|
Wilhelm Heinrich Erb (HeidICON 53028) (cropped)
Wilhelm Heinrich Erb (30 November 1840 – 29 October 1921) was a German neurologist. He was born in Winnweiler, and died in Heidelberg. Academic career In 1864 he received his medical degree from the University of Heidelberg, where for several years he served as an assistant to pathologist Nikolaus Friedreich (1825–1882). As a young man, he also worked for a period of time under Ludwig von Buhl (1816–1880) in Munich. In 1880 Erb attained the chair of special pathology at the University of Leipzig, where he was also appointed head of its policlinic. In 1883 he succeeded Friedreich at the University of Heidelberg, where he worked until his retirement in 1907. Psychiatrist Emil Kraepelin (1856–1926) and neurologists Ernst Julius Remak (1849–1911), Max Nonne (1861–1959) and Paul Julius Möbius (1853–1907) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winnweiler
Winnweiler is a municipality in the Donnersbergkreis, in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is situated on the upper course of the river Alsenz, approx. north-east of Kaiserslautern. Winnweiler is the seat of the '' Verbandsgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") Winnweiler. Winnweiler station is on the Alsenz Valley Railway (''Alsenztalbahn''), running between Hochspeyer and Bad Münster am Stein. The settlement in Rhenish Franconia was first mentioned in an 891 deed, from the 12th century onwards it was a possession of the Counts of Falkenstein. As a Lorraine exclave it fell to the House of Habsburg upon the marriage of Maria Theresa of Austria with Duke Francis III Stephen in 1736. It was thereafter administered as an ''Oberamt'' of Further Austria until its occupation by French troops in 1797. Geography Winnweiler is located in the Saar-Nahe-Bergland and on the edge of the Donnersberg nature reserve. The municipality is divided into the following districts * A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Leipzig
Leipzig University (german: Universität Leipzig), in Leipzig in Saxony, Germany, is one of the world's oldest universities and the second-oldest university (by consecutive years of existence) in Germany. The university was founded on 2 December 1409 by Frederick I, Elector of Saxony and his brother William II, Margrave of Meissen, and originally comprised the four scholastic faculties. Since its inception, the university has engaged in teaching and research for over 600 years without interruption. Famous alumni include Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Leopold von Ranke, Friedrich Nietzsche, Robert Schumann, Richard Wagner, Tycho Brahe, Georgius Agricola, Angela Merkel and ten Nobel laureates associated with the university. History Founding and development until 1900 The university was modelled on the University of Prague, from which the German-speaking faculty members withdrew to Leipzig after the Jan Hus crisis and the Decree of Kutná H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabes Dorsalis
