|
Wilhelm Dachauer
Wilhelm Dachauer (5 April 1881 – 26 February 1951) was an Austrian painter. He studied at the Akademie der bildenden Künste in Vienna from 1899 to 1907 and was a professor at the academy from 1928 to 1944. Life Dachauer was in Ried im Innkreis on 5 April 1881 into a family of clockmakers. He was intended to continue his father's business but after some struggle, he was allowed to move to Vienna, where he had a time full of privations. He started an apprenticeship as decoration painter and in the nighttime he prepared for the Academy of Applied Arts. In 1899, 17-year-old Dachauer began his studies under the supervision of Professor Griepenkerl. In 1913, he had his first arguably successful exhibition at the Secession. He was appointed to an honored professorship of the Akademie der bildenden Künste (Academy of Fine Arts) in Vienna in 1928, a position that he occupied until 1944. Temporarily, he was rector of the institution. Among his students were Hildegard Joos, Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Dachauer WWI Poster 1
Wilhelm may refer to: People and fictional characters * William Charles John Pitcher, costume designer known professionally as "Wilhelm" * Wilhelm (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or surname Other uses * Mount Wilhelm, the highest mountain in Papua New Guinea * Wilhelm Archipelago, Antarctica * Wilhelm (crater), a lunar crater See also * Wilhelm scream, a stock sound effect * SS Kaiser Wilhelm II, SS ''Kaiser Wilhelm II'', or USS ''Agamemnon'', a German steam ship * Wilhelmus, the Dutch national anthem {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nibelungen
The term Nibelung (German) or Niflungr (Old Norse) is a personal or clan name with several competing and contradictory uses in Germanic heroic legend. It has an unclear etymology, but is often connected to the root ''nebel'', meaning mist. The term in its various meanings gives its name to the Middle High German heroic epic the ''Nibelungenlied''. The most widespread use of Nibelung is used to denote the Burgundian royal house, also known as the Gibichungs (German) or Gjúkingar (Old Norse). A group of royal brothers led by king Gunther or Gunnar, the Gibichungs are responsible for the death of the hero Siegfried or Sigurd and are later destroyed at the court of Attila the Hun (called Etzel in German and Atli in Old Norse). This is the only use of the term attested in the Old Norse legends. In medieval German, several other uses of the term Nibelung are documented besides the reference to the Gibichungs: it refers to the king and inhabitants of a mythical land inhabited by d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1951 Deaths
Events January * January 4 – Korean War: Third Battle of Seoul – Chinese and North Korean forces capture Seoul for the second time (having lost the Second Battle of Seoul in September 1950). * January 9 – The Government of the United Kingdom announces abandonment of the Tanganyika groundnut scheme for the cultivation of peanuts in the Tanganyika Territory, with the writing off of £36.5M debt. * January 15 – In a court in West Germany, Ilse Koch, The "Witch of Buchenwald", wife of the commandant of the Buchenwald concentration camp, is sentenced to life imprisonment. * January 20 – Winter of Terror: Avalanches in the Alps kill 240 and bury 45,000 for a time, in Switzerland, Austria and Italy. * January 21 – Mount Lamington in Papua New Guinea erupts catastrophically, killing nearly 3,000 people and causing great devastation in Oro Province. * January 25 – Dutch author Anne de Vries releases the first volume of his children's novel '' Journey Through the Nigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1881 Births
Events January–March * January 1– 24 – Siege of Geok Tepe: Russian troops under General Mikhail Skobelev defeat the Turkomans. * January 13 – War of the Pacific – Battle of San Juan and Chorrillos: The Chilean army defeats Peruvian forces. * January 15 – War of the Pacific – Battle of Miraflores: The Chileans take Lima, capital of Peru, after defeating its second line of defense in Miraflores. * January 24 – William Edward Forster, chief secretary for Ireland, introduces his Coercion Bill, which temporarily suspends habeas corpus so that those people suspected of committing an offence can be detained without trial; it goes through a long debate before it is accepted February 2. * January 25 – Thomas Edison and Alexander Graham Bell form the Oriental Telephone Company. * February 13 – The first issue of the feminist newspaper ''La Citoyenne'' is published by Hubertine Auclert. * February 16 – The Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essling
Essling Essling entry in the Viennese government's history wiki (German) () is part of Donaustadt, the 22nd district of Vienna. History The oldest form of the place name was Ezzelaren. The Eslarn family had important roles in the Vienna city administration. Konrad von Eslarn was mayor of Vienna in 1287. From about 1590, the place name changed into Ehsling or Essling. The area is known for the Battle of Aspern-Essling, which was fought nearby between May 21 and May 22, 1809.Sports clubs The district is also known for their own soccer-team called SV Essling, which was founded in 1931, currently playing in the minor leagues.Sights [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viktor Kaplan
Viktor Kaplan (27 November 1876 – 23 August 1934) was an Austrian engineer and the inventor of the Kaplan turbine. Life Kaplan was born in Mürzzuschlag, Austria into a railroad worker's family. He graduated from high school in Vienna in 1895, after which he attended the Technical University of Vienna, where he studied civil engineering and specialised in diesel engines. From 1900 to 1901 he was drafted into military service in Pula. After working in Vienna with a specialisation in motors, he moved to the German Technical University in Brno to conduct research at the institute of civil engineering. He spent the next three decades of his life in Brno, and nearly all his inventions and research are connected with his professorship there. In 1913 he was appointed head of the institute for water turbines. In 1912 he published his most notable work: the Kaplan turbine, a revolutionary water turbine that was especially fitted to produce electricity from large streams with only a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Wagner-Jauregg
Julius Wagner-Jauregg (; 7 March 1857 – 27 September 1940) was an Austrian physician, who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1927, and is the first psychiatrist to have done so. His Nobel award was "for his discovery of the therapeutic value of malaria inoculation in the treatment of dementia paralytica". Early life Julius Wagner-Jauregg was born Julius Wagner on 7 March 1857 in Wels, Upper Austria, the son of Adolph Johann Wagner and Ludovika Jauernigg Ranzoni."Physiology or medicine, 1922-1941" Jan Lindsten. World Scientific, 1999. p. 170. , . His family name was changed to "Wagner von Jauregg" when his father was given the title of " |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
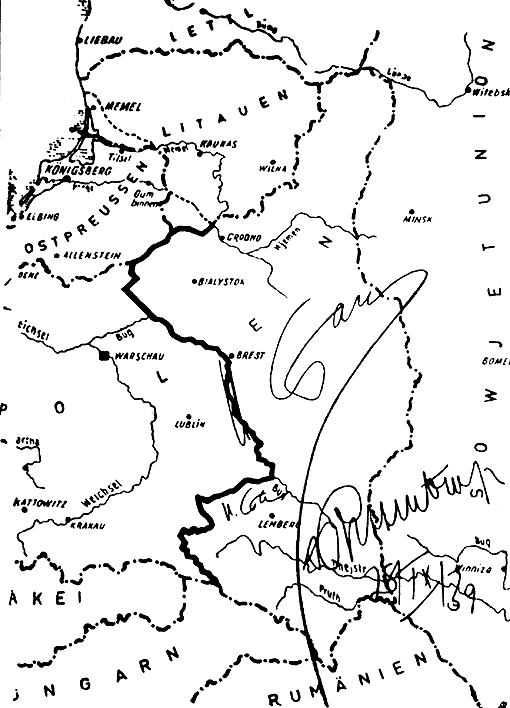
General Government
The General Government (german: Generalgouvernement, pl, Generalne Gubernatorstwo, uk, Генеральна губернія), also referred to as the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region (german: Generalgouvernement für die besetzten polnischen Gebiete), was a German zone of occupation established after the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany, Slovakia and the Soviet Union in 1939 at the onset of World War II. The newly occupied Second Polish Republic was split into three zones: the General Government in its centre, Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany in the west, and Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union in the east. The territory was expanded substantially in 1941, after the German Invasion of the Soviet Union, to include the new District of Galicia. The area of the ''Generalgouvernement'' roughly corresponded with the Austrian part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth after the Third Partition of Poland in 1795. The basis for the formation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Reich
German ''Reich'' (lit. German Realm, German Empire, from german: Deutsches Reich, ) was the constitutional name for the German nation state that existed from 1871 to 1945. The ''Reich'' became understood as deriving its authority and sovereignty entirely from a continuing unitary German Volk ("national people"), with that authority and sovereignty being exercised at any one time over a unitary German "state territory" with variable boundaries and extent. Although commonly translated as "German Empire", the word ''Reich'' here better translates as "realm" or territorial "reach", in that the term does not in itself have monarchical connotations. The Federal Republic of Germany asserted, following its establishment in 1949, that within its boundaries it was the sole legal continuation of the German Reich, and consequently ''not'' a successor state. Nevertheless, the Federal Republic did not maintain the specific title ''German Reich'', and so consistently replaced the prefix ''Reich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annexation
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act.: "Annexation means the forcible acquisition of territory by one State at the expense of another State. It is one of the principal modes of acquiring territory... in contrast to acquisition a) of terra nullius by means of effective occupation accompanied by the intent to appropriate the territory; b) by cession as a result of a treaty concluded between the States concerned (Treaties), or an act of adjudication, both followed by the effective peaceful transfer of territory; c) by means of prescription defined as the legitimization of a doubtful title to territory by passage of time and presumed acquiescence of the former sovereign; d) by accretion constituting the physical process by which new land is formed close to, or becomes attached to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groschen
Groschen (; from la, grossus "thick", via Old Czech ') a (sometimes colloquial) name for various coins, especially a silver coin used in various states of the Holy Roman Empire and other parts of Europe. The word is borrowed from the late Latin description of a tornose, a ''grossus denarius Turnosus,'' in English the "thick denarius of Tours". Groschen was frequently abbreviated in old documents to ''gl'', whereby the second letter was not an '' l'' (12th letter of the alphabet), but an abbreviation symbol; later it was written as ''Gr'' or ''g''. Names and etymology The name was introduced in 13th-century France as ', lit. "thick penny", whence Old French ', Italian ', Middle High German ', Low German and Dutch ' and English '' groat''. In the 14th century, it appeared as Old Czech ', whence Modern German '. Names in other modern European languages include: * sq, grosh * Church Slavonic-derived languages: Bulgarian, Macedonian, Russian and Serbo-Croatian ('), Ukrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_–_Gerd_Hruška.png)