|
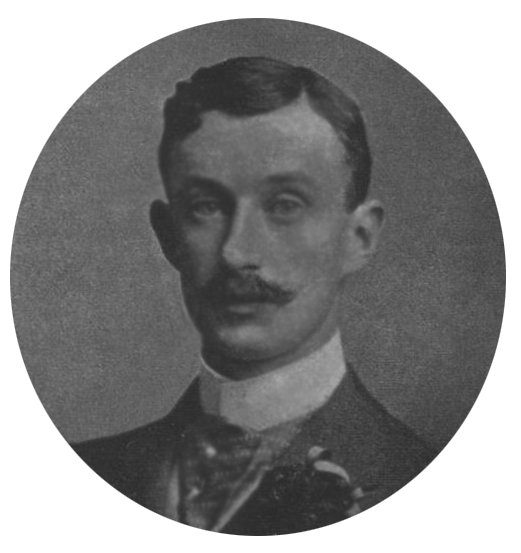
William Dowdeswell (politician, Born 1721)
William Dowdeswell PC (12 March 17216 February 1775) was a British politician who was a leader of the Rockingham Whig faction. Background and education A son of William Dowdeswell of Pull Court, Bushley, Worcestershire, he was educated at Westminster School, at Christ Church, Oxford, then at the University of Leiden. One of his fellow students was Baron d'Holbach. He spent the summer of 1746 with him at the uncle´s Messire François-Adam, Baron d’Holbach, Seigneur de Heeze, Leende et autres Lieux (ca. 1675–1753) estate Heeze-Leende. Political career Dowdeswell became member of Parliament for the family borough of Tewkesbury in 1747, retaining this seat until 1754, and from 1761 until his death he was one of the representatives of Worcestershire. Becoming prominent among the Whigs, Dowdeswell was made Chancellor of the Exchequer in 1765 under the Marquess of Rockingham, and his short tenure of this position appears to have been a successful one, he being in Lecky's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Right Honourable
''The Right Honourable'' ( abbreviation: ''Rt Hon.'' or variations) is an honorific style traditionally applied to certain persons and collective bodies in the United Kingdom, the former British Empire and the Commonwealth of Nations. The term is predominantly used today as a style associated with the holding of certain senior public offices in the United Kingdom, Canada, New Zealand, and to a lesser extent, Australia. ''Right'' in this context is an adverb meaning 'very' or 'fully'. Grammatically, ''The Right Honourable'' is an adjectival phrase which gives information about a person. As such, it is not considered correct to apply it in direct address, nor to use it on its own as a title in place of a name; but rather it is used in the third person along with a name or noun to be modified. ''Right'' may be abbreviated to ''Rt'', and ''Honourable'' to ''Hon.'', or both. ''The'' is sometimes dropped in written abbreviated form, but is always pronounced. Countries with common or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bredon School
Bredon School, formerly Pull Court, is a private school in Bushley, Worcestershire, England. The house was built for the Reverend Canon E. C. Dowdeswell by Edward Blore between 1831 and 1839. The site is much older and Blore's house replaced an earlier mansion. The Dowdeswells had been prominent in local and national politics since the 18th century, with many serving as members of Parliament. The family sold the house in 1934 to the parents of Richard Seaman, a prominent pre-war racing driver, who lived there until his death in a crash in the 1939 Belgian Grand Prix. In 1962, the court became a school, Bredon School, founded by Lt-Col Tony Sharp and Hugh Jarrett, for the education of boys who had failed the Common Entrance Examination. It remains a specialist school with a focus on educating children with specific learning difficulties, such as dyslexia and dyspraxia. History The political fortunes of the Dowdeswell family were established by Richard Dowdeswell (-1673). His f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Commons Of The United Kingdom