Tabes dorsalis is a late consequence of neurosyphilis, characterized by the slow degeneration (specifically, demyelination) of the neural tracts primarily in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord (nerve root). These patients have lancinating nerve root pain which is aggravated by coughing, and features of sensory ataxia with ocular involvement. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms may not appear for decades after the initial infection and include weakness, diminished reflexes, paresthesias (shooting and burning pains, pricking sensations, and formication), hypoesthesias (abnormally diminished sense of touch), tabetic gait (locomotor ataxia), progressive degeneration of the joints, loss of coordination, episodes of intense pain and disturbed sensation (including glossodynia), personality changes, urinary incontinence, dementia, deafness, visual impairment, positive Romberg's test, and impaired response to light (Argyll Robertson pupil). The skeletal musculature is hypotonic d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary). The primary stage classically presents with a single chancre (a firm, painless, non-itchy skin ulceration usually between 1 cm and 2 cm in diameter) though there may be multiple sores. In secondary syphilis, a diffuse rash occurs, which frequently involves the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There may also be sores in the mouth or vagina. In latent syphilis, which can last for years, there are few or no symptoms. In tertiary syphilis, there are gummas (soft, non-cancerous growths), neurological problems, or heart symptoms. Syphilis has been known as "the great imitator" as it may cause symptoms similar to many other diseases. Syphilis is most commonly spread through sexual activity. It may also be transmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
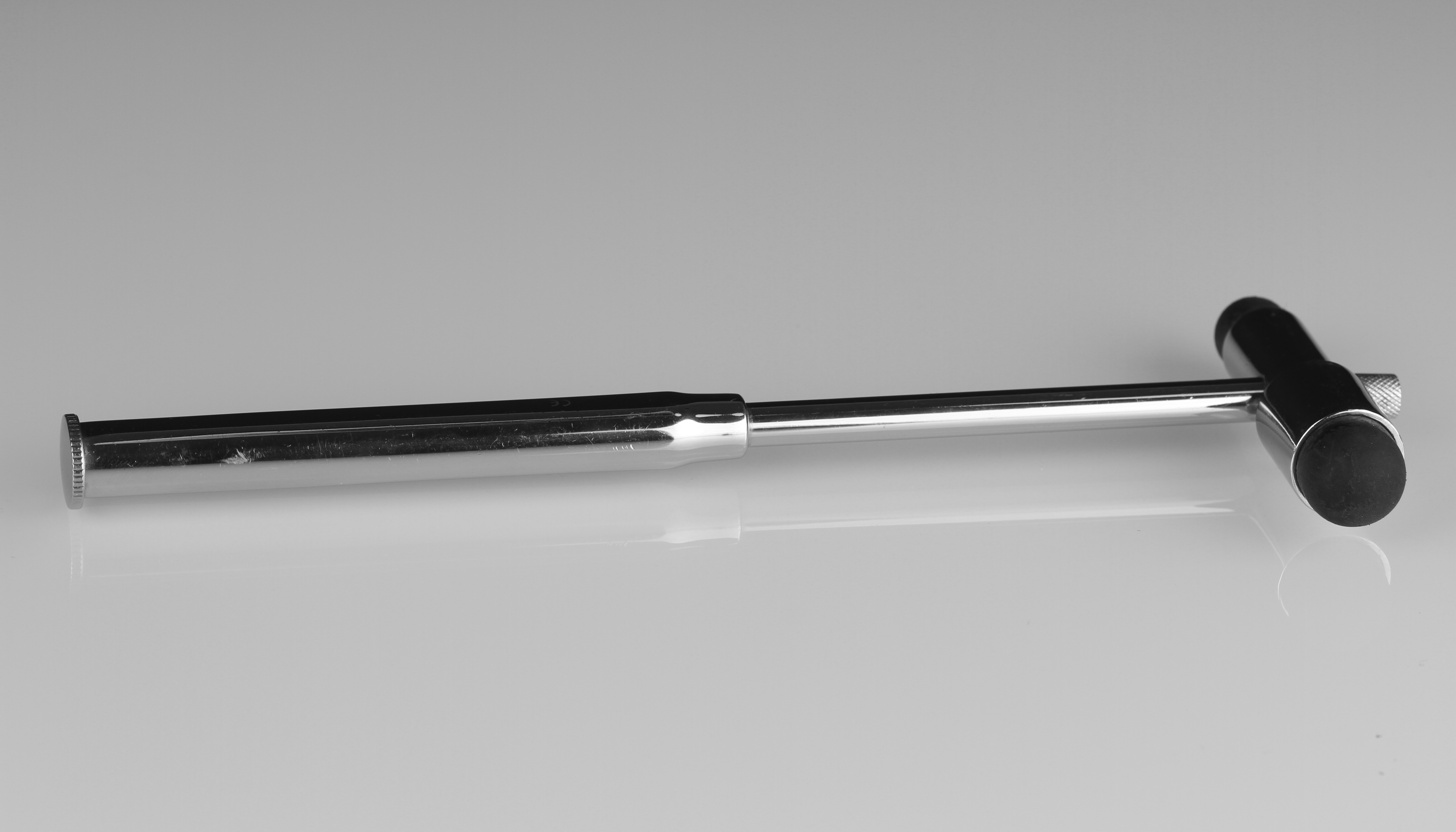
Reflex Hammer
A reflex hammer is a medical instrument used by practitioners to test deep tendon reflexes. Testing for reflexes is an important part of the neurological physical examination in order to detect abnormalities in the central or peripheral nervous system. Reflex hammers can also be used for chest percussion.Swartz MH. ''Textbook of Physical Diagnosis: History and Examination.'' Third edition. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1998 Models of reflex hammer Prior to the development of specialized reflex hammers, hammers specific for percussion of the chest were used to elicit reflexes.Lanska DJ. The history of reflex hammers. ''Neurology''. 1989 Nov;39(11):1542-9. However, this proved to be cumbersome, as the weight of the chest percussion hammer was insufficient to generate an adequate stimulus for a reflex. Starting in the late 19th century, several models of specific reflex hammers were created: *The Taylor or tomahawk reflex hammer was designed by John Madison Taylor in 1888 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetanus
Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is a bacterial infection caused by ''Clostridium tetani'', and is characterized by muscle spasms. In the most common type, the spasms begin in the jaw and then progress to the rest of the body. Each spasm usually lasts a few minutes. Spasms occur frequently for three to four weeks. Some spasms may be severe enough to fracture bones. Other symptoms of tetanus may include fever, sweating, headache, trouble swallowing, high blood pressure, and a fast heart rate. Onset of symptoms is typically three to twenty-one days following infection. Recovery may take months. About ten percent of cases prove to be fatal. ''C. tetani'' is commonly found in soil, saliva, dust, and manure. The bacteria generally enter through a break in the skin such as a cut or puncture wound by a contaminated object. They produce toxins that interfere with normal muscle contractions. Diagnosis is based on the presenting signs and symptoms. The disease does not spread between pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Nerve
A motor nerve is a nerve that transmits motor signals from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles of the body. This is different from the motor neuron, which includes a cell body and branching of dendrites, while the nerve is made up of a bundle of axons. Motor nerves act as efferent nerves which carry information out from the CNS to muscles, as opposed to afferent nerves (also called sensory nerves), which transfer signals from sensory receptors in the periphery to the CNS. Efferent nerves can also connect to glands or other organs/issues instead of muscles (and so motor nerves are not equivalent to efferent nerves). In addition, there are nerves that serve as both sensory and motor nerves called mixed nerves. Structure and function Motor nerve fibers transduce signals from the CNS to peripheral neurons of proximal muscle tissue. Motor nerve axon terminals innervate skeletal and smooth muscle, as they are heavily involved in muscle control. Motor nerves tend to be r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrodiagnostic Testing
Electrodiagnosis (EDX) is a method of medical diagnosis that obtains information about diseases by passively recording the electrical activity of body parts (that is, their natural electrophysiology) or by measuring their response to external electrical stimuli (evoked potentials). The most widely used methods of recording spontaneous electrical activity are various forms of electrodiagnostic testing ( electrography) such as electrocardiography (ECG), electroencephalography (EEG), and electromyography (EMG). Electrodiagnostic medicine (also EDX) is a medical subspecialty of neurology, clinical neurophysiology, cardiology, and physical medicine and rehabilitation. Electrodiagnostic physicians apply electrophysiologic techniques, including needle electromyography and nerve conduction studies to diagnose, evaluate, and treat people with impairments of the neurologic, neuromuscular, and/or muscular systems. The provision of a quality electrodiagnostic medical evaluation requires exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurology
