|
William St. Clair Tisdall
William St. Clair Tisdall (1859–1928) was a British Anglican priest, linguist, historian and philologist who served as the Secretary of the Church of England's Missionary Society in Isfahan, Persia. Career Tisdall was the principal at the Training College in Amritsar and later was the missionary in charge of the C.M.S. Muhammadan Mission in Bombay. He was fluent in several Middle Eastern languages, including Arabic, and spent much time researching the sources of Islam and the Qur'an in the original languages. He also wrote grammars for Persian, Hindustani, Punjabi and Gujarati. As an early scholar of Gujarati grammar, he defined three major varieties of Gujarati: a standard 'Hindu' dialect, a 'Parsi' dialect and a 'Muslim' dialect. Recent criticisms of Tisdall Clinton Bennett, in his ''Victorian Images of Islam'' (1992), paints Tisdall as a confrontationalist perpetuating a traditional Christian anti-Muslim polemic. Tisdall was one of thirteen authors whose essays were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historian
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human race; as well as the study of all history in time. Some historians are recognized by publications or training and experience.Herman, A. M. (1998). Occupational outlook handbook: 1998–99 edition. Indianapolis: JIST Works. Page 525. "Historian" became a professional occupation in the late nineteenth century as research universities were emerging in Germany and elsewhere. Objectivity During the ''Irving v Penguin Books and Lipstadt'' trial, people became aware that the court needed to identify what was an "objective historian" in the same vein as the reasonable person, and reminiscent of the standard traditionally used in English law of "the man on the Clapham omnibus". This was necessary so that there would be a legal benchmark to compare and contrast the scholar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
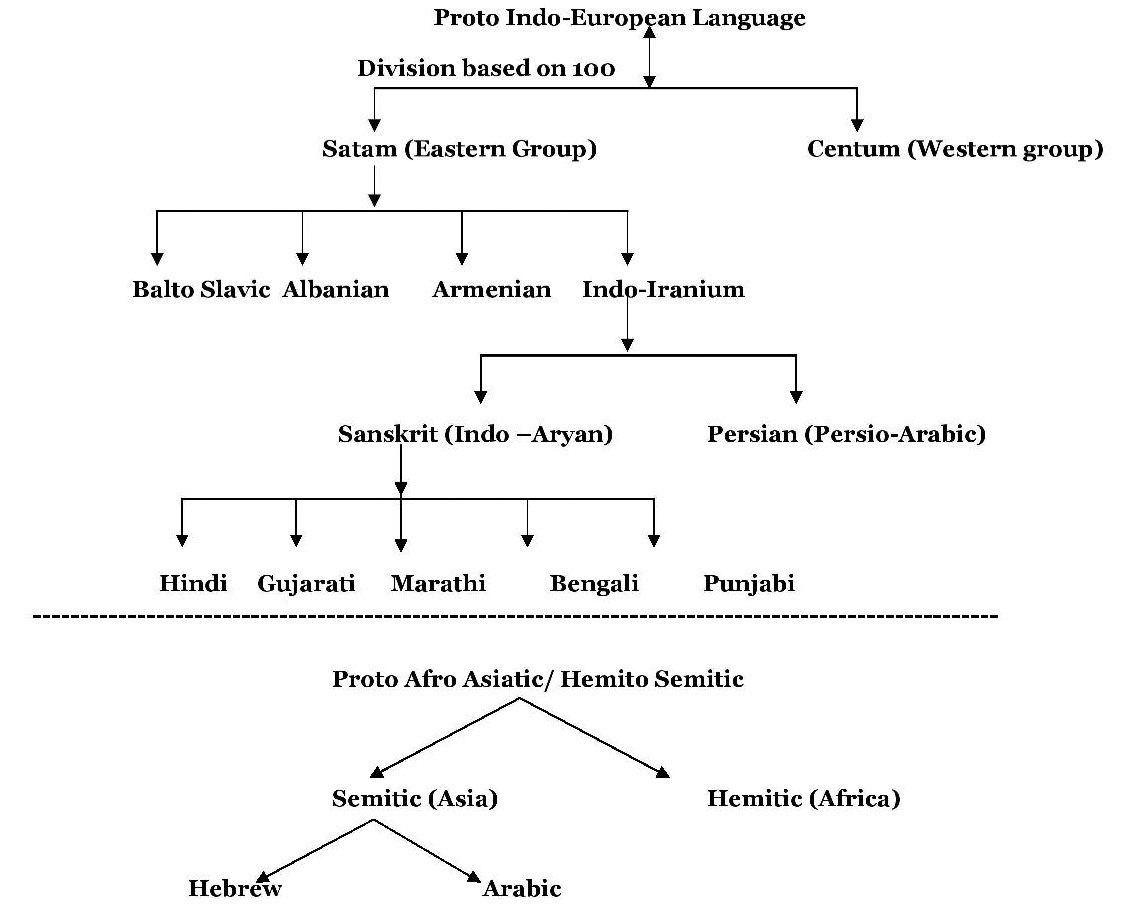
Gujarati Language
Gujarati (; gu, ગુજરાતી, Gujarātī, translit-std=ISO, label=Gujarati script, ) is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Indian state of Gujarat and spoken predominantly by the Gujarati people. Gujarati is descended from Old Gujarati (). In India, it is one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Union. It is also the official language in the state of Gujarat, as well as an official language in the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. As of 2011, Gujarati is the 6th most widely spoken language in India by number of native speakers, spoken by 55.5 million speakers which amounts to about 4.5% of the total Indian population. It is the 26th most widely spoken language in the world by number of native speakers as of 2007.Mikael Parkvall, "Världens 100 största språk 2007" (The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007), in ''Nationalencyklopedin''. Asterisks mark th2010 estimatesfor the top dozen languages. Outside of Gujarat, Gujarati is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1928 Deaths