The House of Commons is the lower house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the upper house, the House of Lords, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. The House of Commons is an elected body consisting of 650 members known as members of Parliament (MPs). MPs are elected to represent constituencies by the first-past-the-post system and hold their seats until Parliament is dissolved. The House of Commons of England started to evolve in the 13th and 14th centuries. In 1707 it became the House of Commons of Great Britain after the political union with Scotland, and from 1800 it also became the House of Commons for Ireland after the political union of Great Britain and Ireland. In 1922, the body became the House of Commons of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland after the independence of the Irish Free State. Under the Parliament Acts 1911 and 1949, the Lords' power to reject legislation was reduced to a delaying power. The g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Pitt, 1st Earl Of Chatham
William Pitt, 1st Earl of Chatham, (15 November 170811 May 1778) was a British statesman of the Whig group who served as Prime Minister of Great Britain from 1766 to 1768. Historians call him Chatham or William Pitt the Elder to distinguish him from his son William Pitt the Younger, who was also a prime minister. Pitt was also known as the Great Commoner, because of his long-standing refusal to accept a title until 1766. Pitt was a member of the British cabinet and its informal leader from 1756 to 1761 (with a brief interlude in 1757), during the Seven Years' War (including the French and Indian War in the American colonies). He again led the ministry, holding the official title of Lord Privy Seal, between 1766 and 1768. Much of his power came from his brilliant oratory. He was out of power for most of his career and became well known for his attacks on the government, such as those on Walpole's corruption in the 1730s, Hanoverian subsidies in the 1740s, peace with France ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Edward Hartpole Lecky
William Edward Hartpole Lecky (26 March 1838 – 22 October 1903) was an Irish historian, essayist, and political theorist with Whig proclivities. His major work was an eight-volume ''History of Ireland during the Eighteenth Century''. Early life Born at Newtown Park, near Dublin, he was the eldest son of John Hartpole Lecky, a landowner. He was educated at Kingstown, Armagh, at Cheltenham College, and at Trinity College Dublin, where he graduated BA in 1859 and MA in 1863, and where he studied divinity with a view to becoming a priest in the Church of Ireland. Career In 1860, Lecky published anonymously a small book entitled ''The Religious Tendencies of the Age'', but on leaving college he turned to historiography. In 1861 he published ''Leaders of Public Opinion in Ireland'', containing brief sketches of Jonathan Swift, Henry Flood, Henry Grattan and Daniel O'Connell, originally anonymous, republished in 1871; the essay on Swift, rewritten and amplified, appeared again in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whig (British Political Party)
The Whigs were a political faction and then a political party in the Parliaments of England, Scotland, Ireland, Great Britain and the United Kingdom. Between the 1680s and the 1850s, the Whigs contested power with their rivals, the Tories. The Whigs merged into the new Liberal Party with the Peelites and Radicals in the 1850s, and other Whigs left the Liberal Party in 1886 to form the Liberal Unionist Party, which merged into the Liberals' rival, the modern day Conservative Party, in 1912. The Whigs began as a political faction that opposed absolute monarchy and Catholic Emancipation, supporting constitutional monarchism with a parliamentary system. They played a central role in the Glorious Revolution of 1688 and were the standing enemies of the Roman Catholic Stuart kings and pretenders. The period known as the Whig Supremacy (1714–1760) was enabled by the Hanoverian succession of George I in 1714 and the failure of the Jacobite rising of 1715 by Tory rebels. The Whigs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worcestershire (UK Parliament Constituency)
Worcestershire was a county constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of England then of the Parliament of Great Britain from 1707 to 1800 and of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1801 to 1832. It was represented until 1832 by two Members of Parliament traditionally referred to as Knights of the Shire. It was split then into two two-member divisions, for Parliamentary purposes, Worcestershire Eastern and Worcestershire Western constituencies. Boundaries Worcestershire was one of the historic counties of England. The constituency comprised the whole county, except for the boroughs of Bewdley, Droitwich, Evesham and Worcester. Members of Parliament 1294–1478 Source: Treadway Russell Nash.Treadway Russell Nash, ''Collections for a History of Worcestershire'' (1783) 1479–1552 1553–1649 Source: TR Nash Commonwealth Parliaments Source: T. R. Nash, ''Collections for a History of Worcestershire'' (1783) MPs 1660–1832 Elections The county fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tewkesbury (UK Parliament Constituency)
Tewkesbury is a constituency represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since its 1997 recreation by Laurence Robertson, a Conservative. History 1610 to 1918 Tewkesbury existed in this period, first in the parliamentary borough form. It returned two MPs until this was reduced to one in 1868, then saw itself become instead a larger county division under the Redistribution of Seats Act 1885, and it was abolished in 1918. ;Prominent politicians * William Dowdeswell was Chancellor of the Exchequer for two years under Rockingham, and his short tenure of this position appears to have been a successful one, he being in Lecky's words a good financier, but nothing more. To general astonishment, he refused to abandon his friends and to take an office under The 1st Earl of Chatham ("Pitt the Elder"), who succeeded Rockingham in August 1766. Dowdeswell then led the Rockingham party in the House of Commons, taking an active part in debate until his death. In 1774 he warne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of Great Britain
The Parliament of Great Britain was formed in May 1707 following the ratification of the Acts of Union by both the Parliament of England and the Parliament of Scotland. The Acts ratified the treaty of Union which created a new unified Kingdom of Great Britain and created the parliament of Great Britain located in the former home of the English parliament in the Palace of Westminster, near the City of London. This lasted nearly a century, until the Acts of Union 1800 merged the separate British and Irish Parliaments into a single Parliament of the United Kingdom with effect from 1 January 1801. History Following the Treaty of Union in 1706, Acts of Union ratifying the Treaty were passed in both the Parliament of England and the Parliament of Scotland, which created a new Kingdom of Great Britain. The Acts paved the way for the enactment of the treaty of Union which created a new parliament, referred to as the 'Parliament of Great Britain', based in the home of the former Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
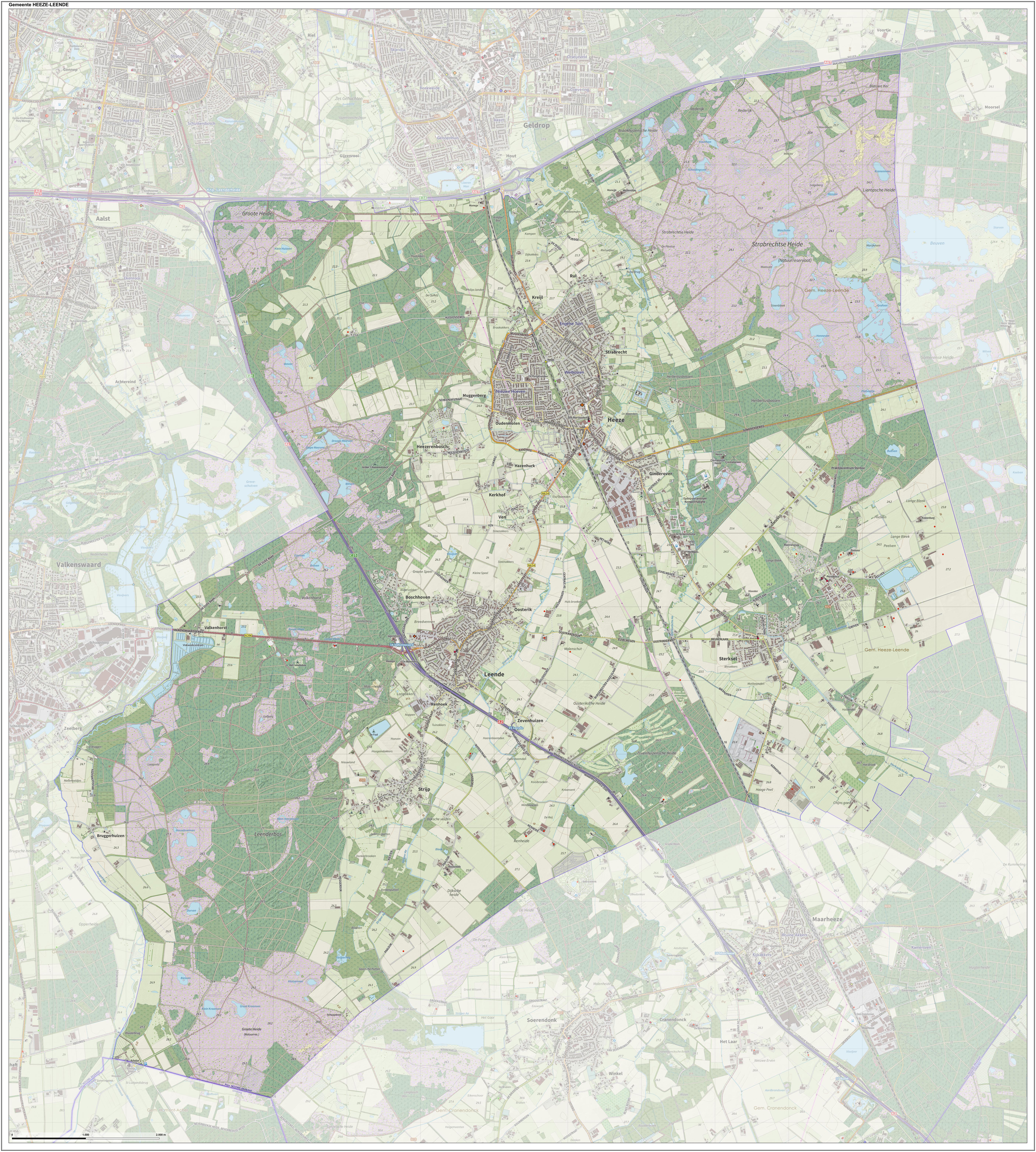
Heeze-Leende
Heeze-Leende () is a municipality in the southern Netherlands, near Eindhoven. It is known for Heeze Castle (''Kasteel Heeze''). The spoken language is "Heeze-en-Leendes", a distinct dialect within the East Brabantian dialect group and is very similar to colloquial Dutch. Population centres *Heeze *Leende * Sterksel Topography ''Dutch Topographic map of the municipality of Heeze-Leende, June 2015'' Notable people * Jan Moninckx (ca.1656 in Leende - 1714) a Dutch botanical artist and painter * Laurentius Nicolaas Deckers (1883 in Heeze – 1978) a Dutch politician, diplomat and agronomist. * Thomas Horsten Thomas Horsten (born 5 January 1994) is a Dutch footballer who plays as a midfielder for UNA. Career Horsten made his professional debut for Jong PSV, the second team of PSV Eindhoven, in the Eerste Divisie, the Dutch second tier, on 3 August 2 ... (born 1994 in Heeze) a Dutch professional footballer Gallery File:Catharinakerk, Beukenlaan 1, Sterksel.JPG, Catharin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baron D'Holbach
Paul-Henri Thiry, Baron d'Holbach (; 8 December 1723 – 21 January 1789), was a French-German philosopher, encyclopedist, writer, and prominent figure in the French Enlightenment. He was born Paul Heinrich Dietrich in Edesheim, near Landau in the Rhenish Palatinate, but lived and worked mainly in Paris, where he kept a ''salon''. He helped in the dissemination of "Protestant and especially German thought", particularly in the field of the sciences, but was best known for his atheism and for his voluminous writings against religion, the most famous of them being ''The System of Nature'' (1770) and '' The Universal Morality'' (1776). Biography Sources differ regarding d'Holbach's dates of birth and death. His exact birthday is unknown, although records show that he was baptised on 8 December 1723. Some authorities incorrectly give June 1789 as the month of his death. D'Holbach's mother, Catherine Jacobina (''née'' Holbach; 1684–1743), was the daughter of Johannes Jacob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiden University
Leiden University (abbreviated as ''LEI''; nl, Universiteit Leiden) is a Public university, public research university in Leiden, Netherlands. The university was founded as a Protestant university in 1575 by William the Silent, William, Prince of Orange, as a reward to the city of Leiden for its Siege of Leiden, defence against Spanish attacks during the Eighty Years' War. As the oldest institution of higher education in the Netherlands, it enjoys a reputation across Europe and the world. Known for its historic foundations and emphasis on the social sciences, the university came into particular prominence during the Dutch Golden Age, when scholars from around Europe were attracted to the Dutch Republic due to its climate of intellectual tolerance and Leiden's international reputation. During this time, Leiden became the home to individuals such as René Descartes, Rembrandt, Christiaan Huygens, Hugo Grotius, Baruch Spinoza and Baron d'Holbach. The university has seven academic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(cropped).jpg)