|
White Serbs
The Sorbs, also known as White Serbs in Serbian historiography, were an Early Slavic tribe settled between Saale-Elbe valley up to Lusatian Neisse (in present-day Saxony and Thuringia), and part of the Wends. In the 7th century, the tribe joined Samo's Empire and part of them emigrated from their homeland White Serbia to the Balkans. The tribe is last mentioned in the late 10th century, but its descendants are an ethnic group of Sorbs and Serbs. Etymology They are mentioned between the 6th and 10th century as ''Cervetiis'' (''Servetiis''), ''gentis (S)urbiorum'', ''Suurbi'', ''Sorabi'', ''Soraborum'', ''Sorabos'', ''Surpe'', ''Sorabici'', ''Sorabiet'', ''Sarbin'', ''Swrbjn'', ''Servians'', ''Zribia'', and ''Suurbelant''. It is generally considered that their ethnonym ''*Sŕbъ'' (plur. ''*Sŕby'') originates from Proto-Slavic language with a appellative meaning of a "family kinship" and "alliance", while other argue a derivation from Iranian-Sarmatian language. History 7th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythian Languages
The Scythian languages ( or or ) are a group of Eastern Iranian languages of the classical antiquity, classical and late antiquity, late antique period (the Middle Iranian languages, Middle Iranian period), spoken in a vast region of Eurasia by the populations belonging to the Scythian cultures and their descendants. The dominant ethnic groups among the Scythian-speakers were nomadic pastoralists of Central Asia and the Pontic–Caspian steppe. Fragments of their speech known from inscriptions and words quoted in ancient authors as well as analysis of their names indicate that it was an Indo-European language, more specifically from the Iranian languages, Iranian group of Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian languages. Most of the Scythian languages eventually became extinct, except for modern Ossetian language, Ossetian (which descends from the Alanian dialect of Scytho-Sarmatian), Wakhi language, Wakhi (which descends from the Kingdom of Khotan, Khotanese and Tumxuk, Tumshuqe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part of Scythia at the time; the Huns' arrival is associated with the migration westward of an Iranian people, the Alans. By 370 AD, the Huns had arrived on the Volga, and by 430, they had established a vast, if short-lived, dominion in Europe, conquering the Goths and many other Germanic peoples living outside of Roman borders and causing many others to flee into Roman territory. The Huns, especially under their King Attila, made frequent and devastating raids into the Eastern Roman Empire. In 451, they invaded the Western Roman province of Gaul, where they fought a combined army of Romans and Visigoths at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, and in 452, they invaded Italy. After the death of Attila in 453, the Huns ceased to be a major thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serboi
__NOTOC__ The Serboi ( grc, Σέρβοι, Sérboi) was a tribe mentioned in Greco-Roman geography as living in the North Caucasus, believed by scholars to have been Sarmatian. Etymology Moszyński derived the name from Indo-European ''*ser-'', ''*serv-'', meaning "guard, protect" (cognate of Latin ''servus''), and originally, it may have meant "guardians of animals", that is "shepherds". Similar toponyms were mentioned earlier farther away. History Greco-Roman Ptolemy (100–170) mentioned in his ''Geography'' (ca. 150) the Serboi as inhabiting, along with other tribes, the land between the northeastern foothills of the Caucasus and the Volga. The tribe was included on maps of the antique Sarmatia Asiatica as ''Serbi'', ''Sirbi'', in the Early modern period. The Sarmatians were eventually decisively assimilated (e.g. Slavicisation) and absorbed by the Proto-Slavic population of Eastern Europe around the Early Medieval Age. Scholars have connected the ethnonym with those of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suevi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names such as the Marcomanni, Quadi, Hermunduri, Semnones, and Lombards. New groupings formed later, such as the Alamanni and Bavarians, and two kingdoms in the Migration Period were simply referred to as Suebian. Although Tacitus specified that the Suebian group was not an old tribal group itself, the Suebian peoples are associated by Pliny the Elder with the Irminones, a grouping of Germanic peoples who claimed ancestral connections. Tacitus mentions Suebian languages, and a geographical "Suevia". The Suevians were first mentioned by Julius Caesar in connection with the invasion of Gaul by the Germanic king Ariovistus during the Gallic Wars. Unlike Tacitus he described them as a single people, distinct from the Marcomanni, within the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibius Sequester
Vibius Sequester (active in the 4th or 5th century AD) is the Latin author of lists of geographical names. Work ''De fluminibus, fontibus, lacubus, nemoribus, gentibus, quorum apud poëtas mentio fit'' is made up of seven alphabetical lists of geographical names mentioned by poets, especially Virgil, Ovid and Lucan. Several of the names do not appear in our copies of the poets; unless this is the result of carelessness or ignorance by the compiler, he must have had access to sources no longer extant. The lists are: # ''Flumina'' (rivers/waterways) # ''Fontes'' (springs) # ''Lacus'' (lakes) # ''Nemora'' (forests) # ''Paludes'' (marshes) # ''Montes'' (mountains) # ''Gentes'' (peoples) The work was mainly copied by Italian humanists in the second half of the 9th century. The work is best known for preserving a dactylic pentameter line quoted from Cornelius Gallus, ''uno tellures dividit amne duas'' (" Scythian Hypanis">Southern_Bug.html" ;"title="he Southern Bug">Scythian Hypa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Heather
Peter John Heather (born 8 June 1960) is a British historian of late antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Heather is Chair of the Medieval History Department and Professor of Medieval History at King's College London. He specialises in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the Goths, on which he for decades has been considered the world's leading authority. Biography Heather was born in Northern Ireland on 8 June 1960. He was educated at Maidstone Grammar School, and received his M.A. and D.Phil. from New College, Oxford. Among his teachers at Oxford were John Matthews and James Howard-Johnston. Heather subsequently lectured at Worcester College, Oxford, Yale University and University College London. In January 2008, Heather was appointed chair of the Medieval History Department and professor of medieval history at King's College London. Research As a historian, Heather specialises in late antiquity and the Early Middle Ages, especially the relationships between the Roman Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prague-Korchak Culture
The Prague-Korchak culture was an archaeological culture attributed to the Early Slavs. The other contemporary main Early Slavic culture was the Penkovka culture, Prague-Penkovka culture situated further south, with which it makes up the "Prague-type pottery" group.; The largest part of sites dates to the late 5th and early 6th century AD according to Late Roman iron fibulae. Settlements were as a rule placed at rivers, near water sources, and were typically unfortified, with 8–20 households with courtyards. Burial sites were both flat graves and barrows (kurgans), and cremation was dominant. Scholar Michel Kazanski, M. Kazanski identified the 6th-century Prague (Prague-Korchak) culture and Sukow-Dziedzice group as Sclaveni archaeological cultures, and the Penkovka culture (Prague-Penkovka) was identified as Antes. See also *Korchak culture *Penkovka culture *Ipotesti-Candesti culture *Kolochin culture *Sclaveni *Antes people *Early Slavs References Sources * * * {{re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tornow Group
