|
William Thomas Beck
William Thomas Beck (7 May 1865 – 15 January 1947) was a New Zealand Army Officer and one of the first New Zealand soldiers to land on Gallipoli on 25 April 1915. Early life and family Born in Castlemaine, Australia on 7 May 1865, Beck was the son of Sarah Beck ( Taylor) and her husband Richard Beck. Beck and his family settled in Dunedin, New Zealand shortly after his birth. Beck married Edith Chick on 8 June 1896, in Port Chalmers, New Zealand. They had three children during their marriage. Military career Beck was a Torpedoman Second Class in No 2 Service Company, Permanent Militia, Port Chalmers, in the 1890s. With the Garrison Torpedo Boat Corps abandoned by Imperial decree just after the turn of the century. Beck relocated to Auckland and by 1904 was employed by the Defence Stores Department as the Defence Storekeeper for the Northern District Stores Depot, Goal Reserve, Mount Eden, with the rank of Honorary Lieutenant in the New Zealand Staff Corps. In 1914 he was th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castlemaine, Victoria
Castlemaine ( , Variation in Australian English, non-locally also ) is a small city in Victoria (Australia), Victoria, Australia, in the Goldfields region of Victoria, Goldfields region about 120 kilometres (75 miles) northwest by road from Melbourne and about 40 kilometres (25 miles) from the major provincial centre of Bendigo, Victoria, Bendigo. It is the administrative and economic centre of the Shire of Mount Alexander. The population at the 2021 Census was 7,506. Castlemaine was named by the chief goldfield commissioner, Captain W. Wright, in honour of his Irish people, Irish uncle, William Handcock, 1st Viscount Castlemaine, Viscount Castlemaine. Castlemaine began as a Victorian gold rush, gold rush boomtown in 1851 and developed into a major regional centre, being officially City of Castlemaine, proclaimed a City on 4 December 1965, although since declining in population. It is home to many cultural institutions including the Theatre Royal, the oldest continuously ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand And Australian Division
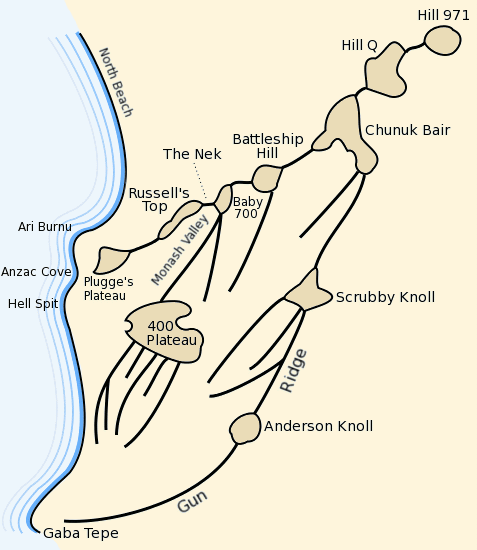
The New Zealand and Australian Division was a composite army division raised for service in the First World War under the command of Major General Alexander Godley. Consisting of several mounted and standard infantry brigades from both New Zealand and Australia, it served in the Gallipoli Campaign between April and December 1915. At Gallipoli, the division landed at Anzac Cove on 25 April 1915, coming ashore as follow-on troops to the initial assault force that had made it ashore earlier in the day, and later occupied the northern areas of the Allied lodgement. After the initial Allied assault at Anzac Cove, elements of the division were sent to Cape Helles in early May, where they participated in the Second Battle of Krithia, launching an unsuccessful attack towards the Achi Baba peak. The division's mounted units were sent to Gallipoli in mid-May without their horses, to serve as dismounted infantry, making up for previous losses. Later that month, the division helped repel an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal New Zealand Army Ordnance Corps
The Royal New Zealand Army Ordnance Corps (RNZAOC) concerned itself with the provisioning of troops with the means to fight; specifically uniforms, weapons and equipment. Ordnance functions go back hundreds of years; the first Ordnance Officer in the British military appeared in the year 1299. Designated "Keeper of the King's Wardrobe", his duties included the care and accounting of heavy equipment such as battering rams and catapults. The title of "Master of Ordnance" can be traced to 1414; this individual cared for the king's military stores, particularly his artillery pieces. He retained control over engineer and artillery personnel until 1716. In the 1840s, the British military set up ordnance stores in New Zealand, with full control passing to New Zealand authorities after 1870. In 1917 the New Zealand Army Ordnance Corps was formed, taking over duties performed formerly by the New Zealand Defence Stores Department. Creditable service in the Second World War led to the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Army Ordnance Department
The New Zealand Army Ordnance Department (NZAOD) was the organisation of commissioned officers who were responsible for the supply, maintenance and repair of equipment, small arms and all stores required for the Defence Force from 1917 to 1923. Establishment Gazetted by regulations published on 1 February 1917, the NZAOD was established as part of the permanent staff of the Defence Forces of New Zealand, replacing the New Zealand Defence Stores Department, absorbing its existing staff and also those handling military equipment and stores in the districts and training camps. Previously the Defence Stores Department had been under the control of the Public Service Commission. The establishment of the new Ordnance organisations, ended the anomaly of having civilians in the army who are really outside it, and were not subject to military discipline and control, and placed staff who had worn civilian clothes into uniform and under army discipline. Organisation The Gazetted regulations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Advanced Ordnance Depot
The ANZUK Ordnance Depot was established in 1971 to provide logistical support to Australian, New Zealand and British forces stationed in Singapore and Malaysia as part of ANZUK Force. It was commanded by a Royal Army Ordnance Corps officer of the rank of lieutenant colonel and staffed by Australian, New Zealand and United Kingdom personnel and Locally Employed Civilians. This organisation operated for only a short period. Australia changed Government in 1972 and the incoming Labor Government decided to withdraw Australia’s commitment to the region. This took effect in 1974 and was followed later by the withdrawal of the British forces. It was then decided that New Zealand should form its own Advanced Ordnance Depot, designated the New Zealand Advanced Ordnance Depot (NZAOD). This was the start of a commitment which was to last until December 1989. Formation and personnel The NZAOD came into being on 1 October 1974 to support the New Zealand Force which was to remain behind a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maryborough Military And Colonial Museum
The Maryborough Military & Colonial Museum is a non-profit museum located at 106 Wharf Street, Maryborough, Queensland, Australia. It was established and is operated by John and Else Meyers for the benefit of the Fraser Coast community. Displays The museum houses a number of displays of subject such as Keith Payne, VC OAM; Herbert James, VC MC; Timothy Britten, CV; John Cantwell, AO DSC; Harry Smith, SG MC; and James Runham, SC AFSM OAM. The museum has the largest number of Victoria Crosses in a private museum collection in Australia. The museum also has the only Cross of Valour (Australia) medal on public display; the one awarded to Timothy Britten following the 2002 Bali bombings. Heritage property The museum occupies the former J. E. Brown warehouse, which is listed on the Queensland Heritage Register The Queensland Heritage Register is a heritage register, a statutory list of places in Queensland, Australia that are protected by Queensland legislation, the Queensland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
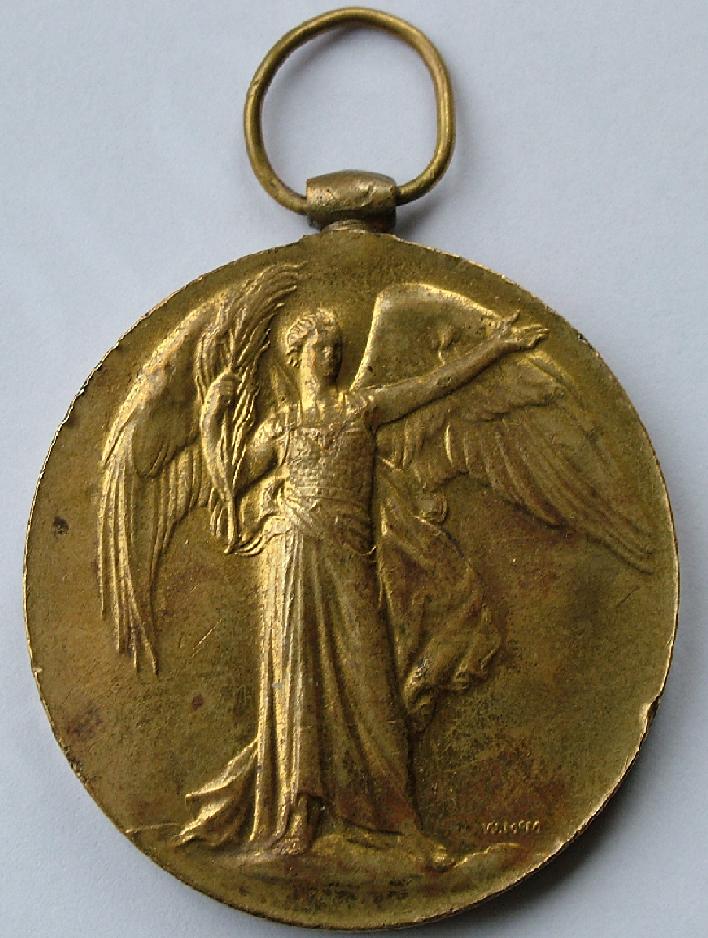
Victory Medal (United Kingdom)
The Victory Medal (also called the Inter-Allied Victory Medal) is a United Kingdom and British Empire First World War campaign medal. The award of a common allied campaign medal was recommended by an inter-allied committee in March 1919. Each allied nation would design a 'Victory Medal' for award to their own nationals, all issues having certain common features, including a winged figure of victory on the obverse and the same ribbon. Fourteen countries finally awarded the medal. Eligibility The Victory Medal (United Kingdom) was issued to all those who received the 1914 Star or the 1914–15 Star, and to most of those who were awarded the British War Medal. It was not awarded singly. To qualify, recipients need to have served in the armed forces of the United Kingdom or the British Empire, or with certain recognised voluntary organisations, and have entered any theatre of war between 5 August 1914 and 11 November 1918. While home service did not count, United Kingdom based m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British War Medal
The British War Medal is a campaign medal of the United Kingdom which was awarded to officers and men of British and Imperial forces for service in the First World War. Two versions of the medal were produced. About 6.5 million were struck in silver and 110,000 in bronze, the latter awarded to, among others, the Chinese, Maltese and Indian Labour Corps. Institution The British War Medal was instituted on 26 July 1919 for award to those who had rendered service between 5 August 1914, the day following the British declaration of war against the German Empire, and the armistice of 11 November 1918, both dates inclusive.The National Archives – British Army medal index cards 1914–1920 (Access date 24 June 2018) Consideration was given to the award of clasps to com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1914–15 Star
The 1914–15 Star is a campaign medal of the British Empire which was awarded to officers and men of British and Imperial forces who served in any theatre of the First World War against the Central European Powers during 1914 and 1915. The medal was never awarded singly and recipients also received the British War Medal and Victory Medal. Institution The 1914–15 Star was instituted in December 1918 and was awarded to officers and men of British and Imperial forces who served against the Central European Powers in any theatre of the Great War between 5 August 1914 and 31 December 1915, provided they had not already received the 1914 Star. The period of eligibility was prior to the Military Service Act 1916, which introduced conscription in Britain. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mentioned In Dispatches
To be mentioned in dispatches (or despatches, MiD) describes a member of the armed forces whose name appears in an official report written by a superior officer and sent to the high command, in which their gallant or meritorious action in the face of the enemy is described. In some countries, a service member's name must be mentioned in dispatches as a condition for receiving certain decorations. United Kingdom, British Empire, and Commonwealth of Nations Servicemen and women of the British Empire or the Commonwealth who are mentioned in despatches (MiD) are not awarded a medal for their actions, but receive a certificate and wear an oak leaf device on the ribbon of the appropriate campaign medal. A smaller version of the oak leaf device is attached to the ribbon when worn alone. Prior to 2014, only one device could be worn on a ribbon, irrespective of the number of times the recipient was mentioned in despatches. Where no campaign medal is awarded, the oak leaf is worn direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distinguished Service Order
The Distinguished Service Order (DSO) is a military decoration of the United Kingdom, as well as formerly of other parts of the Commonwealth, awarded for meritorious or distinguished service by officers of the armed forces during wartime, typically in actual combat. Since 1993 it has been awarded specifically for 'highly successful command and leadership during active operations', with all ranks being eligible. History Instituted on 6 September 1886 by Queen Victoria in a royal warrant published in ''The London Gazette'' on 9 November, the first DSOs awarded were dated 25 November 1886. The order was established to reward individual instances of meritorious or distinguished service in war. It was a military order, until recently for officers only and typically awarded to officers ranked major (or equivalent) or higher, with awards to ranks below this usually for a high degree of gallantry, just short of deserving the Victoria Cross. Whilst normally given for service un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Army Ordnance Corps
The New Zealand Army Ordnance Corps (NZAOC) was a Corps whose function was to provide, receive, store, repair, maintain, and issue: ordnance stores, vehicles, ammunition, foodstuffs, and ammunition. Ordnance Organisations had previously existed in the Royal New Zealand Artillery and the New Zealand Defence Stores Department, who for the Territorial Army established a temporary Ordnance Deport organisation and trained staff in Ordnance functions for the 1913 and 1914 Annual camps, so that on the eve of the great war a cadre existed within the Territorial Army to establish an Ordnance Corps to support the NZEF. Between 1914 and 1947 the New Zealand Army Ordnance Corps existed in three distinct iterations; *NZAOC as part of the NZEF, 1914–1919 *NZAOC alongside the NZAOD, 1917–1924 *NZAOC 1924–1947 NZEF (1914–1920) The New Zealand Expeditionary Force (NZEF) was originally established with Captain W T Beck as Deputy Assistant Director of Ordnance Services(DADOS), and a small s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_1852.jpg)



_Oak_Leaf_Cluster.jpg)
_-_Tallinn_Museum_of_Orders.jpg)