|
Wilhelm Neumann
Carl Johann Wilhelm Neumann ( lv, Kārlis Johans Vilhelms Neimanis; russian: Карл Иоганн Вильгельм Нейман; born 5 October 1849 in Grevesmühlen – died 6 March 1919 in Riga) was a Baltic German architect and art historian. Neumann's family moved to Kreutzburg (then in Russian Empire) during Wilhelm's childhood. When he was 15 years old, he worked as an apprentice at Paul Max Bertschy's engineering office during the construction of the Riga–Dünaburg Railway. After this he studied at the Riga Polytechnicum, and beginning 1875 at the Imperial Academy of Arts in Saint Petersburg. Beginning 1873 Neumann worked as an architect in Dünaburg (Daugavpils), and 1878 he was promoted to be chief architect of Dünaburg. In 1887 he began to publish art historical publications. In 1895 he moved to Riga, where numerous prominent buildings in the style of historicism was created, amongst these the Peitav Synagogue. Furthermore, Neumann was the planner of many manor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grevesmühlen
Grevesmühlen () is a municipality in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, northern Germany. It was the seat of the Nordwestmecklenburg district until 2011, when Wismar became the seat. It is situated 33 km east of Lübeck, and 29 km northwest of Schwerin. It is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region. History The name Grevesmühlen goes back as far as 1226, which makes it one of the oldest towns in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Personalities *Carsten Jancker *Manfred W. Jürgens *Rudolph Karstadt * Astrid Kumbernuss *Jens Voigt Jens Voigt (; born 17 September 1971) is a German former professional road bicycle racer and, upon retirement, became a cycling sports broadcast commentator. During his cycling career, Voigt raced for several teams, the last one being UCI ProTe ... References Cities and towns in Mecklenburg Nordwestmecklenburg Populated places established in the 13th century 1260s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1261 establishments in Europe Grand Duchy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
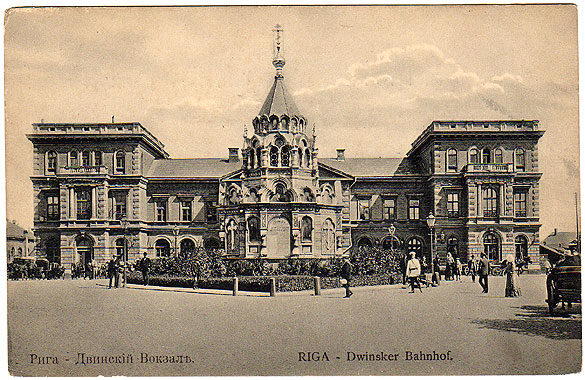
Riga–Daugavpils Railway
The Riga–Daugavpils railway line ( lv, Dzelzceļa līnija Rīga—Daugavpils) is a long railway line in Latvia which connects the cities of Riga in central Latvia and Daugavpils in south-eastern Latvia. The railway line is double track between Riga and Krustpils and single track between Krustpils and Daugavpils. The track gauge is (Russian gauge). It was built in 1861, and is one the oldest railway lines in Latvia. History The railway line was opened on 21 September 1861 as one of the first railway lines in the present territory of Latvia. It was a part of the Riga–Oryol railway line, a long railway line in the Russian Empire, constructed to connect the Baltic Sea at Riga with Oryol in central Russia. At Daugavpils the line connected with the Saint Petersburg–Warsaw Railway Saint Petersburg–Warsaw Railway (() (transliteration: Sankt-Peterburgo–Varshavskaya zheleznaya doroga)) is a long railway, built in the 19th century by the Russian Empire to connect Russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Grevesmühlen
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historians From The Russian Empire
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human race; as well as the study of all history in time. Some historians are recognized by publications or training and experience.Herman, A. M. (1998). Occupational outlook handbook: 1998–99 edition. Indianapolis: JIST Works. Page 525. "Historian" became a professional occupation in the late nineteenth century as research universities were emerging in Germany and elsewhere. Objectivity During the ''Irving v Penguin Books Ltd, Irving v Penguin Books and Lipstadt'' trial, people became aware that the court needed to identify what was an "objective historian" in the same vein as the reasonable person, and reminiscent of the standard traditionally used in English law of "the man on the Clapham omnibus". This was necessary so that there would be a legal benchmark to comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architects From The Russian Empire
An architect is a person who plans, designs and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that have human occupancy or use as their principal purpose. Etymologically, the term architect derives from the Latin ''architectus'', which derives from the Greek (''arkhi-'', chief + ''tekton'', builder), i.e., chief builder. The professional requirements for architects vary from place to place. An architect's decisions affect public safety, and thus the architect must undergo specialized training consisting of advanced education and a ''practicum'' (or internship) for practical experience to earn a license to practice architecture. Practical, technical, and academic requirements for becoming an architect vary by jurisdiction, though the formal study of architecture in academic institutions has played a pivotal role in the development of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic-German People
Baltic Germans (german: Deutsch-Balten or , later ) were ethnic German inhabitants of the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea, in what today are Estonia and Latvia. Since their coerced resettlement in 1939, Baltic Germans have markedly declined as a geographically determined ethnic group. However, it is estimated that several thousand people with some form of (Baltic) German identity still reside in Latvia and Estonia. Since the Middle Ages, native German-speakers formed the majority of merchants and clergy, and the large majority of the local landowning nobility who effectively constituted a ruling class over indigenous Latvian and Estonian non-nobles. By the time a distinct Baltic German ethnic identity began emerging in the 19th century, the majority of self-identifying Baltic Germans were non-nobles belonging mostly to the urban and professional middle class. In the 12th and 13th centuries, Catholic German traders and crusaders (''see '') began settling in the eastern Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1919 Deaths
Events January * January 1 ** The Czechoslovak Legions occupy much of the self-proclaimed "free city" of Pressburg (now Bratislava), enforcing its incorporation into the new republic of Czechoslovakia. ** HMY ''Iolaire'' sinks off the coast of the Hebrides; 201 people, mostly servicemen returning home to Lewis and Harris, are killed. * January 2– 22 – Russian Civil War: The Red Army's Caspian-Caucasian Front begins the Northern Caucasus Operation against the White Army, but fails to make progress. * January 3 – The Faisal–Weizmann Agreement is signed by Emir Faisal (representing the Arab Kingdom of Hejaz) and Zionist leader Chaim Weizmann, for Arab–Jewish cooperation in the development of a Jewish homeland in Palestine, and an Arab nation in a large part of the Middle East. * January 5 – In Germany: ** Spartacist uprising in Berlin: The Marxist Spartacus League, with the newly formed Communist Party of Germany and the Independent Social Democ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1849 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – France begins issue of the Ceres series, the nation's first postage stamps. * January 5 – Hungarian Revolution of 1848: The Austrian army, led by Alfred I, Prince of Windisch-Grätz, enters in the Hungarian capitals, Buda and Pest. The Hungarian government and parliament flee to Debrecen. * January 8 – Hungarian Revolution of 1848: Romanian armed groups massacre 600 unarmed Hungarian civilians, at Nagyenyed.Hungarian HistoryJanuary 8, 1849 And the Genocide of the Hungarians of Nagyenyed/ref> * January 13 ** Second Anglo-Sikh War – Battle of Tooele: British forces retreat from the Sikhs. ** The Colony of Vancouver Island is established. * January 21 ** General elections are held in the Papal States. ** Hungarian Revolution of 1848: Battle of Nagyszeben – The Hungarian army in Transylvania, led by Josef Bem, is defeated by the Austrians, led by Anton Puchner. * January 23 – Elizabeth Blackwell is awarded her M.D. by the Medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelči Palace
Pelči Palace ( lv, Pelču muižas pils; german: Schloss Pelzen) is a palace located in the region of Kurzeme (formerly Courland), in western Latvia. Built during the time of Prince Anatoly Lieven, it is regarded as one of the early Latvian manors which felt the influence of early Art Nouveau, although presently it also shows German Neo-Renaissance, and Baroque features. History The palace was built from 1903 to 1904 in Art Nouveau style by architect Wilhelm Neumann (1878 in Germany – 1919 in Riga). All building parts, starting with the front doors, windows, wrought iron roof, shutter closure and all the finishing with interior panels, stair railings, were designed by Neumann. The palace is considered a building of exceptional aesthetic level on all elements of the finishing with high quality facilities and innovative technical equipment. The palace basement has a modern drainage system and water supply. Kilns heat the palace through the first central heating system from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latvian National Museum Of Art
The Latvian National Museum of Art ( lv, Latvijas Nacionālais mākslas muzejs) is the richest collection of national art in Latvia. It houses more than 52,000 works of art reflecting the development of professional art in the Baltic area and in Latvia from the middle of the 18th century until the present time. The museum is located in building in Riga, which is historically significant. The building at 1, Janis Rozentāls sq. was designed by the German architect Wilhelm Neumann and built in 1905 latvia.travel — it is one of the most impressive historical buildings on the boulevard and is situated next to the Academy of Art. It was the first building in the Baltics to be built for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurland Provincial Museum And Athenaeum
Kurland Provincial Museum and Athenaeum () was Kurzeme Society of Literature and Art museum with library. It was founded in 1818 in Mitau (since 1917 Jelgava), at that time the capital of Courland Governorate of Russian Empire. History The museum was founded on August 6, 1818 as the Kurzeme Provincial Museum with a lecture club "Athenaeum". Among founding members of new society was Johann Friedrich von Recke. The lectures were initially held on the premises of Jelgava Gymnasium, after 1820 on the second floor of the printing house on ''Kannulējēju'' (now ), where the first museum collection was created. Riga's architect Wilhelm Neumann developed a project for a new museum building, which was built on the site of the demolished Jelgava Theater building in the former Stļļplacis (near the present ) and opened on November 26, 1898. The entrance portal of the house was decorated with the inscription in Latin "Science and Art". In 1916, was established in the museum hall. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Governorates
The Baltic governorates (russian: Прибалтийские губернии), originally the Ostsee governorates (german: Ostseegouvernements, russian: Остзейские губернии), was a collective name for the administrative units of the Russian Empire set up in the territories of Swedish Estonia, Swedish Livonia (1721) and, afterwards, of the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (1795). History The Treaty of Vilnius of 1561 included the ''Privilegium Sigismundi Augusti'' by which the Polish King Sigismund II Augustus guaranteed the Livonian estates several privileges, including religious freedom with respect to the Augsburg Confession, the '' Indigenat'' ( pl, Indygenat), and continuation of the traditional German jurisdiction and administration. The terms regarding religious freedom forbade any regulation of the traditional Protestant order by religious or secular authorities, and ruled that cases of disagreements be judged only by Protestant scholars. When in 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_1938.jpg)