Tornow group, also known as Tornow- Klenica and Tornow- Gostyn in Poland, in archaeology refers to the Middle Slavic pottery and related strongholds of "Tornow-type" which were present in the middle of Obra, Oder, Spree but also Elbe and Saale basins from Greater Poland up to Thuringia.Roslund, 2007, p. 160, 169–171, 190, quote: "...has a distribution mainly ranging in the west to the boundary of Slavic culture on the Elbe-Saale, in the north to the Spree-Havel area, in the east into Great Poland, in the south and south-east to the Sudeten and Beskydy. The core area, however, is between the Elbe and the Warta. It is a derivation of Prague-Korchak (and possibly Sukow-Dziedzice culture in Northeastern part). Tornow-type pottery It is generally named after Lower Lusatian village Tornow (district of Oberspreewald-Lausitz, Brandenburg),Agua et al., 2020, p. 71–72, 81–82 which doesn't exist anymore since mid-20th century and where were held extensive archaeological excavations i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukow-Dziedzice Group
The Sukow or Sukow-Dziedzice group (german: Sukow-Dziedzice-Gruppe) or Sukow-Dziedzice culture ( pl, Kultura Sukow-Dziedzice, russian: Суковско-дзедзицкая культура), also known as Szeligi culture, was an archaeological culture attributed to the Early Slavs. Areal of sites lays between Elbe and Vistula rivers in Northeast Germany and North West Poland. The earliest sites date to the second half of 7th and mid-8th centuries. There exist different views on its origin. It has features of both Przeworsk culture and Prague-Korchak culture. In comparison to Carpathian Slavic-speaking population of Korchak-Mogilany-type some consider Sukow-Dziedzice's had different population, maybe indigenous to Poland or arrived from within Poland and Belarus or a mixture of Korchak Slavs and indigenous post-Przeworsk population. M. Kazanski identified the 6th-century Prague-Korchak culture and later Sukow-Dziedzice group as Sclaveni archaeological cultures, and the Penkovka c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
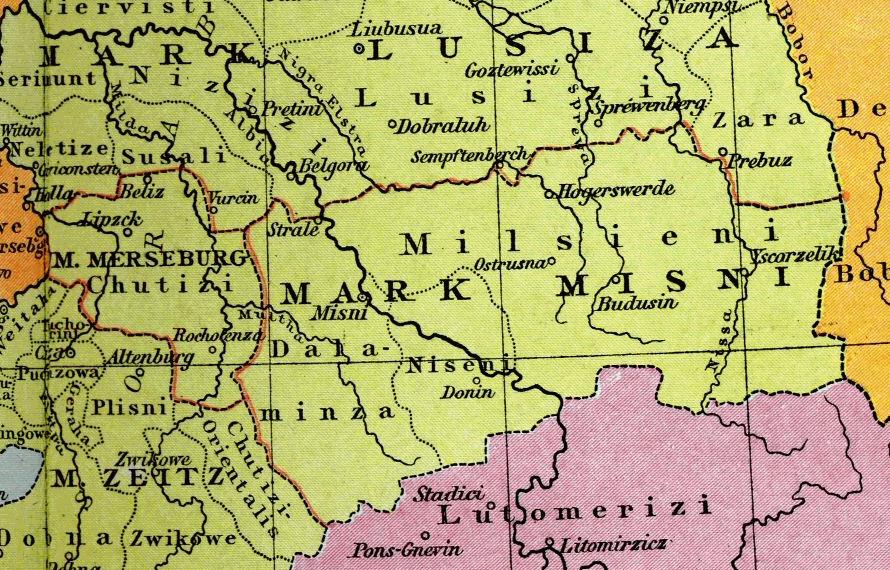
Milceni
The Milceni or Milzeni ( cs, Milčané; german: Milzener; pl, Milczanie) were a West Slavic tribe, who settled in the present-day Upper Lusatia region. They were first mentioned in the middle of the 9th century AD by the Bavarian Geographer, who wrote of 30 ''civitates'' which possibly had fortifications. They were gradually conquered by Germans during the 10th century. Modern descendants of the Milceni are the Sorbs of the Free State of Saxony, Germany.Institut für Sorabistik.About Sorbian Language". Accessed November 8, 2006. History The Milceni travelled to Upper Lusatia in the 7th century during the Migration Period.''Bautzen.de''History. Accessed November 8, 2006. The exact borders of their settlement area are disputed. It is generally accepted that their fielded land had fruitful loess soil and had dimensions of approximately 50 km from east to west and 20 km from north to south. The northern border was in swampy and partially infertile terrain, while the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podunavlje
Podunavlje ( sr-Cyrl, Подунавље) is the name of the Danube river basin parts located in Serbia (Vojvodina, Belgrade and Eastern Serbia) and Croatia (Slavonia, Syrmia, and Baranya). Podunavlje is located on the southern edge of Pannonian Basin. In its wider meaning, the Serbo-Croatian term refers to the area around the entire flow of the river Danube. Naming history In the first half of the 18th century, Sava-Danube (Posavina-Podunavlje) section of the Habsburg Military Frontier existed in the area. Podunavlje segment of the Frontier comprised parts of southern Bačka and northern Syrmia including towns of Petrovaradin, Šid, Bačka Palanka, Bački Petrovac, Petrovaradinski Šanac (Novi Sad), and Titel. Between 1922 and 1929, Podunavlje Oblast was one of the administrative units of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. It included parts of Šumadija and Banat regions and its seat was in Smederevo. Between 1929 and 1941, one of the provinces of the Kingdom of Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |