constitutional republic with a unicameral parliament and a directly elected executive president, president serving a five-year term with a maximum of two terms. The current president is Julius Maada Bio. Sierra Leone is a Secular state, secular nation with Constitution of Sierra Leone, the constitution providing for the separation of state and religion and freedom of conscience (which includes freedom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society For The Suppression Of Vice
The Society for the Suppression of Vice, formerly the Proclamation Society Against Vice and Immorality, or simply Proclamation Society, was a 19th-century English society dedicated to promoting public morality. It was established in 1802, based on a proclamation by George III in 1787, and as a successor to the 18th-century Society for the Reformation of Manners, and continued to function until 1885. History The Society was founded by William Wilberforce following a Royal Proclamation by George III in 1787, the ''Proclamation for the Discouragement of Vice'', on the urging of Wilberforce, as a remedy for the rising tide of immorality. The proclamation commanded the prosecution of those guilty of "excessive drinking, blasphemy, profane swearing and cursing, lewdness, profanation of the Lord's Day, and other dissolute, immoral, or disorderly practices". Greeted largely with public indifference, Wilberforce sought to increase its impact by mobilising public figures to the cause, and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slave Trade Act Of 1807
The Slave Trade Act 1807, officially An Act for the Abolition of the Slave Trade, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom prohibiting the slave trade in the British Empire. Although it did not abolish the practice of slavery, it did encourage British action to press other nation states to abolish their own slave trades. Many of the supporters thought the Act would lead to the end of slavery. Slavery on English soil was unsupported in English law and that position was confirmed in ''Somerset's case'' in 1772, but it remained legal in most of the British Empire until the Slavery Abolition Act in 1833. Background As British historian Martin Meredith writes, "In the decade between 1791 and 1800, British ships made about 1,340 voyages across the Atlantic, landing nearly 400,000 slaves. Between 1801 and 1807, they took a further 266,000. The slave trade remained one of Britain's most profitable businesses." The Committee for the Abolition of the Slave Trade was for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abolitionism In The United Kingdom
Abolitionism in the United Kingdom was the movement in the late 18th and early 19th centuries to end the practice of slavery, whether formal or informal, in the United Kingdom, the British Empire and the world, including ending the Atlantic slave trade. It was part of a wider abolitionism movement in Western Europe and the Americas. The buying and selling of slaves was made illegal across the British Empire in 1807, but owning slaves was permitted until it was outlawed completely in 1833, beginning a process where from 1834 slaves became indentured "apprentices" to their former owners until emancipation was achieved for the majority by 1840 and for remaining exceptions by 1843. Former slave owners received formal compensation for their losses from the British government, known as compensated emancipation. Origins In the 17th and early 18th centuries, English Quakers and a few evangelical religious groups condemned slavery (by then applied mostly to Africans) as un-Christian. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Middleton, 1st Baron Barham
Admiral Charles Middleton, 1st Baron Barham, PC (14 October 172617 June 1813) was a Royal Navy officer and politician. As a junior officer he saw action during the Seven Years' War. Middleton was given command of a guardship at the Nore, a Royal Navy anchorage in the Thames Estuary, at the start of the American War of Independence, and was subsequently appointed Comptroller of the Navy. He went on to be First Naval Lord and then First Lord of the Admiralty. Early life Charles Middleton was born at Leith, Midlothian to Robert, a customs collector of Bo'ness, Linlithgowshire, and Helen, daughter of Captain Charles Dundas RN and granddaughter of Sir James Dundas of Arniston. He was a nephew of Brigadier-General John Middleton (1678–1739), a grandson of George Middleton DD, and a great-grandson of Alexander Middleton (younger brother of John Middleton, 1st Earl of Middleton), the last two having served as Principal of King's College, Aberdeen. Naval career Middleton ente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannah More
Hannah More (2 February 1745 – 7 September 1833) was an English religious writer, philanthropist, poet and playwright in the circle of Johnson, Reynolds and Garrick, who wrote on moral and religious subjects. Born in Bristol, she taught at a school her father founded there and began writing plays. She became involved in the London literary elite and a leading Bluestocking member. Her later plays and poetry became more evangelical. She joined a group opposing the slave trade. In the 1790s she wrote Cheap Repository Tracts on moral, religious and political topics, to distribute to the literate poor (as a retort to Thomas Paine's Rights of Man). Meanwhile, she broadened her links with schools she and her sister Martha had founded in rural Somerset. These curbed their teaching of the poor, allowing limited reading but no writing. More was noted for her political conservatism, being described as an anti-feminist, a "counter-revolutionary", or a conservative feminist. Early life B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granville Sharp
Granville Sharp (10 November 1735 – 6 July 1813) was one of the first British campaigners for the abolition of the slave trade. He also involved himself in trying to correct other social injustices. Sharp formulated the plan to settle black people in Sierra Leone, and founded the St George's Bay Company, a forerunner of the Sierra Leone Company. His efforts led to both the founding of the Province of Freedom, and later on Freetown, Sierra Leone, and so he is considered to be one of the founding fathers of Sierra Leone. He was also a biblical scholar, a classicist, and a talented musician. Life Granville Sharp was the son of Judith Wheler (d. 1757) and Thomas Sharp (1693–1759), Archdeacon of Northumberland, prolific theological writer and biographer of his father, John Sharp, Archbishop of York. Judith was the daughter of travel writer George Wheler and Grace née Higgons, who grew up in the political household of Sir Thomas Higgons. Sharp was born in Durham in 1735. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Clarkson
Thomas Clarkson (28 March 1760 – 26 September 1846) was an English abolitionist, and a leading campaigner against the slave trade in the British Empire. He helped found The Society for Effecting the Abolition of the Slave Trade (also known as the Society for the Abolition of the Slave Trade) and helped achieve passage of the Slave Trade Act 1807, which ended British trade in slaves. He became a pacifist in 1816 and, together with his brother John, was among the twelve founders of the Society for the Promotion of Permanent and Universal Peace. In his later years, Clarkson campaigned for the abolition of slavery worldwide. In 1840, he was the key speaker at the Anti-Slavery Society's (today known as Anti-Slavery International) first conference in London which campaigned to end slavery in other countries. Early life and education Clarkson was the eldest son of the Reverend John Clarkson (1710–1766), a Church of England priest and master of Wisbech Grammar School, and his wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)