Neurology (from el, wikt:νεῦρον, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine), medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system. A neurologist is a physician specializing in neurology and trained to investigate, diagnose and treat neurological disorders. Neurologists treat a myriad of neurologic conditions, including stroke, seizures, movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, autoimmune neurologic disorders such as multiple sclerosis, headache disorders like migraine and dementias such as Alzheimer's disease. Neurologists may also be involved in clinical research, clinical trials, and basic research, basic or translational research. While neurology is a nonsurgical sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
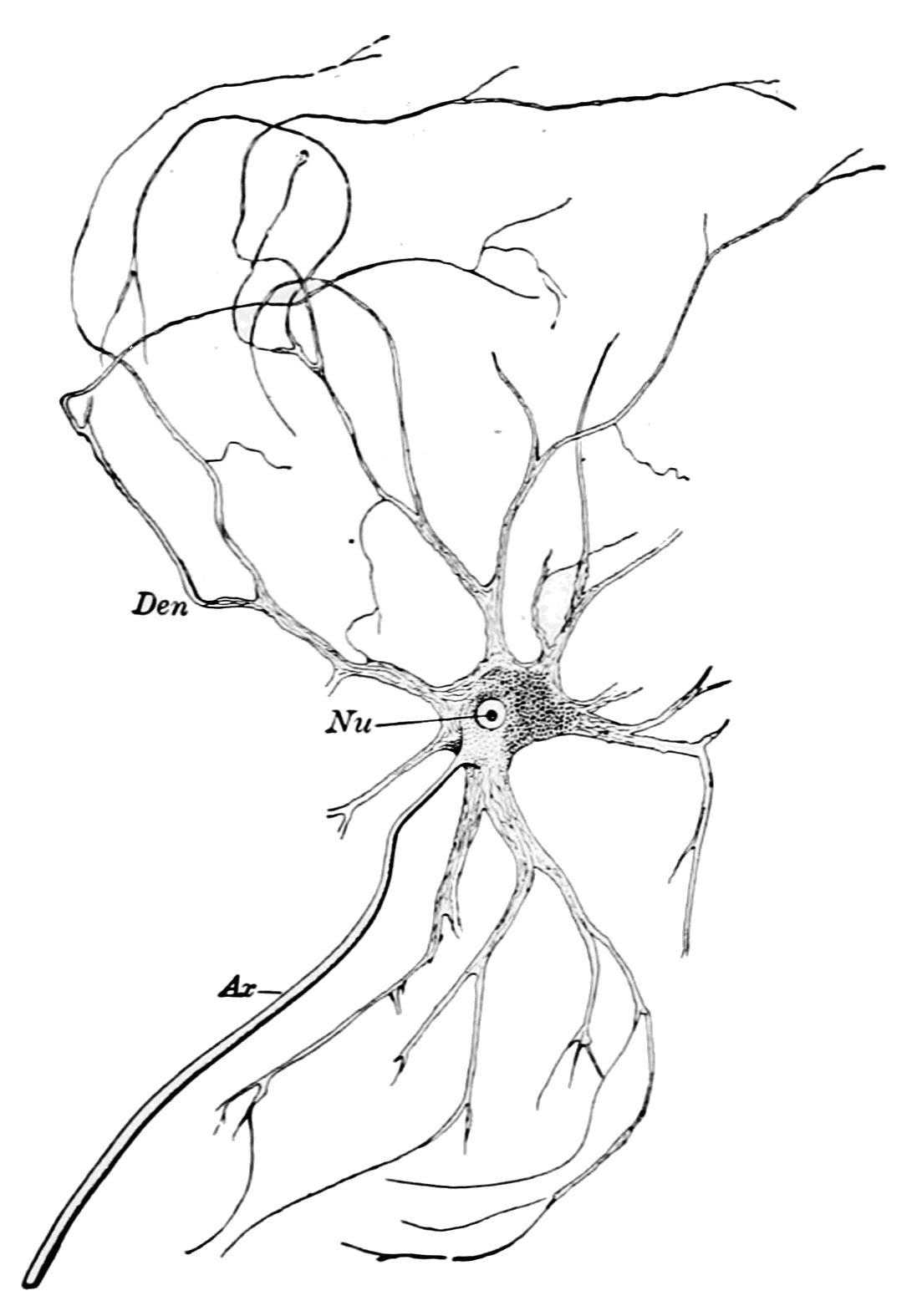
Histology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating exposures to toxins and toxicants. The relationship between dose and its effects on the exposed organism is of high significance in toxicology. Factors that influence chemical toxicity include the dosage, duration of exposure (whether it is acute or chronic), route of exposure, species, age, sex, and environment. Toxicologists are experts on poisons and poisoning. There is a movement for evidence-based toxicology as part of the larger movement towards evidence-based practices. Toxicology is currently contributing to the field of cancer research, since some toxins can be used as drugs for killing tumor cells. One prime example of this is ribosome-inactivating proteins, tested in the treatment of leukemia. The word ''toxicology'' () is a neocla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Julius Möbius
Paul Julius Möbius (January 24, 1853 – January 8, 1907) was a German neurologist born in Leipzig. His grandfather was German mathematician and theoretical astronomer, August Ferdinand Möbius (1790–1868). Prior to entering the medical field in 1873, he studied philosophy and theology at the Universities of Leipzig, Jena and Marburg. After earning his medical doctorate in 1876, he enlisted in the army, attaining the rank of ''Oberstabsarzt'' (senior staff surgeon). After leaving the army, he returned to Leipzig, where he opened a private practice and worked as an assistant to neurologist Adolph Strümpell (1853-1925) at the university policlinic. In 1883 he obtained his habilitation for neurology. He was a prolific writer and is well known for publications in the fields of neurophysiology and endocrinology. Among his writings in psychiatry were psychopathological studies of Goethe, Rousseau, Schopenhauer and Nietzsche. He was also an editor of ''Schmidt's Jahrbücher der in- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_(6009043040).jpg)
_Moebius.jpg)