|
William Harding Carter
William Giles Harding Carter (November 19, 1851 – May 24, 1925) was a US Cavalry officer who served during the American Civil War, Spanish–American War and World War I. He also took part in the Indian Wars seeing extensive service against the Apache and Comanche in Arizona being awarded the Medal of Honor against the Apache during the Comanche Campaign on August 30, 1881. A strong advocate of reform in the United States Army during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Carter and Secretary of War Elihu Root are credited with the creation of the U.S. Army War College and helped pass the General Staff Act of 1903 through the United States Congress, replacing the office of commanding general with a chief of staff and a more efficient reorganization of military staff structure. He was also an active supporter of the Militia Act of 1903 which proposed to replace the obsolete state militia system with the National Guard Bureau. A later historian and military biographer, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nashville, Tennessee
Nashville is the capital city of the U.S. state of Tennessee and the county seat, seat of Davidson County, Tennessee, Davidson County. With a population of 689,447 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, Nashville is the List of municipalities in Tennessee, most populous city in the state, List of United States cities by population, 21st most-populous city in the U.S., and the fourth most populous city in the southeastern United States, southeastern U.S. Located on the Cumberland River, the city is the center of the Nashville metropolitan area, which is one of the fastest growing in the nation. Named for Francis Nash, a general of the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War, the city was founded in 1779. The city grew quickly due to its strategic location as a port on the Cumberland River and, in the 19th century, a railroad center. Nashville seceded with Tennessee during the American Civil War; in 1862 it was the first state capital in the Confederate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commanding General Of The United States Army
The Commanding General of the United States Army was the title given to the service chief and highest-ranking officer of the United States Army (and its predecessor the Continental Army), prior to the establishment of the Chief of Staff of the United States Army in 1903. During the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), the title was Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army. In 1783, the title was simplified to Senior Officer of the United States Army. In 1821, the title was changed to Commanding General of the United States Army. The office was often referred to by various other titles, such as "Major General Commanding the Army" or "General-in-Chief". From 1789 until its abolition in 1903, the position of commanding general was legally subordinate to the United States Secretary of War, Secretary of War; it was replaced by the creation of the statutory Chief of Staff of the United States Army, Chief of Staff of the Army in 1903. Officeholders † denotes people who d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Lieutenant
Second lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces, comparable to NATO OF-1 rank. Australia The rank of second lieutenant existed in the military forces of the Australian colonies and Australian Army until 1986. In the colonial forces, which closely followed the practices of the British military, the rank of second lieutenant began to replace ranks such as ensign and cornet from 1871. New appointments to the rank of second lieutenant ceased in the regular army in 1986. Immediately prior to this change, the rank had been effectively reserved for new graduates from the Officer Cadet School, Portsea which closed in 1985. (Graduates of the Australian Defence Force Academy (ADFA) and the Royal Military College, Duntroon (RMC-D) are commissioned as lieutenants.). The rank of second lieutenant is only appointed to officers in special appointments such as training institutions, university regiments and while under probation during training. Trai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Point
The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known Metonymy, metonymically as West Point or simply as Army, is a United States service academies, United States service academy in West Point, New York. It was originally established as a fort, since it sits on strategic high ground overlooking the Hudson River with a scenic view, north of New York City. It is the oldest of the five American service academies and educates cadets for Commission (document)#United States, commissioning into the United States Army. The academy was founded in 1802, one year after President Thomas Jefferson directed that plans be set in motion to establish it. It was constructed on site of Fort Clinton (West Point), Fort Clinton on West Point overlooking the Hudson, which Colonial General Benedict Arnold conspired to turn over to the British during the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War. The entire central campus is a National Historic Landmark, national landmark and home to scores of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaulx Carter
Vaulx Carter (August 14, 1863 – before 1930) was an American college football player and engineer who is best remembered as the first coach of the Navy Midshipmen football program. He was born in Tennessee and raised there for part of his childhood, until he was orphaned and adopted by family members in Pennsylvania. Starting in 1880, Carter attended the United States Naval Academy; he struggled academically at the school, only excelling in his art classes. Carter failed his final examinations in his final two years at the academy and was recommended for removal following the second failure. This did not happen, as he was forced to voluntarily resign from the school in 1883 due to permanent injuries received from an accident. Carter's time at the Naval Academy was not without success; in his second year, he singlehandedly managed to restart the school's football program after a two-year hiatus. Carter guided his team as a player-coach for the season, leading them to a victory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laura Carter Holloway
Laura Carter Holloway Langford (August 22, 1843 – July 10, 1930) was an American journalist, author, and lecturer from New York. She worked as a reporter and editor for the ''Brooklyn Eagle'' and published several books, notably ''The Ladies of the White House'' (1870), a group biography of the First Ladies of the United States that became a bestseller with 150,000 copies sold worldwide. A spiritualist, suffragist, and progressive who joined the Theosophical Society in the 1870s and held an array of radical and alternative beliefs, Holloway was a lifelong friend of Anna White of the Mount Lebanon Shaker Society. Holloway's papers are held in the Edward Deming Andrews Edward Deming Andrews (March 6, 1894 – June 6, 1964) was an American historian, educator, curator, and preeminent authority on the United Society of Believers in Christ's Second Appearing, or the Shakers. Life and career Born into a working-c ... Shaker Memorial Collection at the Winterthur Library. Refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Cumberland
The Army of the Cumberland was one of the principal Union armies in the Western Theater during the American Civil War. It was originally known as the Army of the Ohio. History The origin of the Army of the Cumberland dates back to the creation of the Army of the Ohio in November 1861, under the command of Brig. Gen. Robert Anderson. The army fought under the name Army of the Ohio until Maj. Gen. William S. Rosecrans assumed command of the army and the Department of the Cumberland and changed the name of the combined entity to the Army of the Cumberland. When Rosecrans assumed command, the army and the XIV Corps were the same unit, divided into three "grand divisions" (wings) commanded by Alexander McCook (Right Wing), George H. Thomas (Center), and Thomas L. Crittenden (Left). General Order No. 168 was the order passed by the Union Army on October 24, 1862, that called for commissioning the XIV Corps into the Army of the Cumberland. The army's first significant combat under th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courier
A courier is a person or organisation that delivers a message, package or letter from one place or person to another place or person. Typically, a courier provides their courier service on a commercial contract basis; however, some couriers are government or state agency employees (for example: a diplomatic courier). Duties and functions Couriers are distinguished from ordinary mail services by features such as speed, security, tracking, signature, specialization and individualization of express services, and swift delivery times, which are optional for most everyday mail services. As a premium service, couriers are usually more expensive than standard mail services, and their use is normally limited to packages where one or more of these features are considered important enough to warrant the cost. Courier services operate on all scales, from within specific towns or cities, to regional, national and global services. Large courier companies include DHL, DTDC, FedEx, EMS Inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
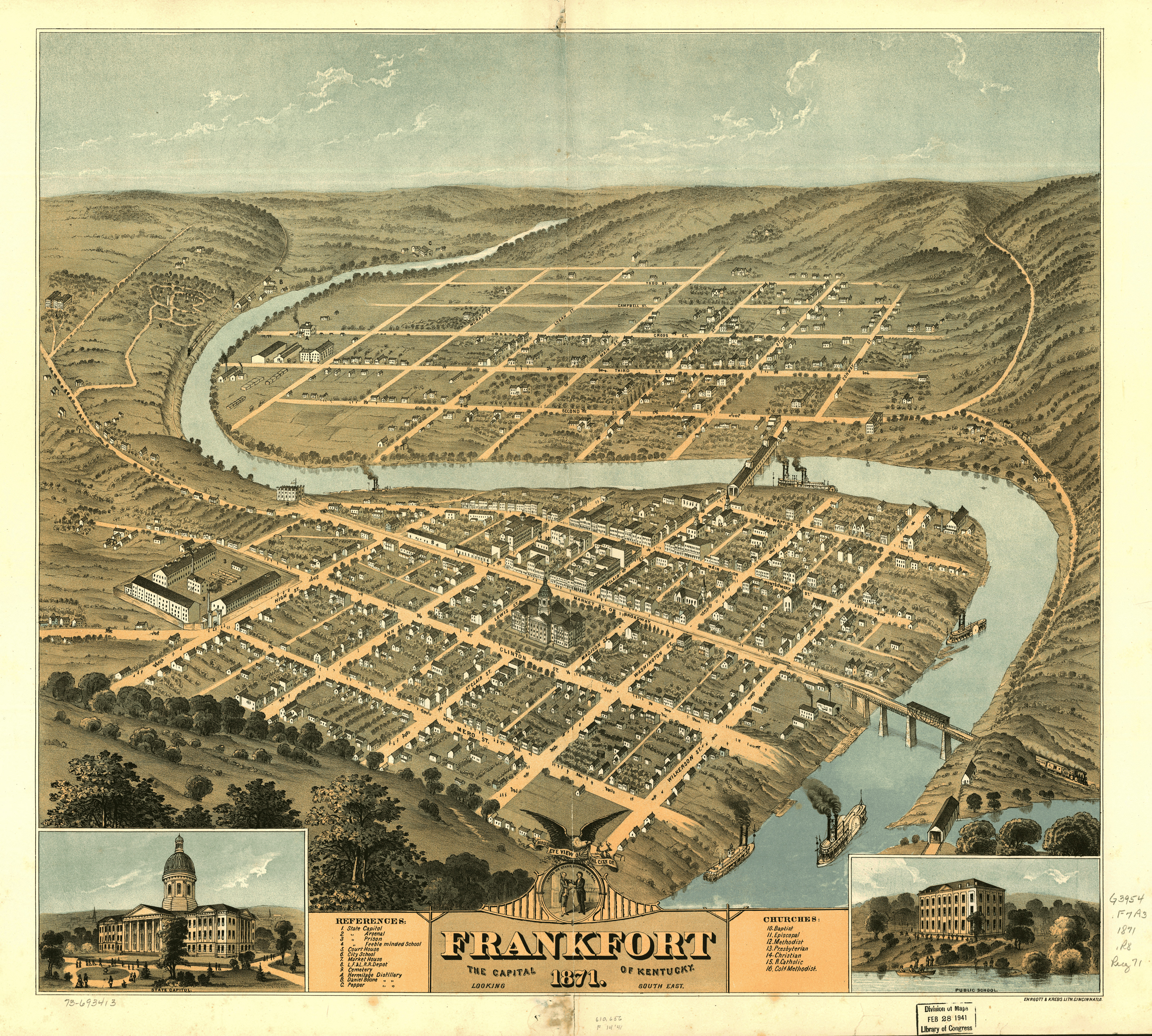
Frankfort, Kentucky
Frankfort is the capital city of the Commonwealth of Kentucky, United States, and the seat of Franklin County. It is a home rule-class city; the population was 28,602 at the 2020 census. Located along the Kentucky River, Frankfort is the principal city of the Frankfort, Kentucky Micropolitan Statistical Area, which includes all of Franklin and Anderson counties. History Pre-1900 The town of Frankfort likely received its name from an event that took place in the 1780s. Native Americans attacked a group of early European colonists from Bryan Station, who were on their way to make salt at Mann's Lick in Jefferson County. Pioneer Stephen Frank was killed at the Kentucky River and the settlers thereafter called the crossing "Frank's Ford". This name was later elided to Frankfort. In 1786, James Wilkinson purchased a tract of land on the north side of the Kentucky River, which developed as downtown Frankfort. He was an early promoter of Frankfort as the state capital. Wilkinso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentucky Military Institute
The Kentucky Military Institute (KMI) was a military preparatory school in Lyndon, Kentucky, and Venice, Florida, in operation from 1845 to 1971. Founding One of the oldest traditional military prep schools in the United States, KMI was maintained in the vein of the Virginia Military Institute, in that all of its students were classified as cadets. It was founded in 1845 by Colonel Robert Thomas Pritchard Allen (September 26, 1813, to July 9, 1888) and chartered by the Commonwealth of Kentucky in 1847. History As the Civil War approached, a student "set the buildings on fire and the school was closed down," according to E. F. Bleiler. During the Civil War, the school remained closed. KMI wintered in Eau Gallie, Florida, beginning in 1907 (when it bought that ghost town) to 1921 (when the Eau Gallie campus burned to the ground). Due to financial troubles, the Florida campus moved many times in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and was closed in 1924; it reopened the next ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biographer
Biographers are authors who write an account of another person's life, while autobiographers are authors who write their own biography. Biographers Countries of working life: Ab=Arabia, AG=Ancient Greece, Al=Australia, Am=Armenian, AR=Ancient Rome, Au=Austria, AH=Austria/Hungary, Ca=Canada, En=England, Fl=Finland, Fr=France, Ge=Germany, Id=Indonesia, In=India, Ir=Ireland, Is=Israel, Jp=Japan, Nw=Norway, SA=South Africa, Sc=Scotland, SL=Sierra Leone, So=Somalia, Sp=Spain, Sw=Sweden, TT=Trinidad & Tobago, US=United States, Ve=Venezuela, Wl=Wales A–G *Hermann Abert (Ge, 1871–1927) – Robert Schumann, Niccolò Jommelli, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, W. A. Mozart *Alfred Ainger (En, 1837–1904) – Charles Lamb *Ellis Amburn (US, 1933–2018) – Roy Orbison, Buddy Holly, Jack Kerouac, Elizabeth Taylor, Warren Beatty and Janis Joplin *Rudolph Angermüller (Ge, born 1940) – Antonio Salieri, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, W. A. Mozart *Núria Añó (Sp. born 1973) – Salka Viertel *Marie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Guard Bureau
The National Guard Bureau is the federal instrument responsible for the administration of the National Guard established by the United States Congress as a joint bureau of the Department of the Army and the Department of the Air Force. It was created by the Militia Act of 1903. The National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2008, elevated the National Guard to a joint function of the Department of Defense. The 2007 NDAA, from the previous year, elevated the chief of the National Guard Bureau from a lieutenant general to a four-star general. Militia Act of 1903 United States Secretary of War Elihu Root militated for reform of the militia, in annual reports of 1901 of 1903 and in public letters. He argued that state militias should be more like the Army in discipline, uniforms, equipment, and training, to mitigate problems that arose in the U.S. Civil War and the recent Spanish–American War of 1898. The Militia Act of 1792 was posited to be obsolete. The resulting Mili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)