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album '' Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slipk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1859 Births
Events January–March * January 21 – José Mariano Salas (1797–1867) becomes Conservative interim President of Mexico. * January 24 ( O. S.) – Wallachia and Moldavia are united under Alexandru Ioan Cuza (Romania since 1866, final unification takes place on December 1, 1918; Transylvania and other regions are still missing at that time). * January 28 – The city of Olympia is incorporated in the Washington Territory of the United States of America. * February 2 – Miguel Miramón (1832–1867) becomes Conservative interim President of Mexico. * February 4 – German scholar Constantin von Tischendorf rediscovers the ''Codex Sinaiticus'', a 4th-century uncial manuscript of the Greek Bible, in Saint Catherine's Monastery on the foot of Mount Sinai, in the Khedivate of Egypt. * February 14 – Oregon is admitted as the 33rd U.S. state. * February 12 – The Mekteb-i Mülkiye School is founded in the Ottoman Empire. * February 17 – French naval forces under Char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 Common Era, CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Muhammad in Islam, Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet Divine inspiration, divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of Adam in Islam, Adam, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, Jesus in Islam, Jesus, and other Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets. He is believed to be the Seal of the Prophets within Islam. Muhammad united Arabian Peninsula, Arabia into a single Muslim polity, with the Quran as well as his teachings and practices forming the basis of Islamic religious belief. Muhammad was born approximately 570CE in Mecca. He was the son of Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Amina bint Wahb. His father Abdullah was the son of Quraysh tribal leader Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim, and he died a few months before Muhammad's birth. His mother Amina died when he was six, lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Berg (religion)
__NOTOC__ Herbert Berg is a scholar of religion. Trained at the University of Toronto's Centre for the Study of Religion in the late 1980s and early 1990s, he is currently a Visiting Assistant Professor of Religious Studies at Rhodes College. He previously taught as a Professor in the Department of International Studies and the Department of Philosophy and Religion at the University of North Carolina Wilmington and was the Director of the International Studies from 2011 to 2018. At UNCW, he has been recognized with the University of North Carolina Board of Governor’s Award for Excellence in Teaching (2019), the Governor’s Award for Excellence for "Outstanding State Government Service" (2013), the Distinguished Faculty Scholar Award (2013), the Board of Trustees Teaching Excellence Award (2012), the Distinguished Teaching Professorship Award (2012), and the Chancellor’s Teaching Excellence Award (2006). Although also recognized as a specialist on the Nation of Islam, Berg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Warraq
Ibn Warraq is the pen name of an anonymous author critical of Islam. He is the founder of the Institute for the Secularisation of Islamic Society and used to be a senior research fellow at the Center for Inquiry, focusing on Quranic criticism. Warraq is the vice-president of the World Encounter Institute. Warraq has written historiographies of the early centuries of the Islamic timeline and has published works which question mainstream conceptions of the period. The pen name Ibn Warraq ( ar, ابن وراق, most literally "son of a papermaker") is used due to his concerns for his personal safety; Warraq stated, "I was afraid of becoming the second Salman Rushdie." It is a name that has been adopted by dissident authors throughout the history of Islam. The name refers to the 9th-century skeptical scholar Abu Isa al-Warraq. Warraq adopted the pseudonym in 1995 when he completed his first book, entitled '' Why I Am Not a Muslim''. Warraq's commentary on Islam has been critic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinton Bennett
Clinton Bennett (born 7 October 1955) is a British-American scholar of religions and participant in interfaith dialogue specialising in the study of Islam and Muslim-non-Muslim encounter. An ordained Baptist minister, he was a missionary in Bangladesh before serving as the second director of interfaith relations at the British Council of Churches in succession to Kenneth Cracknell. Bennett has also taken part in the dialogue activities of the World Council of Churches. A graduate of Manchester, Birmingham and Oxford Universities he has held several academic appointments in the United Kingdom and in the United States, where he now lives. He currently writes for various publications and teaches part-time at the State University of New York at New Paltz. He is a Fellow of the Royal Asiatic Society, of the Royal Anthropological Institute and of the Committee for the Scientific Examination of Religion. He has authored books, chapters in books, journal articles and Encyclopedia ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim Gujarati
