|
William Mirtle
William Mirtle (24 December 1739 – c. 1769) was a Scottish mariner and explorer, primarily known for his time with the Bengal Pilot Service (or the Bombay Marine) and the British East India Company. On 22 December 1768, he was granted a coat of arms for “having been on the 7th day of January 1763 taken by a French Squadron cruising off Bengal in the East Indies and by desperate attempt overcoming the crew of the vessel whereon he was prisoner, by which success he regained his liberty and got safe to Calcutta where his critical intelligence of the enemy proved of essential service to the Commerce which the Factory testified by public thanks. After which engaging as a volunteer he served with reputation having likewise had the happiness to succeed in establishing an important fir trade for masts in the interior parts of Bengal with the Mountain Rajas”.College of Arms record Ms Grants 11/350. Biography Early life William Mirtle was born 24 December 1739 to Thomas Mirtle, bre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth. Edinburgh is Scotland's List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, second-most populous city, after Glasgow, and the List of cities in the United Kingdom, seventh-most populous city in the United Kingdom. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament and the Courts of Scotland, highest courts in Scotland. The city's Holyrood Palace, Palace of Holyroodhouse is the official residence of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarchy in Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scots law, Scottish law, literature, philosophy, the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort William, India
Fort William is a fort in Hastings, Calcutta (Kolkata). It was built during the early years of the Bengal Presidency of British India. It sits on the eastern banks of the Hooghly River, the major distributary of the River Ganges. One of Kolkata's most enduring Raj-era edifices, it extends over an area of 70.9 hectares. The fort was named after King William III. In front of the Fort is the Maidan, the largest park in the country. An internal guard room became the Black Hole of Calcutta. Today it is the Headquarters of Eastern Command of the Indian Army. History There are two Fort Williams. The original fort was built in the year 1696 by the British East India Company under the orders of Sir John Goldsborough which took a decade to complete. The permission was granted by Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb. Sir Charles Eyre started construction near the bank of the Hooghly River with the South-East Bastion and the adjacent walls. It was named after King William III in 1700. John Bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
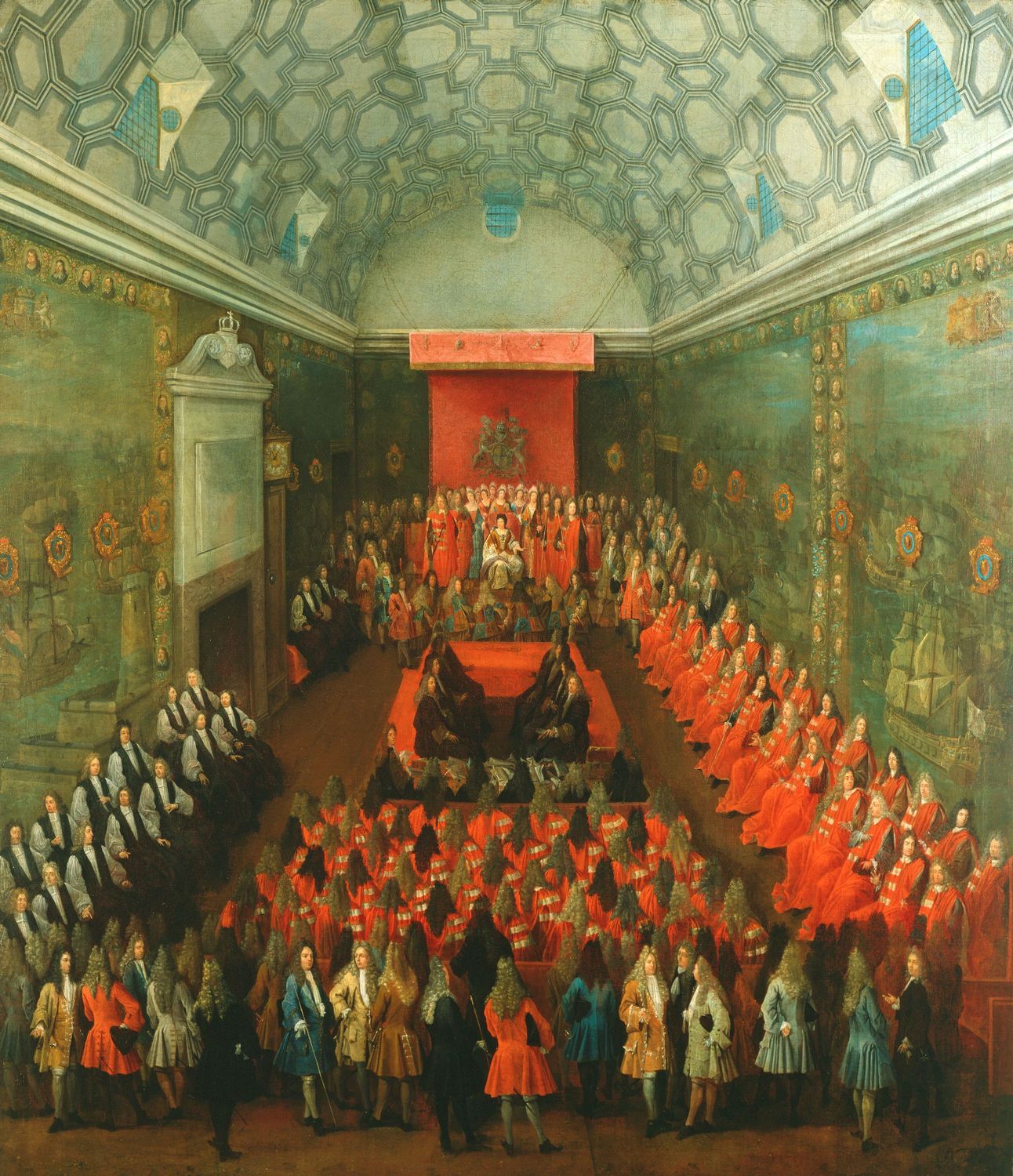
House Of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. The House of Lords scrutinises Bill (law), bills that have been approved by the House of Commons. It regularly reviews and amends bills from the Commons. While it is unable to prevent bills passing into law, except in certain limited circumstances, it can delay bills and force the Commons to reconsider their decisions. In this capacity, the House of Lords acts as a check on the more powerful House of Commons that is independent of the electoral process. While members of the Lords may also take on roles as government ministers, high-ranking officials such as cabinet ministers are usually drawn from the Commons. The House of Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dowry
A dowry is a payment, such as property or money, paid by the bride's family to the groom or his family at the time of marriage. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. While bride price or bride service is a payment by the Bridegroom, groom, or his family, to the bride, or her family, dowry is the wealth transferred from the bride, or her family, to the groom, or his family. Similarly, dower is the property settled on the bride herself, by the groom at the time of marriage, and which remains under her ownership and control. Dowry is an ancient custom that is already mentioned in some of the earliest writings, and its existence may well predate records of it. Dowries continue to be expected and demanded as a condition to accept a marriage proposal in some parts of the world, mainly in parts of Asia, The custom of dowry is most common in cultures that are strongly patrilineal and that expect women to reside with or near their husband's family (patriloca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galashiels
Galashiels (; sco, Gallae, gd, An Geal Àth) is a town in the Scottish Borders with a population of around 12,600. Its name is often colloquially shortened to "Gala". The town is a major commercial centre for the Borders region with extensive history in the textile industry. Galashiels is the location of Heriot-Watt University's School of Textiles and Design. Location Galashiels is south of Edinburgh and north of Carlisle on the A7 road. Gala lies on the border between the historic counties of Roxburghshire and Selkirkshire, on the Gala Water river. History To the west of the town there is an ancient earthwork known as the Picts' Work Ditch or Catrail. It extends many miles south and its height and width vary. There is no agreement about the purpose of the earthwork. There is another ancient site on the north-western edge of the town, at Torwoodlee, an Iron Age hill fort, with a later broch known as Torwoodlee Broch built in the western quarter of the hill fort, and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
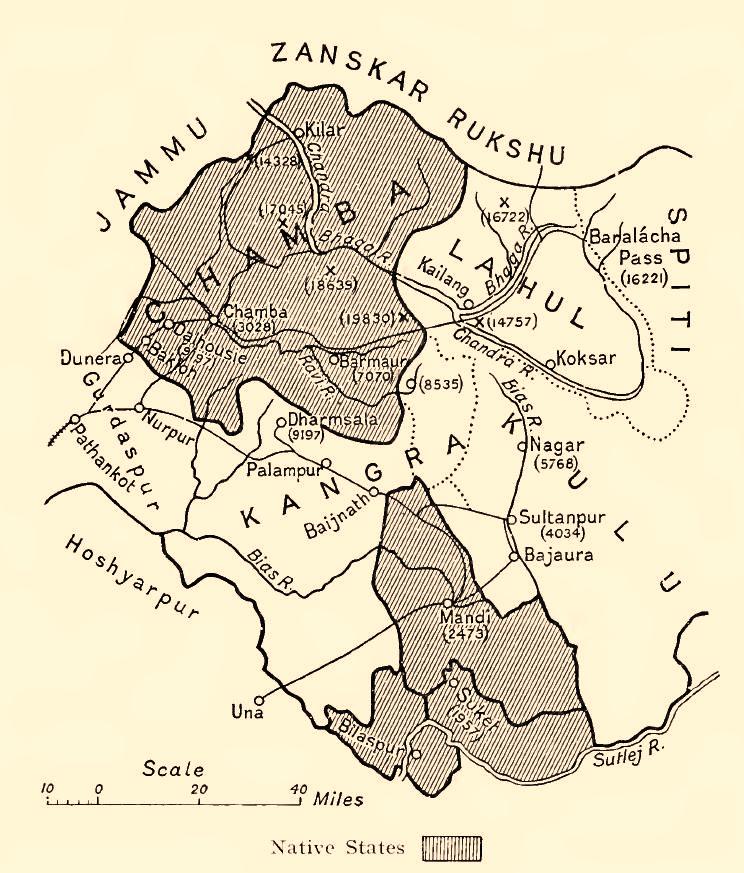
Hill States Of India
The Hill States of India were princely states lying in the northern border regions of the British Indian Empire. History During the colonial Raj period, two groups of princely states in direct relations with the Province of British Punjab became part of the British Indian Empire later than most of the former Mughal Empire, in the context of two wars and an uprising. For its princely rulers the informal term Hill Rajas has been coined. It does not apply to other native hill country princes such as the Rawat of Rajgarh. After the independence and split-up of British India, the Hill States acceded to the new Dominion of India and were later divided between India's constituent states of Punjab (proper), Haryana and Himachal Pradesh. Simla Hills 28 princely states (including feudatory princes and zaildars) in the promontories of the western Himalaya were named after Shimla as the Simla Hill States. These states were ruled mainly by Hindu Rajputs. Three quarters of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purnia District
Purnia District is one of the thirty-eight districts of the Indian state of Bihar. The city of Purnia is the administrative headquarters of this district. The city of Purnia has continued its tradition of hoisting the national flag at 12:07 am on every Independence Day since 1947. Purnia district is a part of Purnia Division. The district extends northwards from the Ganges river. History Purnia is part of the Mithila region. Mithila first gained prominence after it was settled by Indo-Aryan peoples who established the Mithila Kingdom (also called Kingdom of the Videhas). During the late Vedic period (c. 1100–500 BCE), Videha became one of the major political and cultural centers of Ancient India, along with Kuru and Pañcāla. The kings of the Videha Kingdom were called Janakas. The Videha Kingdom was later incorporated into the Vajji confederacy, which had its capital in the city of Vaishali, which is also in Mithila. During the Mughal rule, Purnea was an outlying militar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmyras Point
Palmyras Point or Point Palmyras is a low headland in the Bay of Bengal. It is located at the eastern end of the Brahmani River delta in the state of Odisha, India, close to the Bhitarkanika wildlife sanctuary, an area of mangroves. False Point, located further south, derives its name from the circumstance that vessels proceeding up the Bay of Bengal frequently mistook it for Point Palmyras. Hugh Murray et al., ''Historical and descriptive account of British India'' (1843) See also * False Point *Bhitarkanika Mangroves Bhitarkanika Mangroves is a mangrove wetland in Odisha, India, covering an area of in the Brahmani River and Baitarani River deltas. History The Bhitarkanika Mangroves were zamindari forests until 1952, when the government of Odisha abolish ... References {{reflist Headlands of India Mangroves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepoy
''Sepoy'' () was the Persian-derived designation originally given to a professional Indian infantryman, traditionally armed with a musket, in the armies of the Mughal Empire. In the 18th century, the French East India Company and its other European counterparts employed locally recruited soldiers within India, mainly consisting of infantry designated as "sepoys". The largest sepoy force, trained along European lines, served the British East India Company The term "sepoy" continues in use in the modern Indian, Pakistan and Nepalese armies, where it denotes the rank of private. Etymology In Persian (Aspa) means horse and Ispahai is also the word for cavalrymen. The term ''sepoy'' is derived from the Persian word () meaning the traditional "infantry soldier" in the Mughal Empire. In the Ottoman Empire the term was used to refer to cavalrymen. History The sepoys of the Mughal Empire were infantrymen usually armed with a musket and a talwar, although they some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hooghly River
The Bhagirathi Hooghly River (Anglicized alternatively spelled ''Hoogli'' or ''Hugli'') or the 'Bhāgirathi-Hooghly', called the Ganga or the Kati-Ganga in mythological texts, is the eastern distributary of the Ganges River in West Bengal, India, rising close to Giria in Murshidabad. The main distributary of the Ganges then flows into Bangladesh as the Padma. Today there is a man-made canal called the Farakka Feeder Canal connecting the Ganges to the Bhagirathi. The river flows through the Rarh region, the lower deltaic districts of West Bengal, and eventually into the Bay of Bengal. The upper riparian zone of the river is called Bhagirathi while the lower riparian zone is called Hooghly. Major rivers that drain into the Bhagirathi-Hooghly include Mayurakshi, Jalangi , Ajay, Damodar, Rupnarayan and Haldi rivers other than the Ganges. Hugli-Chinsura, Bandel, Chandannagar, Srirampur, Barrackpur, Rishra, Uttarpara, Titagarh, Kamarhati, Agarpara, Baranagar and Kolkata are loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |