|
William Kirtley (railway Engineer)
William Kirtley (1840 – 7 October 1919) was an English railway engineer, and was the Locomotive Superintendent of the London Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR) in England from 1874 until the merger to form the South Eastern and Chatham Railway at the end of 1898. Biography William was born in Warrington in 1840, the son of the locomotive engineer Thomas Kirtley (1810–1847). He was educated by his uncle Matthew Kirtley, Locomotive Superintendent of the Birmingham and Derby Junction Railway and later of the Midland Railway, following his father's premature death. He served as a pupil at Derby Works from 1854–1860, and from 1861 to 1864 he was Running foreman for the Midland Railway for the London District. In 1864 he was appointed superintendent of Derby Works. In 1874 he was appointed Carriage and Wagon Superintendent on the LCDR following the death of William Martley, and served until the merger to form the South Eastern and Chatham Railway at the end of 1898, when he retir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotive Superintendent
Chief mechanical engineer and locomotive superintendent are titles applied by British, Australian, and New Zealand railway companies to the person ultimately responsible to the board of the company for the building and maintaining of the locomotives and rolling stock. In Britain, the post of ''locomotive superintendent'' was introduced in the late 1830s, and ''chief mechanical engineer'' in 1886. Emerging professional roles In the early Victorian era, projected canal or railway schemes were prepared by groups of promoters who hired specialists such as civil engineers, surveyors, architects or contractors to survey a route; and this resulted in the issue of a prospectus setting out their proposals. Provided that adequate capital could be raised from potential investors, agreements obtained from the landowners along the proposed route and, in Britain, an Act of Parliament obtained (different terminology is used in other countries), then construction might begin either by a new compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCDR A1 Class
The LCDR A class was a class of 0-4-4T steam locomotives of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway The London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR or LC&DR) was a railway company in south-eastern England created on 1 August 1859, when the East Kent Railway was given parliamentary approval to change its name. Its lines ran through London and no .... The class was designed by William Kirtley and introduced in 1875. The A1 and A2 classes were similar, but had larger driving wheels. The differences between the A1 and A2 classes were minor: in particular, the A2 class had a larger heating surface. Numbering Ownership changes All the A, A1 and A2 class locomotives passed to the South Eastern and Chatham Railway in 1899. Number 570 was withdrawn in 1915 but the remaining locomotives passed to the Southern Railway in 1923. All had been withdrawn by 1926. References * * * {{SECR locomotives A 0-4-4T locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1884 Scrapped locomotives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
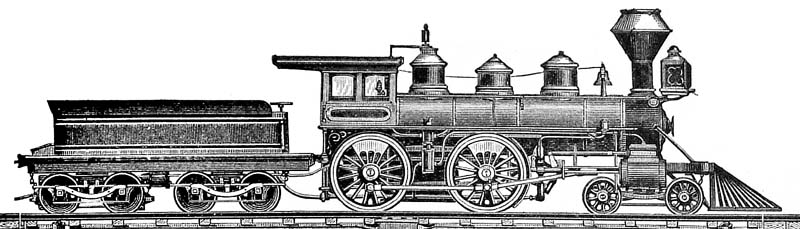
LCDR M3 Class
The LCDR M3 class was a class of 4-4-0 steam locomotives of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway. The class was designed by William Kirtley and introduced in 1891. History The class were an enlargement of Kirtley's earlier M1 and M2 classes intended for the London-Dover boat trains. They proved to be successful for these tasks for more than a decade. The locomotives passed to the South Eastern and Chatham Railway in 1899 after which they were superseded on the heaviest trains by the SECR D class The SECR D class is a class of 4-4-0 tender locomotives designed by Harry Wainwright for the South Eastern and Chatham Railway. Overview The construction of the initial 20 engines was shared between Ashford railway works and the Glasgow bu ... between 1903 and 1905 and transferred to secondary duties. The class was nevertheless considered to be sufficiently useful to be worth re-boilering between 1909 and 1917. The entire class survived into Southern Railway ownership in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCDR M2 Class
The LCDR M2 class was a class of 4-4-0 steam locomotives of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway. The class was designed by William Kirtley and introduced in 1884. History The class were a development of Kirtley's earlier M and M1 classes intended for the London-Dover boat train A boat train is a passenger train operating to a port for the specific purpose of making connection with a passenger ship, such as a ferry, ocean liner, or cruise ship. Through ticketing is normally available. __NOTOC__ Notable named boat tr ...s. They proved to be moderately successful for these tasks but soon needed to superseded on the heaviest trains by the larger M3 class The locomotives passed to the South Eastern and Chatham Railway in 1899 and were considered to be sufficiently useful to be worth re-boilering between 1898 and 1903. The class began to be withdrawn and scrapped from 1912. Only one example survived into Southern Railway ownership in 1923, but was withdrawn almost i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCDR M1 Class
The LCDR M1 class was a class of 4-4-0 steam locomotives of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR), very similar to the earlier M class but with steel frames, larger tenders and other detailed differences. The class was designed by William Kirtley and introduced in 1880. History Kirtley had requested six more examples of his earlier M class built by Neilson and Company for the London-Dover boat train A boat train is a passenger train operating to a port for the specific purpose of making connection with a passenger ship, such as a ferry, ocean liner, or cruise ship. Through ticketing is normally available. __NOTOC__ Notable named boat tr ...s, but this request was turned down by the LCDR board, although he was given permission to build similar locomotives at the company's Longhedge Works in Battersea. Two locomotives were built during 1880 and a further two in 1881. However a fire in the machine shop seriously delayed work on the final two which eventually a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCDR M Class
The LCDR M class was a class of 4-4-0 steam locomotives of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway. The class was designed by William Kirtley and introduced in 1877, intended for the heaviest express services between London and Dover. History William Kirtley took over as locomotive superintendent of the railway following the death of William Martley in 1874. Martley's Europa class 2-4-0 were performing well on the lightly loaded Dover-Flushing boat trains but a larger engine was required for some of the heavier services on the main line. Kirtley therefore designed a 4-4-0 for this purpose. The six locomotives were built by Neilson and Company of Glasgow and introduced during June and July 1877. They proved to be successful for these tasks and were only superseded on the heaviest trains by the larger M3 class The locomotives passed to the South Eastern and Chatham Railway The South Eastern and Chatham Railway Companies Joint Management Committee (SE&CRCJMC),Awdry (1990 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-4-0
4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and a lack of trailing wheels. Due to the large number of the type that were produced and used in the United States, the 4-4-0 is most commonly known as the American type, but the type subsequently also became popular in the United Kingdom, where large numbers were produced.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, pp. 46-. Almost every major railroad that operated in North America in the first half of the 19th century owned and operated locomotives of this type. The first use of the name ''American'' to describe locomotives of this wheel arrangement was made by ''Railroad Gazette'' in April 1872. Prior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCDR T Class
The LCDR T class was a class of steam locomotives of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway. The class was designed by William Kirtley and introduced in 1879. Numbering Source: semgonline ;Notes # Sources differ as to whether 1603 or 1604 entered BR ownership # Number 607 was transferred to the Service Department and numbered 500 S. Ownership changes The locomotives passed to the South Eastern and Chatham Railway in 1899. All 10 (SECR nos. 600-609) survived into Southern Railway ownership in 1923. Three survived into British Railways (BR) ownership in 1948. They had all been withdrawn by 1951. Withdrawal Seven locomotives had been withdrawn by 1948. The remaining 3 were withdrawn as follows: * D500 S in November 1949 from Meldon Quarry * 31603 in November 1950 from Reading South shed (shed code British Railways shed codes were used to identify the motive power depot, engine sheds that its locomotives and multiple units were allocated to for maintenance purposes. The for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCDR B2 Class
The LCDR B2 class was a class of 0-6-0 steam locomotives of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway The London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR or LC&DR) was a railway company in south-eastern England created on 1 August 1859, when the East Kent Railway was given parliamentary approval to change its name. Its lines ran through London and no .... The class was designed by William Kirtley and introduced in 1891. Ownership changes The locomotives passed to the South Eastern and Chatham Railway in 1899. All 6 (LCDR nos. 652-657) survived into Southern Railway ownership in 1923. They had all been withdrawn by 1933. References B2 0-6-0 locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1891 Scrapped locomotives Standard gauge steam locomotives of Great Britain {{England-steam-loco-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCDR B1 Class
The LCDR B1 class was a class of 0-6-0 steam locomotives of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway. The class was designed by William Kirtley (railway engineer), William Kirtley and introduced in 1877. Ownership changes The locomotives passed to the South Eastern and Chatham Railway in 1899. Two (LCDR nos. 612 and 613) survived into Southern Railway (Great Britain), Southern Railway ownership in 1923. All had been withdrawn by 1924. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCDR B Class
The LCDR B class was a class of 0-6-0 steam locomotives of the London, Chatham and Dover Railway. The class was designed by William Kirtley and introduced in 1876. The locomotives passed to the South Eastern and Chatham Railway The South Eastern and Chatham Railway Companies Joint Management Committee (SE&CRCJMC),Awdry (1990), page 199 known as the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR), was a working union of two neighbouring rival railways, the South Easter ... in 1899. And given new boilers between 1899 and 1903. They were all withdrawn and scrapped between 1912 and 1915. References B 0-6-0 locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1876 Scrapped locomotives Standard gauge steam locomotives of Great Britain {{England-steam-loco-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0-6-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. This was the most common wheel arrangement used on both tender and tank locomotives in versions with both inside and outside cylinders. In the United Kingdom, the Whyte notation of wheel arrangement was also often used for the classification of electric and diesel-electric locomotives with side-rod coupled driving wheels. Under the UIC classification, popular in Europe, this wheel arrangement is written as C if the wheels are coupled with rods or gears, or Co if they are independently driven, the latter usually being electric and diesel-electric locomotives. Overview History The 0-6-0 configuration was the most widely used wheel arrangement for both tender and tank steam locomotives. The type was also widely used for diesel switchers (shunters). Because they lack leading a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)