Lisaan ud-Da'wat or ''Lisaan o Da'wat il Bohra'' or ''Lisan ud-Dawat'' ( ar, لسان الدعوة, lit=language of the Da'wat, ''da'wat ni zabaan''; abbreviated LDB) is the language of the Dawoodi Bohras and Alavi Bohras, two Isma'ili Shi'a Muslim communities primarily in Gujarat, following the Taiyebi"Taiyebi" refers to the 21st Imam at-Taiyeb from the progeny of Lady Fatimah, the daughter of Prophet Mohammmad. After the seclusion of at-Taiyeb, the doctrines that emerged and propagated by his missionaries in Yemen is followed by Bohra communities of Gujarat doctrines and theology. The language is based on a Neo-Indo-Aryan language Gujarati, but incorporates a heavy amount of Arabic, Urdu, and Persian vocabulary and is written in the Arabic script '' naskh'' style. Originally a ritual language, since the period of the missionaries- in Ahmedabad around 1005 AH/1597 AD it has also been propagated as the vernacular language for members of the Bohra communities, but the version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
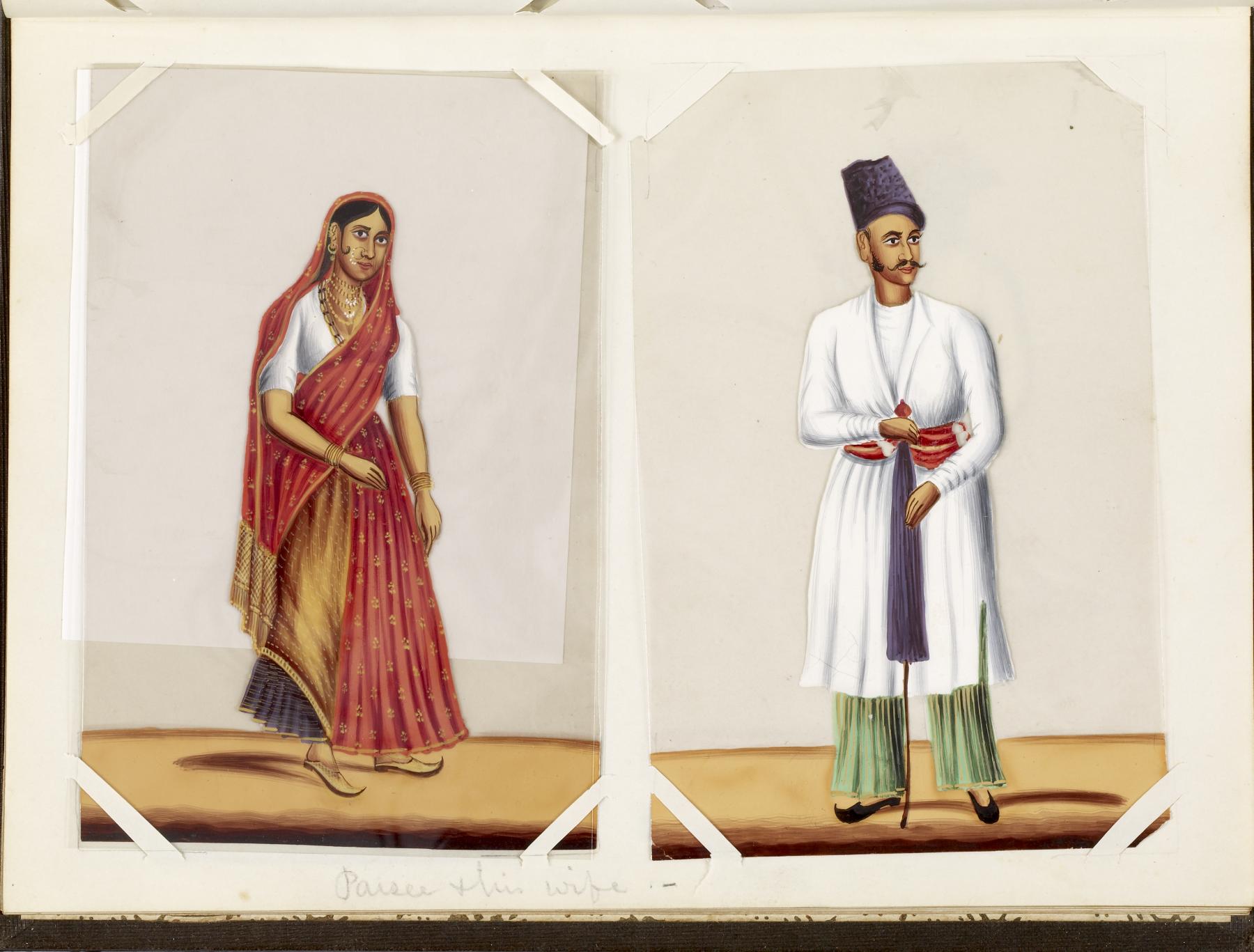
Parsi
Parsis () or Parsees are an ethnoreligious group of the Indian subcontinent adhering to Zoroastrianism. They are descended from Persians who migrated to Medieval India during and after the Arab conquest of Iran (part of the early Muslim conquests) in order to preserve their Zoroastrian identity. The Parsi people comprise the older of the Indian subcontinent's two Zoroastrian communities vis-à-vis the Iranis, whose ancestors migrated to British-ruled India from Qajar-era Iran. According to a 16th-century Parsi epic, ''Qissa-i Sanjan'', Zoroastrian Persians continued to migrate to the Indian subcontinent from Greater Iran in between the 8th and 10th centuries, and ultimately settled in present-day Gujarat after being granted refuge by a local Hindu king. Prior to the 7th-century fall of the Sassanid Empire to the Rashidun Caliphate, the Iranian mainland (historically known as 'Persia') had a Zoroastrian majority, and Zoroastrianism had served as the Iranian state religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarati Grammar
The grammar of the Gujarati language is the study of the word order, case marking, verb conjugation, and other morphological and syntactic structures of the Gujarati language, an Indo-Aryan language native to the Indian state of Gujarat and spoken by the Gujarati people. This page overviews the grammar of standard Gujarati, and is written in a romanization (see '' Gujarati script#Romanization''). Hovering the mouse cursor over forms will reveal the appropriate English translation. Nominals Nouns Gujarati has three genders, two numbers, and three cases (nominative, oblique/vocative, and to a certain extent, locative). Nouns may be divided into declensional subtypes: marked nouns displaying characteristic declensional vowel terminations, and unmarked nouns which do not. These are the paradigms for the termination — Two things must be noted about the locative case and its limited nature. First, it only exists as a case for masculines and neuters, which is why the corresponding f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |