|
William A. Barnett
William Arnold Barnett (born October 30, 1941) is an American economist, whose current work is in the fields of chaos, bifurcation, and nonlinear dynamics in socioeconomic contexts, econometric modeling of consumption and production, and the study of the aggregation problem and the challenges of measurement in economics. Education Barnett received his B.S. degree in mechanical engineering from M.I.T., his M.B.A. from the University of California, Berkeley, and his M.A. and Ph.D. from Carnegie Mellon University. Positions Barnett is currently the Oswald Distinguished Professor of Macroeconomics at the University of Kansas and Director of thCenter for Financial Stability in New York City. He is also a Fellow of thIC² Instituteat the University of Texas at Austin and a Fellow of the Johns Hopkins Institute for Applied Economics, Global Health, and the Study of Business Enterprise. He is the founder and President of the Society for Economic Measurement. He is also the Director ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Economics
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics in which the production, consumption and valuation (pricing) of goods and services are observed as driven by the supply and demand model. According to this line of thought, the value of a good or service is determined through a hypothetical maximization of utility by income-constrained individuals and of profits by firms facing production costs and employing available information and factors of production. This approach has often been justified by appealing to rational choice theory, a theory that has come under considerable question in recent years. Neoclassical economics historically dominated macroeconomics and, together with Keynesian economics, formed the neoclassical synthesis which dominated mainstream economics as "neo-Keynesian economics" from the 1950s to the 1970s.Clark, B. (1998). ''Principles of political economy: A comparative approach''. Westport, Connecticut: Praeger. Nadeau, R. L. (2003). ''The Wealth of Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society For Economic Measurement (SEM)
The Society for Economic Measurement, or SEM, is a scientific learned society in the field of economics. It was founded on August 24, 2013 by William A. Barnett in order to "promote research on economic measurement, using advanced tools from economic theory, econometrics, aggregation theory, experimental economics, mathematics, and statistics". Nobel Laureate James Heckman will take over as the society's second president in 2019 for a three-year term in office. The goal of the SEM is to promote in economics—given the constraints of a social science—the implementation of the strict rules of measurement and data gathering standards used in the physical sciences. Carnegie Mellon University, thCenter for Financial Stability and the University of Kansas are sponsors of the society. Activities * The inaugural conference of the SEM was held at thHarper Centerof the University of Chicago's Booth School of Business on August 18–20, 2014. It was co-sponsored by the Becker Friedman In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society For Economic Measurement
The Society for Economic Measurement, or SEM, is a scientific learned society in the field of economics. It was founded on August 24, 2013 by William A. Barnett in order to "promote research on economic measurement, using advanced tools from economic theory, econometrics, aggregation theory, experimental economics, mathematics, and statistics". Nobel Laureate James Heckman will take over as the society's second president in 2019 for a three-year term in office. The goal of the SEM is to promote in economics—given the constraints of a social science—the implementation of the strict rules of measurement and data gathering standards used in the physical sciences. Carnegie Mellon University, thCenter for Financial Stability and the University of Kansas are sponsors of the society. Activities * The inaugural conference of the SEM was held at thHarper Centerof the University of Chicago's Booth School of Business on August 18–20, 2014. It was co-sponsored by the Becker Friedman In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute For Applied Economics, Global Health, And The Study Of Business Enterprise
Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hemisphere. It consistently ranks among the most prestigious universities in the United States and the world. The university was named for its first benefactor, the American entrepreneur and Quaker philanthropist Johns Hopkins. Hopkins' $7 million bequest to establish the university was the largest Philanthropy, philanthropic gift in U.S. history up to that time. Daniel Coit Gilman, who was inaugurated as :Presidents of Johns Hopkins University, Johns Hopkins's first president on February 22, 1876, led the university to revolutionize higher education in the U.S. by integrating teaching and research. In 1900, Johns Hopkins became a founding member of the American Association of Universities. The university has led all Higher education in the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix ''makro-'' meaning "large" + ''economics'') is a branch of economics dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. For example, using interest rates, taxes, and government spending to regulate an economy's growth and stability. This includes regional, national, and global economies. According to a 2018 assessment by economists Emi Nakamura and Jón Steinsson, economic "evidence regarding the consequences of different macroeconomic policies is still highly imperfect and open to serious criticism." Macroeconomists study topics such as Gross domestic product, GDP (Gross Domestic Product), unemployment (including Unemployment#Measurement, unemployment rates), national income, price index, price indices, output (economics), output, Consumption (economics), consumption, inflation, saving, investment (macroeconomics), investment, Energy economics, energy, international trade, and international finance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant university and the founding campus of the University of California system. Its fourteen colleges and schools offer over 350 degree programs and enroll some 31,800 undergraduate and 13,200 graduate students. Berkeley ranks among the world's top universities. A founding member of the Association of American Universities, Berkeley hosts many leading research institutes dedicated to science, engineering, and mathematics. The university founded and maintains close relationships with three national laboratories at Berkeley, Livermore and Los Alamos, and has played a prominent role in many scientific advances, from the Manhattan Project and the discovery of 16 chemical elements to breakthroughs in computer science and genomics. Berkeley is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It is one of the oldest and broadest of the engineering branches. Mechanical engineering requires an understanding of core areas including mechanics, dynamics, thermodynamics, materials science, structural analysis, and electricity. In addition to these core principles, mechanical engineers use tools such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and product lifecycle management to design and analyze manufacturing plants, industrial equipment and machinery, heating and cooling systems, transport systems, aircraft, watercraft, robotics, medical devices, weapons, and others. Mechanical engineering emerged as a field during the Industrial Revolution in Europe in the 18th century; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measurement In Economics
The measures used in economics are physical measures, nominal price value measures and fixed price value measures. These measures differ from one another by the variables they measure and by the variables excluded from measurements. The measurable variables in economics are quantity, quality and distribution. Excluding variables from measurement makes it possible to better focus the measurement on a given variable, yet, this means a more narrow approach. The table was compiled to compare the basic types of measurement. The first column presents the measure types, the second the variables being measured, and the third column gives the variables excluded from measurement. Variables The measurable variables in economics are quantity, quality and distribution. Measuring quantity in economics follows the rules of measuring in physics. Quality as a variable refers to qualitative changes in the production process. Qualitative changes take place when relative of different constant-price i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggregation Problem
An ''aggregate'' in economics is a summary measure. It replaces a vector that is composed of many real numbers by a single real number, or a scalar. Consequently there occur various problems that are inherent in the formulations that use aggregated variables.Franklin M. Fisher (1987). "aggregation problem," '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 1, pp.53-55 The aggregation problem is the difficult problem of finding a valid way to treat an empirical or theoretical aggregate as if it reacted like a less-aggregated measure, say, about behavior of an individual agent as described in general microeconomic theory. The second meaning of "aggregation problem" is the theoretical difficulty in using and treating laws and theorems that include aggregate variables. A typical example is the aggregate production function. Another famous problem is Sonnenschein-Mantel-Debreu theorem. Most of macroeconomic statements comprise this problem. Examples of aggregates in micro- and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Econometric
Econometrics is the application of statistical methods to economic data in order to give empirical content to economic relationships. M. Hashem Pesaran (1987). "Econometrics," '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 2, p. 8 p. 8–22 Reprinted in J. Eatwell ''et al.'', eds. (1990). ''Econometrics: The New Palgrave''p. 1 p. 1–34Abstract (2008 revision by J. Geweke, J. Horowitz, and H. P. Pesaran). More precisely, it is "the quantitative analysis of actual economic phenomena based on the concurrent development of theory and observation, related by appropriate methods of inference". An introductory economics textbook describes econometrics as allowing economists "to sift through mountains of data to extract simple relationships". Jan Tinbergen is one of the two founding fathers of econometrics. The other, Ragnar Frisch, also coined the term in the sense in which it is used today. A basic tool for econometrics is the multiple linear regression model. ''Econometri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Dynamics
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists because most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a linear combination of the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
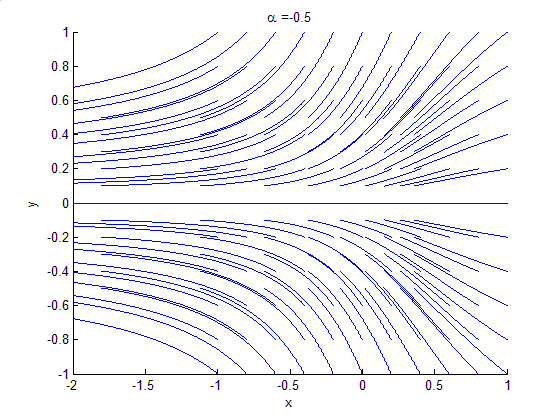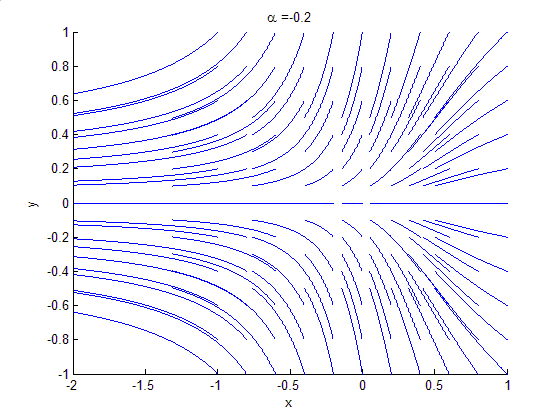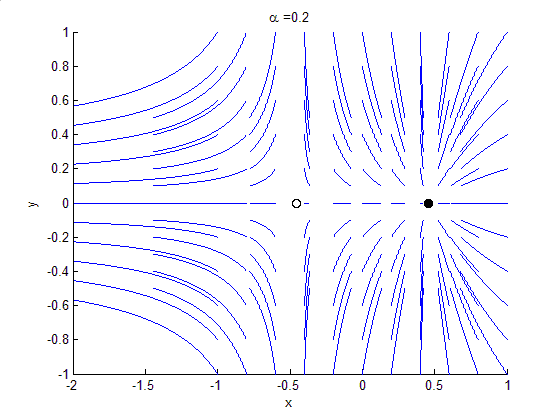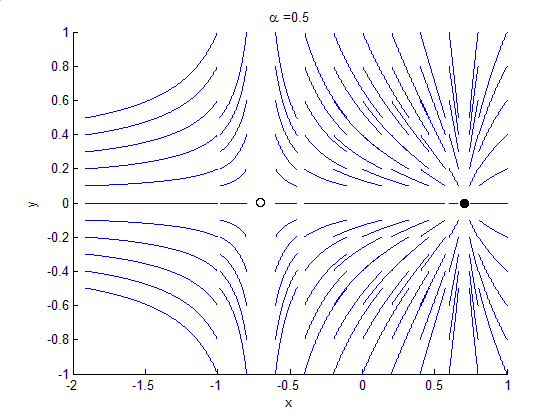
Bifurcation Theory
Bifurcation theory is the mathematical study of changes in the qualitative or topological structure of a given family of curves, such as the integral curves of a family of vector fields, and the solutions of a family of differential equations. Most commonly applied to the mathematical study of dynamical systems, a bifurcation occurs when a small smooth change made to the parameter values (the bifurcation parameters) of a system causes a sudden 'qualitative' or topological change in its behavior. Bifurcations occur in both continuous systems (described by ordinary, delay or partial differential equations) and discrete systems (described by maps). The name "bifurcation" was first introduced by Henri Poincaré in 1885 in the first paper in mathematics showing such a behavior. Henri Poincaré also later named various types of stationary points and classified them . Bifurcation types It is useful to divide bifurcations into two principal classes: * Local bifurcations, which can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |