|
White Armour
White armour, or ''alwyte armour'', was a form of plate armour worn in the Late Middle Ages characterized by full-body steel plate without a surcoat. Around 1420 the surcoat, or "coat of arms" as it was known in England, began to disappear, in favour of uncovered plate. Areas not covered by plate were protected by mail sewn to the gambeson underneath. During the fifteenth century national styles of armour emerged. 'White armour' was a term used synonymously with Italian design, which was innovative in expanding the use of plate armour to cover joints that had been previously protected by mail. The descriptive term ''white armour'' referred both to the absence of a surcoat and the absence of decorative trimmings: the rival German style was fluted, both for aesthetic reasons and for structural advantage in resisting crushing blows. Unlike its predecessors, white armour had a very plain and simple finish, as opposed to intricate patterns or symbols emblazoned on its plates. White arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Couter
The couter (also spelled "cowter") is the defense for the elbow in a piece of plate armour. Initially just a curved piece of metal, as plate armor progressed the couter became an articulated joint. Couters were popular by the 1320s. In fighting reenactment groups such as the Society for Creative Anachronism, a couter/cowter is often called an ''elbow cop''. See also * Poleyn The poleyn or genouillere was a component of Medieval and Renaissance armor that protected the knee. During the transition from mail armor to plate armor, this was among the earliest plate components to develop. They first appeared around 1230 ... Citations References * External links Armour Glossary Western plate armour {{medieval-armour-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
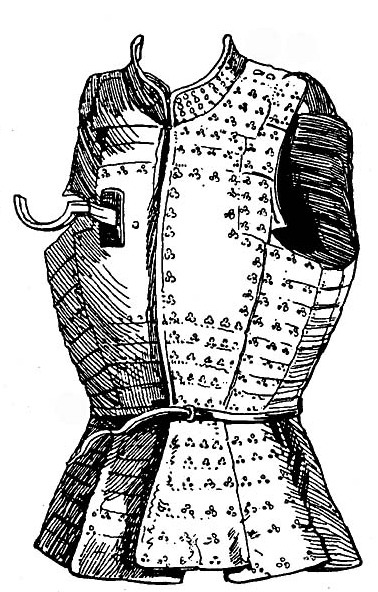
Brigandine
A brigandine is a form of body armour from the Middle Ages. It is a garment typically made of heavy cloth, canvas, or leather, lined internally with small oblong steel plates riveted to the fabric, sometimes with a second layer of fabric on the inside. Origins Protective clothing and armour have been used by armies from earliest recorded history; the King James Version of the Bible (Jeremiah 46:4) translates the Hebrew סריון ''ÇiRYON'' or שריון ''SiRYoN'' "coat of mail" as "brigandine". Medieval brigandines were essentially a refinement of the earlier coat of plates, which developed in the late 12th century, typically of simpler construction with larger metal plates. This armour of Asian origin reached Europe after the Mongol invasion in 1240 that destroyed the Kievan Rus' and severely damaged the Kingdom of Hungary in 1241. The new armour became very popular first in Eastern Europe, especially in Hungary, towards the end of the 13th century and was adopted in west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian - Sallet - Walters 51580
Italian(s) may refer to: * Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries ** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom ** Italian language, a Romance language *** Regional Italian, regional variants of the Italian language ** Languages of Italy, languages and dialects spoken in Italy ** Italian culture, cultural features of Italy ** Italian cuisine, traditional foods ** Folklore of Italy, the folklore and urban legends of Italy ** Mythology of Italy, traditional religion and beliefs Other uses * Italian dressing, a vinaigrette-type salad dressing or marinade * Italian or Italian-A, alternative names for the Ping-Pong virus, an extinct computer virus See also * * * Italia (other) * Italic (other) * Italo (other) * The Italian (other) * Italian people (other) Italian people may refer to: * in terms of ethnicity: all ethnic Italians, in and outside of Italy * in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
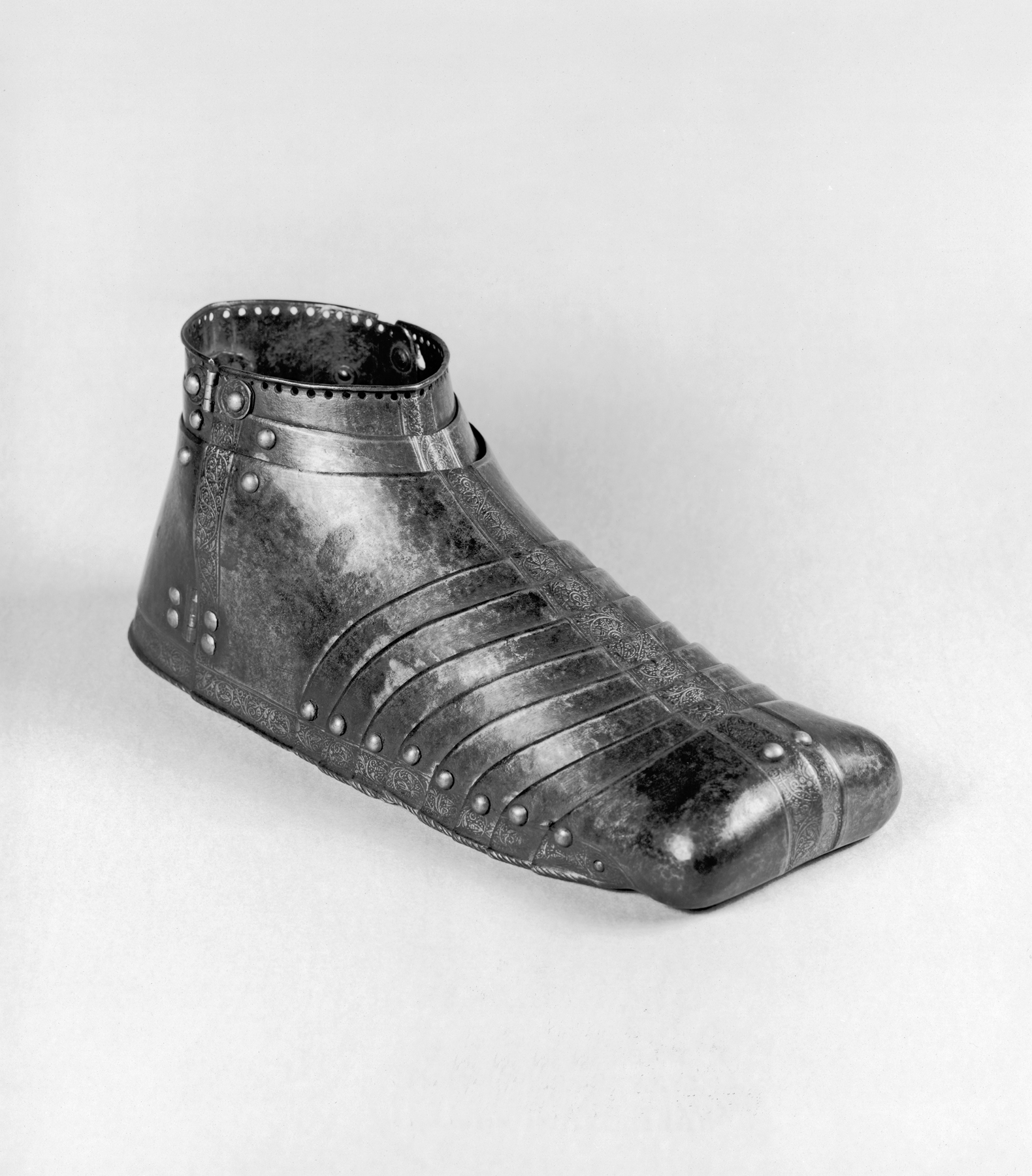
Sabaton
A sabaton or solleret is part of a knight's body armor that covers the foot. History Fourteenth and fifteenth century sabatons typically end in a tapered point well past the actual toes of the wearer's foot, following fashionable shoe shapes of the fourteenth century. Sabatons of the first half of sixteenth century end at the tip of the toe and may be wider than the actual foot. They were the first piece of armour to be put on, and were made of riveted iron plates called '' lames''. These plates generally covered only the top of the foot. Some sources maintain that the broad-toed variant is the true sabaton, whereas the earlier versions should be referred to as a solleret. At least in theory, French princes and dukes were allowed to have toes of Gothic sabatons long, lords (barons and higher) 2 feet long and gentry only long.Fred & Liliane Funcken, ''Le Costume, l'Armure et les Armes au Temps de la Chevalerie'', "2: Le siècle de la Renaissance (2)" (in French) The sabaton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greave
A greave (from the Old French ''greve'' "shin, shin armour") or jambeau is a piece of armour that protects the leg. Description The primary purpose of greaves is to protect the tibia from attack. The tibia, or shinbone, is very close to the skin, and is therefore extremely vulnerable to just about any kind of attack. Furthermore, a successful attack on the shin results in that leg being rendered useless, greatly hampering one's ability to maneuver in any way. Greaves were used to counteract this. They usually consisted of a metal exterior with an inner padding of felt. The felt padding was particularly important because, without it, any blow would transfer directly from the metal plating to the shin. History Ancient Greece and Rome The reference to greaves (Ancient Greek: κνημίδες) exists in various texts of classical antiquity, including ''The Shield of Heracles'', ''The Iliad'' and ''The Odyssey'', ''The Bibliotheca of Pseudo-Apollodorus'', and ''The Aeneid''. In the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poleyn
The poleyn or genouillere was a component of Medieval and Renaissance armor that protected the knee. During the transition from mail armor to plate armor, this was among the earliest plate components to develop. They first appeared around 1230 and remained in use until 1650 when firearms made them obsolete. The specifics of poleyn design varied considerably over that period. The earliest poleyns were strapped over mail chausses. Fourteenth century and early fifteenth century poleyns usually attached to padded leggings or plate cuisses. During the fifteenth century poleyns developed an articulated construction that attached to the cuisses and schynbalds or greaves. A characteristic of late fifteenth century Gothic plate armor was a projection that guarded the side of the knee. Gallery File:Villard de Honnecourt.jpg, An early example of poleyns worn over chausses, from an illustration by Villard de Honnecourt (1230). File:Ludwig III in der Schlacht von Kulm.jpg, Ludwig III wear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuisse
Cuisses (; ; ) are a form of medieval armour worn to protect the thigh. The word is the plural of the French word ''cuisse'' meaning 'thigh'. While the skirt of a maille shirt or tassets of a cuirass could protect the upper legs from above, a thrust from below could avoid these defenses. Thus, cuisses were worn on the thighs to protect from such blows. Padded cuisses made in a similar way to a gambeson were commonly worn by knights in the 12th and 13th centuries, usually over chausses, and may have had poleyns directly attached to them. Whilst continental armours typically had cuisses that did not protect the back of the thigh, English cuisses were typically entirely encapsulating, due to the English preference for foot combat over the mounted cavalry charges favoured by continental armies. Cuisses could also be made of brigandine or splinted leather, but beginning around 1340 they were typically made from steel plate armour. From 1370 onward they were made from a single plate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culet (armour)
A culet (also spelled ''culette'') is a piece of plate armour consisting of small, horizontal lames that protect the small of the back or the buttocks. Usually a skirt of chain mail Chain mail (properly called mail or maille but usually called chain mail or chainmail) is a type of armour consisting of small metal rings linked together in a pattern to form a mesh. It was in common military use between the 3rd century BC and ... or a mail brayette was worn underneath. This armour was also referred to as a ''garde de rein'' or ''garde rein'',Harold Leslie Peterson, ''Arms and Armor in Colonial America, 1526-1783'' (2000, Courier Corporation, , page 120 or ''hoguine''.Francis M. Kelly, Randolph Schwabe, ''A Short History of Costume & Armour: Two Volumes Bound as One'' (2013, Courier Corporation, : "that rmorguarding the loins as known asas the HOGUINE or CULET." References Western plate armour {{medieval-armour-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tassets
Tassets are a piece of plate armour designed to protect the upper thighs. They take the form of separate plates hanging from the breastplate or faulds. They may be made from a single piece or segmented. The segmented style of tassets connected by sliding rivets produced during the 16th century is also known as ''almain rivets''. From the 16th century onward, the tassets were sometimes integrated with the cuisses to create fully articulated leg defenses that continued from the lower edge of the breastplate down to the poleyn The poleyn or genouillere was a component of Medieval and Renaissance armor that protected the knee. During the transition from mail armor to plate armor, this was among the earliest plate components to develop. They first appeared around 1230 .... External links *Cleveland Museum of Artglossary of arms and armor Western plate armour {{medieval-armour-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faulds (plate Armour)
Faulds are pieces of plate armour worn below a breastplate to protect the waist and hips, which began to appear in Western Europe from about 1370. They consist of overlapping horizontal lames of metal, articulated for flexibility, that form an apron-like skirt in front. When worn with a cuirass, faulds are often paired with a similar defense for the rump called a culet, so that the faulds and culet form a skirt that surrounds the hips in front and back; the culet is often made of fewer lames than the fauld, especially on armor for a horseman. The faulds can either be riveted to the lower edge of the breastplate or made as a separate piece that the breastplate snugly overlaps. Although faulds varied in length, most faulds for field use ended above the knees. A pair of tassets Tassets are a piece of plate armour designed to protect the upper thighs. They take the form of separate plates hanging from the breastplate or faulds. They may be made from a single piece or segmented. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_by_Wendelin_Boeheim.jpg)


_MET_DP-13125-029.jpg)
_MET_29.158.270a_001Sept2014.jpg)

